|
Gyrobus
A gyrobus is an electric bus that uses flywheel energy storage, not overhead wires like a trolleybus. The name comes from the Greek language term for flywheel, ''gyros''. There are no gyrobuses currently in use commercially. Development The concept of a flywheel-powered bus was developed and brought to fruition during the 1940s by Oerlikon (of Switzerland), with the intention of creating an alternative to trolleybuses for quieter, lower-frequency routes, where full overhead-wire electrification could not be justified. Rather than carrying an internal combustion engine or batteries, or connecting to overhead powerlines, a gyrobus carries a large flywheel that is spun at up to 3,000 RPM by a "squirrel cage" motor. Power for charging the flywheel was sourced by means of three booms mounted on the vehicle's roof, which contacted charging points located as required or where appropriate (at passenger stops en route, or at terminals, for instance). To obtain tractive power, capa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyrobus G3-1
A gyrobus is an electric bus that uses flywheel energy storage, not overhead wires like a trolleybus. The name comes from the Greek language term for flywheel, ''gyros''. There are no gyrobuses currently in use commercially. Development The concept of a flywheel-powered bus was developed and brought to fruition during the 1940s by Oerlikon (of Switzerland), with the intention of creating an alternative to trolleybuses for quieter, lower-frequency routes, where full overhead-wire electrification could not be justified. Rather than carrying an internal combustion engine or batteries, or connecting to overhead powerlines, a gyrobus carries a large flywheel that is spun at up to 3,000 RPM by a "squirrel cage" motor. Power for charging the flywheel was sourced by means of three booms mounted on the vehicle's roof, which contacted charging points located as required or where appropriate (at passenger stops en route, or at terminals, for instance). To obtain tractive power, capacito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
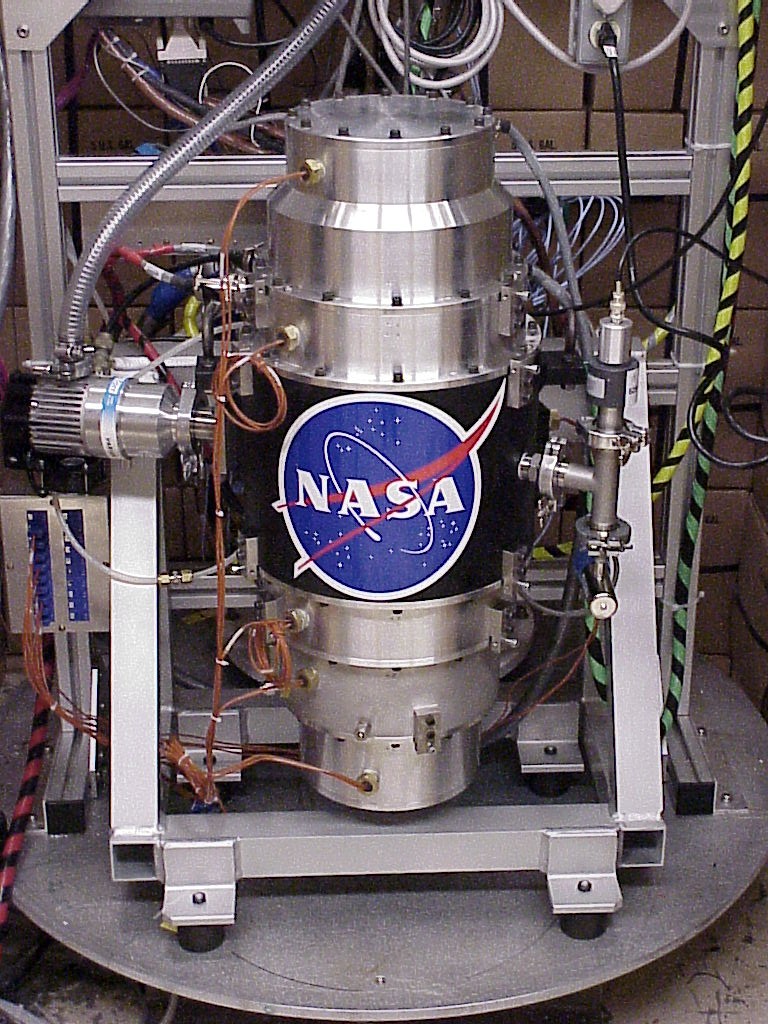
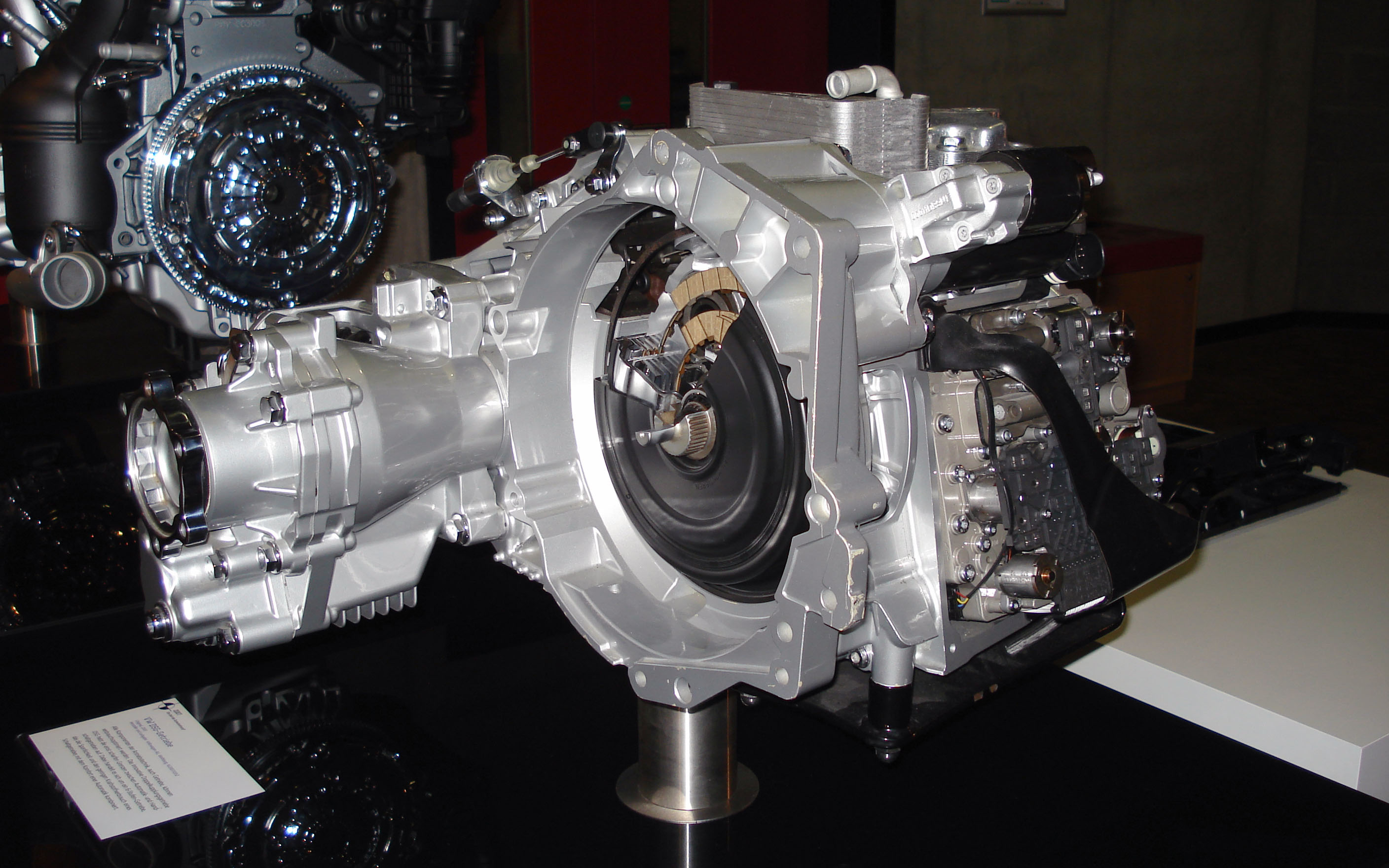
Flywheel Energy Storage
Flywheel energy storage (FES) works by accelerating a rotor (flywheel) to a very high speed and maintaining the energy in the system as rotational energy. When energy is extracted from the system, the flywheel's rotational speed is reduced as a consequence of the principle of conservation of energy; adding energy to the system correspondingly results in an increase in the speed of the flywheel. Most FES systems use electricity to accelerate and decelerate the flywheel, but devices that directly use mechanical energy are being developed.Torotrak Toroidal variable drive CVT , retrieved June 7, 2007. Advanced FES systems have rotors made of high strength carbon-fiber composites, suspended by magnetic bearings, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Bus
An electric bus is a bus that is propelled using electric motors, as opposed to a conventional internal combustion engine. Electric buses can store the needed electrical energy on board, or be fed mains electricity continuously from an external source such as overhead lines. The majority of buses using on-board energy storage are battery electric buses (which is what this article mostly deals with), where the electric motor obtains energy from an electric vehicle battery, onboard battery pack, although examples of other storage modes do exist, such as the gyrobus that uses flywheel energy storage. When electricity is not stored on board, it is supplied by contact with outside power supplies, for example, via a current collector (like the trolley pole, overhead conduction poles in trolleybuses), or with a ground-level power supply, or through Inductive charging#Dynamic charging, inductive charging. As of 2017, 99% of all battery electric buses in the world have been deployed in M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Republic Of The Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is the List of African countries by area, second-largest country in Africa and the List of countries and dependencies by area, 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 112 million, the DR Congo is the most populous nominally List of countries and territories where French is an official language, Francophone country in the world. Belgian French, French is the official and most widely spoken language, though there are Languages of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, over 200 indigenous languages. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the economic center. The country is bordered by the Republic of the Congo, the Cabinda Province, Cabinda exclave of Angola, and the South Atlantic Ocean to the west; the Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinshasa
Kinshasa (; ; ), formerly named Léopoldville from 1881–1966 (), is the Capital city, capital and Cities of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, largest city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Kinshasa is one of the world's fastest-growing Megacity, megacities, with an estimated population of 17 million in 2024. It is the List of cities and towns in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, most densely populated city in the DRC, the List of cities in Africa by population, most populous city and List of urban areas in Africa by population, third-largest metropolitan area in Africa, and the world's List of largest cities, twenty-second most populous city and List of national capitals by population, fourth-most populous capital city. It is the leading Economy, economic, Politics, political, and cultural center of the DRC, housing several industries including manufacturing, telecommunications, List of banks in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, banking, and entertainment. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgian Congo
The Belgian Congo (, ; ) was a Belgian colonial empire, Belgian colony in Central Africa from 1908 until independence in 1960 and became the Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville). The former colony adopted its present name, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), in 1964. Colonization of the Congo Basin, Colonial rule in the Congo began in the late 19th century. Leopold II of the Belgians, King Leopold II of the Belgians attempted to persuade the Federal Government of Belgium, Belgian government to support colonial expansion around the then-largely unexploited Congo Basin. Their ambivalence resulted in Leopold establishing a colony himself. With support from a number of Berlin Conference, Western countries, Leopold achieved international recognition of the Congo Free State in 1885. By the turn of the century, the violence used by Free State officials against indigenous Congolese and a ruthless system of economic exploitation led to intense diplomatic pressure on Belgium to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grandson, Switzerland
Grandson () is a municipality in the district of Jura-Nord Vaudois in the canton of Vaud in Switzerland. It is situated on the south-west tip of Lake Neuchâtel, about 25 km (15 miles) north of Lausanne. It was part of the Kingdom of Upper Burgundy until the death of Rudolph III of Burgundy (993-1032), also King of Lower Burgundy, the last in the male line, when it was united with the Holy Roman Empire. On 2 March 1476, during the Burgundian Wars, Charles the Bold was defeated here in the Battle of Grandson. History The Grandson family is first mentioned in the second half of the 11th century as ''Grancione''. The town was first mentioned around 1100 as ''de castro Grancione''. Around 1126 it was mentioned as ''castri Grandissoni'' and in 1154 it was called ''apud Grantionem''. Prehistoric settlements In May 1895 a farmer discovered a buried underground menhir weighing about three tons and about tall in Les Echâtelards. The monolith now stands in the vicinity of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and energy production, the research and development of nuclear power, the military's nuclear weapons program, nuclear reactor production for the United States Navy, energy-related research, and energy conservation. The DOE was created in 1977 in the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis. It sponsors more physical science research than any other U.S. federal agency, the majority of which is conducted through its system of National Laboratories. The DOE also directs research in genomics, with the Human Genome Project originating from a DOE initiative. The department is headed by the secretary of energy, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the Cabinet. The current secretary of energy is Chris Wright, who has served in the position since February 2025. The department's headquarters are in sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghent
Ghent ( ; ; historically known as ''Gaunt'' in English) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of East Flanders, and the third largest in the country, after Brussels and Antwerp. It is a Port of Ghent, port and Ghent University, university city. The city originally started as a settlement at the confluence of the Rivers Scheldt and Leie. In the Late Middle Ages Ghent became one of the largest and richest cities of northern Europe, with some 50,000 people in 1300. After the late 16th century Ghent became a less important city, resulting in an extremely well-preserved historic centre, that now makes Ghent an important destination of tourism. The municipality comprises the city of Ghent proper and the surrounding suburbs of Afsnee, Desteldonk, Drongen, Gentbrugge, Ledeberg, Mariakerke, East Flanders, Mariakerke, Mendonk, Oostakker, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center For Transportation And The Environment
Center or centre may refer to: Mathematics *Center (geometry), the middle of an object * Center (algebra), used in various contexts ** Center (group theory) ** Center (ring theory) * Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentricity * Central tendency, measures of the central tendency (center) in a set of data Places United States * Centre, Alabama * Center, Colorado * Center, Georgia * Center, Indiana * Center, Warrick County, Indiana * Center, Kentucky * Center, Missouri * Center, Nebraska * Center, North Dakota * Centre County, Pennsylvania * Center, Portland, Oregon * Center, Texas * Center, Washington * Center, Outagamie County, Wisconsin * Center, Rock County, Wisconsin **Center (community), Wisconsin *Center Township (other) *Centre Township (other) *Centre Avenue (other) *Center Hill (other) Other countries * Centre region, Hainaut, Belgium * Centre Region, Burkina Faso * Centre Region (Cameroon) * Centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechatronics
Mechatronics engineering, also called mechatronics, is the synergistic integration of mechanical, electrical, and computer systems employing mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, electronic engineering and computer engineering, and also includes a combination of robotics, computer science, telecommunications, systems, control, automation and product engineering. As technology advances over time, various subfields of engineering have succeeded in both adapting and multiplying. The intention of mechatronics is to produce a design solution that unifies each of these various subfields. Originally, the field of mechatronics was intended to be nothing more than a combination of mechanics, electrical and electronics, hence the name being a portmanteau of the words "mechanics" and "electronics"; however, as the complexity of technical systems continued to evolve, the definition had been broadened to include more technical areas. No later than in 1951, the word ''mechatronics' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |