|
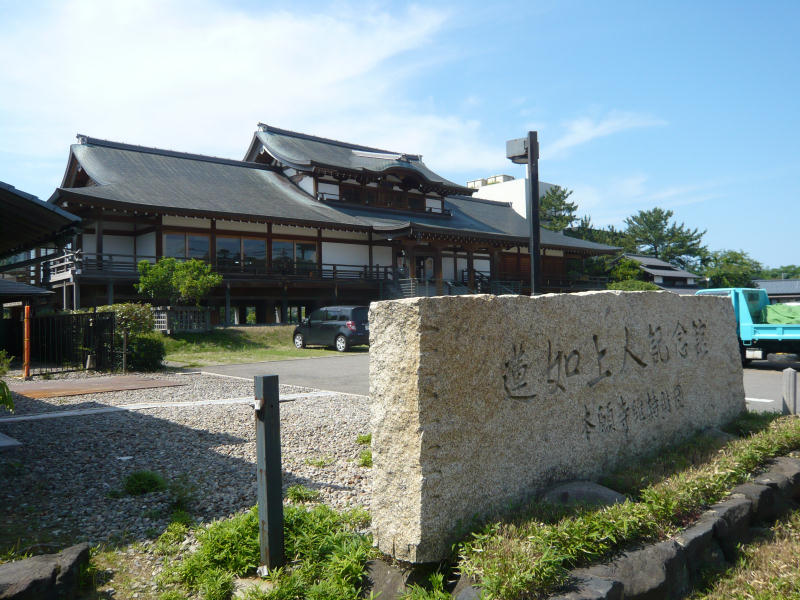
Gyotoku-ji
Gyotoku-ji (行徳寺) is a temple located in the Nishiao district of Nanto City, Toyama Prefecture. It is one of the oldest Gokayama temples. History In the latter half of the Muromachi period, during the Bunmei (1392–1573), Rennyo(蓮如), the 8th head of Hongan-ji Temple, stayed at Yoshizaki-gobō in Echizen Province, which led to a rapid increase in Shinshū followers in the Hokuriku region, and the spread of Shinshū in earnest in the Gokayama area. The first to extend their teachings to the Gokayama region was in Echizen Province, and there was a monk named Jotoku(浄徳) from Akaodani who was a follower of Hongakuji Temple. The nephew of Jotoku was (赤尾道宗), a well-known Myokonin, and Doshu is positioned as the founder of Gyotoku-ji Temple. Although there are various traditions about Doso's origin and history in later times, there is no doubt that he was a contemporary of Rennyo, as he is often mentioned in Rennyo's writings. Gyotoku-ji Temple still retains a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gokayama
is an area within the city of Nanto in Toyama Prefecture, Japan. It has been inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List due to its traditional '' gasshō-zukuri'' houses, alongside nearby Shirakawa-gō in Gifu Prefecture. The survival of this traditional architectural style is attributed to the region's secluded location in the upper reaches of the Shōgawa river. This is also the reason that Gokayama's lifestyle and culture remained very traditional for many years after the majority of the country had modernized. Many of the houses surpass 300 years in age. The Gokayama region includes the former villages of Taira, Kamitaira, and Toga. The ''gasshō'' hamlet of Ainokura is located in Taira, while that of Suganuma is in Kamitaira; both are nationally designated Historic Sites. Ainokura , in the Gokayama region, was inscribed on the World Heritage List in December 1995 as one of the three villages of ''gassho''-style houses. Ainokura has 20 gassho-style houses known as ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
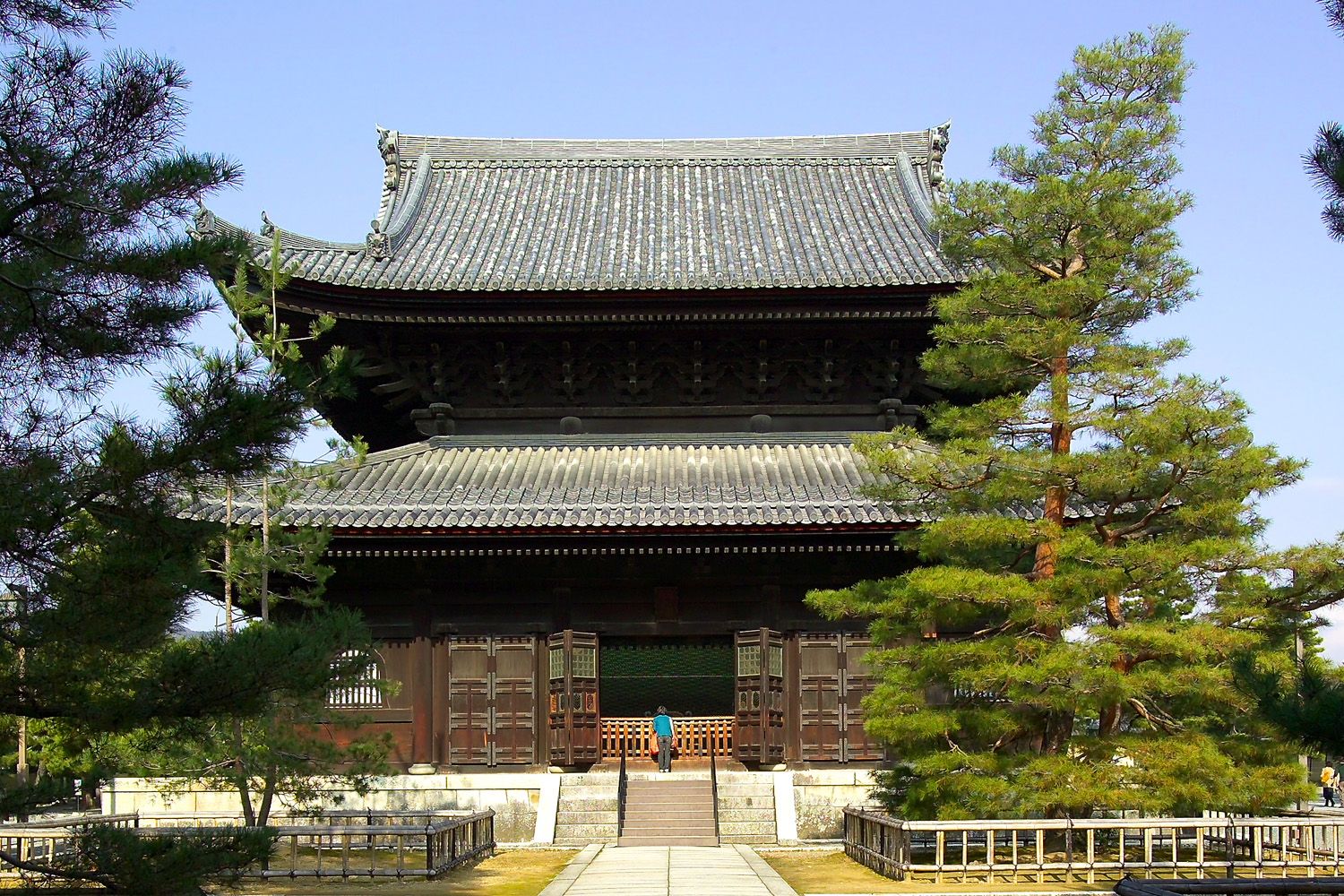
Main Hall (Japanese Buddhism)
Main hall or Main Temple is the building within a Japanese Buddhist monastery compound ('' garan'') which enshrines the main object of veneration.Kōjien Japanese dictionary Because the various denominations deliberately use different terms, this single English term translates several Japanese words, among them ''butsuden'', ''butsu-dō'', ''kondō'', ''konpon-chūdō'', and ''hondō''. ''Hondō'' is its exact Japanese equivalent, while the others are more specialized words used by particular sects or for edifices having a particular structure. Kondō (Asuka and Nara periods) The term started to be used during the Asuka and Nara periods. A ''kondō'' is the centerpiece of an ancient Buddhist temple's ''garan'' in Japan. The origin of the name is uncertain, but it may derive from the perceived preciousness of its content, or from the fact that the interior was lined with gold. This is the name used by the oldest temples in the country.Iwanami Nihonshi Jiten A ''kondō'', for exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hokuriku Region
The is located in the northwestern part of Honshu, the main island of Japan. It lies along the Sea of Japan and is part of the larger Chūbu region. It is almost equivalent to the former Koshi Province (Japan), Koshi Province and Hokurikudō area in pre-modern Japan. From the Heian period until the Edo period, the region was a core recipient of population, and grew to be proportionately much larger than it is today, despite the rural character; in modern times, its population has remained consistent, with most urban growth in the 20th century instead taking place in Kantō region, Kanto, Nagoya, Chūkyō, and Kansai region, Kansai. The Hokuriku region is also known for traditional culture that originated from elsewhere that has been long lost along the Taiheiyō Belt. The Hokuriku region includes the four prefectures of Ishikawa Prefecture, Ishikawa, Fukui Prefecture, Fukui, Niigata Prefecture, Niigata and Toyama Prefecture, Toyama, although Niigata is sometimes included as an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taira, Toyama
was a village located in Higashitonami District, Toyama Prefecture, Japan. As of 2003, the village had an estimated population of 1,322 and a density of 14.06 persons per km2. The total area was 94.02 km2. On November 1, 2004, Taira, along with the towns of Fukuno, Inami and Jōhana, the villages of Inokuchi, Kamitaira and Toga The toga (, ), a distinctive garment of Ancient Rome, was a roughly semicircular cloth, between in length, draped over the shoulders and around the body. It was usually woven from white wool, and was worn over a tunic. In Roman historical tra ... (all from Higashitonami District), and the town of Fukumitsu (from Nishitonami District), was merged to create the city of Nanto. References External links Nanto City official website (in English) Dissolved municipalities of Toyama Prefecture Nanto, Toyama {{Toyama-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toga, Toyama
was a village located in Higashitonami District, Toyama Prefecture, Japan. Historically, along with neighbouring Taira, Kami-Taira and Shirakawa-go, the four villages formed what was known as the Gokayama region. The region is renowned for a unique type of A-frame housing design. These "gassho-zukuri" houses traditionally had thatched roofs and were 3-4 stories high. The design helped keep snow from piling up in the heavy winter conditions. As of 2003, Toga had an estimated population of 999 and a density of 5.63 persons per km2. The total area was 177.58 km2. However, the actual population is probably far less as many people who were registered in the village actually reside in neighboring areas. On November 1, 2004, Toga, along with the towns of Fukuno, Inami and Jōhana, the villages of Inokuchi, Kamitaira and Taira The was one of the four most important clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian period of Japanese history – the others being the Min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gassho-zukuri
are vernacular houses constructed in any one of several traditional Japanese building styles. In the context of the four divisions of society, were the dwellings of farmers, artisans, and merchants (i.e., the three non-samurai castes).Nishi & Hozumi (1996), p82 This connotation no longer exists in the modern Japanese language, and any traditional Japanese-style residence of appropriate age could be referred to as . are characterized by their basic structure, their roof structure, and their roof shape. developed through history with distinctive styles emerging in the Edo period. Types come in a wide range of styles and sizes, largely as a result of differing geographic and climatic conditions as well as the lifestyle of the inhabitants. They generally fall into one of four classifications: farmhouses town houses , fishermen's dwellings and mountain dwellings . Unlike other forms of Japanese architecture (such as those of the style), it is the structure rather than t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himi, Toyama
is a city in western Toyama Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 48,275 in 17,632 households, and a population density of 210 persons per km2. Its total area is . Himi is known primarily for its commercial fishing industry. The city was founded on August 1, 1952. Geography Himi is in the far northwestern Toyama Prefecture, and is bordered by Ishikawa Prefecture (the Noto Peninsula to the west and north, and the Sea of Japan ( Toyama Bay) to the east. Much of the area is a dispersed settlement typical of this region of Japan. Surrounding municipalities *Ishikawa Prefecture ** Hakui ** Hōdatsushimizu ** Nakanoto ** Nanao *Toyama Prefecture ** Takaoka Climate Himi has a humid continental climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by mild summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Himi is 13.9 °C. The average annual rainfall is 2409 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on aver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuri (kitchen)
A or is the kitchen of a Zen monastery, typically located behind the '' butsuden'' (or, Buddha Hall). Historically the ''kuri'' was a kitchen which prepared meals only for the abbot and his guests, though in modern Japan it now functions as the kitchen and administrative office for the entire monastery.Baroni, 201Watanabe, 34 See also *'' Kaisando'' *''Umpan An ''umpan'' (, , literally "cloud plate") is a flat gong, usually bronze, which is rung at mealtime in a Zen monastery. Literally translated as "cloud plate," the umpan is also sounded to "signal other events,"Baroni, 364 such as a call to the c ...'' Notes References * * * Zen {{zen-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characterized by prolonged peace and stability, urbanization and economic growth, strict social order, Isolationism, isolationist foreign policies, and popular enjoyment of Japanese art, arts and Culture of Japan, culture. In 1600, Tokugawa Ieyasu prevailed at the Battle of Sekigahara and established hegemony over most of Japan, and in 1603 was given the title ''shogun'' by Emperor Go-Yōzei. Ieyasu resigned two years later in favor of his son Tokugawa Hidetada, Hidetada, but maintained power, and defeated the primary rival to his authority, Toyotomi Hideyori, at the Siege of Osaka in 1615 before his death the next year. Peace generally prevailed from this point on, making samurai largely redundant. Tokugawa sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dojo
A is a hall or place for immersive learning, experiential learning, or meditation. This is traditionally in the field of martial arts. The term literally means "place of the Tao, Way" in Japanese language, Japanese. History The word ''dōjō'' originates from bodhimaṇḍa, Buddhism. Initially, ''dōjō'' were adjunct to Buddhist temple, temples and were formal training places for any of the Japanese arts ending in "''-dō''", from the Chinese ''Dao'', meaning "way" or "path". Sometimes meditation halls where Zen Buddhists practice ''zazen'' meditation were called ''dōjō''. The alternative term ''zendo, zen-do'' is more specific, and more widely used. European ''Sōtō Zen'' groups affiliated with the International Zen Association prefer to use ''dōjō'' instead of ''zendo'' to describe their meditation halls as did their founding master, Taisen Deshimaru. In Japan, any facility for physical training, including List of professional wrestling terms#S, professional wres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myokonin
The are pious followers of the Jōdo Shinshū and Jōdo-shū sects of Japanese Buddhism. ''Myōkōnin'', which means "a wondrous, excellent person", refers to a devout follower of Pure Land Buddhism who lives a life of total dedication to Amida, the Buddha of the Western Pure Land, and whose acts and sayings, though they may often run counter to common sense, reveal the depth of faith and true humanity. ''Myōkōnin'' were largely unheard of in the West until D. T. Suzuki introduced them in his lectures and writings on Jōdo Shinshū. Most ''myōkōnin'' left few, if any, written records, but one of them, Saichi, is noted for his numerous poems expressing his devotion to Amida Buddha. ''Myōkōnin'' have been documented from the Tokugawa period The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoshizaki-gobō
The was a Buddhist temple located in what is the Yoshizaki neighbourhood of the city of Awara, Fukui, Japan. It is known for its connection to Rennyo, the founder of the Ikkō sect of Japanese Buddhism. The ruins of the temple were designated a National Historic Site in 2012. Overview In 1457, Rennyo was appointed as the eighth chief abbot of Hongan-ji, on the outskirts of Kyoto. Under Rennyo's leadership, Hongan-ji began to expand the teachings of Shinran's Pure Land Buddhism to areas beyond the capital. However, the rapid growth of Hongan-ji was met with hostility by the orthodox Tendai sect based at Enryaku-ji on Mount Hiei, and in 1465, Hongan-ji was destroyed by militant monks from Enryaku-ji and Rennyo was forced to flee Kyoto. In 1471, he re-established Hongaki-ji at the small village of Yoshizaki on the border of Echizen Province with Kaga Province. This rectory, known as the "Yoshizaki-gobō" was the location from which he sent out many epistles explaining the teachin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |