|
Guszczewina
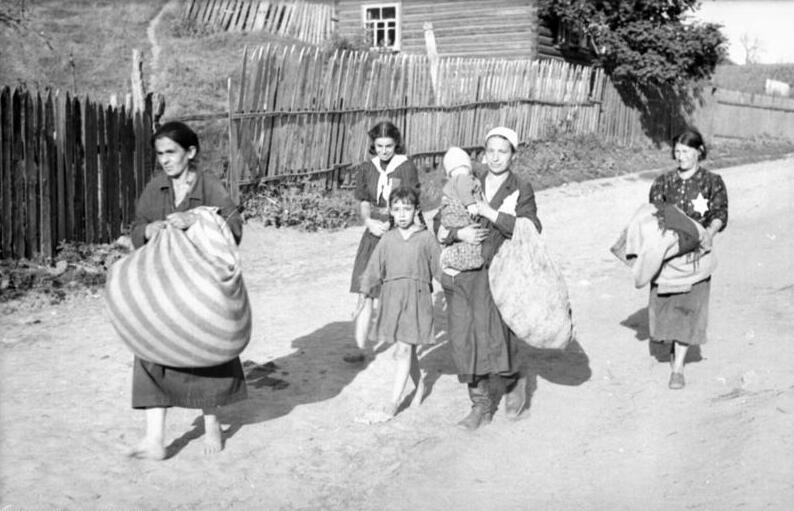
Guszczewina is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Narewka, within Hajnówka County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland, close to the border with Belarus. It lies approximately east of Narewka, north-east of Hajnówka, and south-east of the regional capital Białystok. The village has a population of 61. The settlement Gruszki is considered part of the village. During the German occupation of Poland (World War II), the German Police Battalion 322 expelled the entire population (and murdered two Polish inhabitants), and then plundered and destroyed the village (see ''Nazi crimes against the Polish nation''). After the war the village was rebuilt. Danuta Siedzikówna, member of the Polish resistance movement in World War II The Polish resistance movement in World War II (''Polski ruch oporu w czasie II wojny światowej''), with the Polish Home Army at its forefront, was the largest underground resistance movement in all of occupied Europe, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danuta Siedzikówna
Danuta Helena Siedzikówna (nom de guerre: ''Inka''; underground name: ''Danuta Obuchowicz''; 3 September 1928 – 28 August 1946) was a Polish medical orderly in the 4th Squadron of the 5th Wilno Brigade in Home Army. In 1946 she served with the Brigade's 1st Squadron in Poland's Pomerania region. Considered a national heroine, she was captured, tortured and sentenced to death at the age of 17 by the communist authorities. Early life Siedzikówna was born on 3 September 1928 in Guszczewina, near Narewka, Bielsk Podlaski. Her father, Wacław Siedzik, was a forester who had been sent to Siberia under the Tsar for being involved in pro-Polish independence organisations. He came back to Poland in 1923. In 1940 he was arrested by the NKVD and once again deported to Russia. In 1941 her father Wacław Siedzik joined Władysław Anders' Polish Army (he died in Teheran in 1943). Her mother, Eugenia, ''née'' Tymińska Prus III coat of arms, was a member of the Home Army and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gmina Narewka
__NOTOC__ Gmina Narewka ( be, Гміна Нараўка) is a rural gmina (administrative district) in Hajnówka County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland, on the border with Belarus. Its seat is the village of Narewka, which lies approximately north-east of Hajnówka and south-east of the regional capital Białystok. The gmina covers an area of , and as of 2006 its total population is 4,019. It is one of five Polish/ Belarusian bilingual Gmina in Podlaskie Voivodeship regulated by the ''Act of 6 January 2005 on National and Ethnic Minorities and on the Regional Languages'', which permits certain gminas with significant linguistic minorities to introduce a second, auxiliary language to be used in official contexts alongside Polish.Dz. U. z 2005 r. Nr 17, poz. 141 Villages Gmina Narewka contains the villages and settlements of Babia Góra, Baczyńscy, Bazylowe, Bernacki Most, Bielscy, Bokowe, Borowe, Chomińszczyzna, Cieremki, Dąbrowa, Eliaszuki, Gnilec, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gruszki, Hajnówka County
Gruszki is a settlement, part of the village of Guszczewina, in the administrative district of Gmina Narewka, within Hajnówka County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland, close to the border with Belarus. It lies approximately east of Narewka, north-east of Hajnówka, and south-east of the regional capital Białystok. During the German occupation of Poland (World War II), the German Police Battalion 322 expelled the inhabitants, and then plundered and destroyed the settlement (see ''Nazi crimes against the Polish nation''). After the war the village was rebuilt. In Gruszki there is a memorial to Danuta Siedzikówna, member of the Polish resistance movement in World War II The Polish resistance movement in World War II (''Polski ruch oporu w czasie II wojny światowej''), with the Polish Home Army at its forefront, was the largest underground resistance movement in all of occupied Europe, covering both German ... and the anti-communist resistance moveme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hajnówka
Hajnówka (; be, Гайнаўка, ''Hajnaŭka''; uk, Гайнівка, ''Hainivka''; yi, האַדזשנאָװקאַ, ''Hachnovka''; russian: Хайнувка) is a town and a powiat seat in eastern Poland (Podlaskie Voivodeship) with 21,442 inhabitants (2014). It is the capital of Hajnówka County. The town is also notable for its proximity to the Białowieża Forest, the biggest primaeval forest in Europe. Through Hajnówka flows the river Leśna Prawa ( be, links=no, Лясная Правая). It is one of the centres of Orthodox faith and a notable centre of Belarusian culture in Poland. Belarusians comprised 26.4% of the town's population in 2002. It is one of five Polish/ Belarusian bilingual Gmina in Podlaskie Voivodeship regulated by the ''Act of 6 January 2005 on National and Ethnic Minorities and on the Regional Languages'', which permits certain gminas with significant linguistic minorities to introduce a second, auxiliary language to be used in official contexts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Resistance Movement In World War II
The Polish resistance movement in World War II (''Polski ruch oporu w czasie II wojny światowej''), with the Polish Home Army at its forefront, was the largest underground resistance movement in all of occupied Europe, covering both German and Soviet zones of occupation. The Polish resistance is most notable for disrupting German supply lines to the Eastern Front (damaging or destroying 1/8 of all rail transports), providing intelligence reports to the British intelligence agencies (providing 43% of all reports from occupied Europe), and for saving more Jewish lives in the Holocaust than any other Western Allied organization or government. It was a part of the Polish Underground State. Organizations The largest of all Polish resistance organizations was the Armia Krajowa (Home Army, AK), loyal to the Polish government in exile in London. The ''AK'' was formed in 1942 from the Union of Armed Struggle (''Związek Walki Zbrojnej'' or ZWZ, itself created in 1939) and wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Crimes Against The Polish Nation
Crimes against the Polish nation committed by Nazi Germany and Axis collaborationist forces during the invasion of Poland, along with auxiliary battalions during the subsequent occupation of Poland in World War II, consisted of the murder of millions of ethnic Poles and the systematic extermination of Jewish Poles. These mass murders were enacted by the Nazis with further plans that were justified by their racial theories, which regarded Poles and other Slavs, as well as Jews, as racially inferior '' Untermenschen''. By 1942, the Nazis were implementing their plan to murder every Jew in German-occupied Europe, and had also developed plans to eliminate the Polish people through mass murder, ethnic cleansing, enslavement and extermination through labor, and assimilation into German identity of a small minority of Poles deemed "racially valuable". During World War II, the Germans not only murdered millions of Poles, but ethnically cleansed millions more through forced depo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expulsion Of Poles By Nazi Germany
The Expulsion of Poles by Nazi Germany during World War II was a massive operation consisting of the forced resettlement of over 1.7 million Poles from the territories of German-occupied Poland, with the aim of their Germanization (see Lebensraum) between 1939 and 1944. The German Government had plans for the extensive colonisation of territories of occupied Poland, which were annexed directly into Nazi Germany in 1939. Eventually these plans grew bigger to include parts of the General Government. The region was to become a "purely German area" within 15–20 years, as explained by Adolf Hitler in March 1941. By that time the General Government was to be cleared of 15 million Polish nationals, and resettled by 4–5 million ethnic Germans. The operation was the culmination of the expulsion of Poles by Germany carried out since the 19th century, when Poland was partitioned among foreign powers including Germany. Racial policies Following the German invasion of the count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Police Battalion 322
The Police Battalion 322 (''Polizeibattalion 322'') was a formation of the German Order Police (uniformed police) during the Nazi era. During Operation Barbarossa, it was subordinated to the SS and deployed in German-occupied areas, specifically the Army Group Centre Rear Area, of the Soviet Union, as part of Police Regiment Centre. Alongside detachments from the ''Einsatzgruppen'' and the SS Cavalry Brigade, it perpetrated mass murder during the Holocaust and was responsible for large-scale crimes against humanity targeting civilian populations. In mid-1942, the battalion was reassigned to the 5th Police Regiment and operated in German-occupied territories of Slovenia. Background and formation The German Order Police (uniformed police) was a key instrument of the security apparatus of Nazi Germany. In the prewar period, Heinrich Himmler, the head of the SS, and Kurt Daluege, chief of the Order Police, cooperated in transforming the police force of the Weimar Republic into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million Military personnel, personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Air warfare of World War II, Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupation Of Poland (1939–1945)
The occupation of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union during World War II (1939–1945) began with the German-Soviet invasion of Poland in September 1939, and it was formally concluded with the End of World War II in Europe, defeat of Germany by the Allies in May 1945. Throughout the entire course of the occupation, the territory of Poland was divided between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union (USSR) both of which intended to eradicate Poland's culture and subjugate its people. In the summer-autumn of 1941, the Territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union, lands which were annexed by the Soviets were overrun by Germany in the course of the initially successful Operation Barbarossa, German attack on the USSR. After a few years of fighting, the Red Army drove the Wehrmacht, German forces out of the USSR and crossed into Poland from the rest of Central and Eastern Europe. Sociologist Tadeusz Piotrowski (sociologist), Tadeusz Piotrowski argues that both occupying power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area. Białystok is located in the Białystok Uplands of the Podlachian Plain on the banks of the Biała River, by road northeast of Warsaw. It has historically attracted migrants from elsewhere in Poland and beyond, particularly from Central and Eastern Europe. This is facilitated by the nearby border with Belarus also being the eastern border of the European Union, as well as the Schengen Area. The city and its adjacent municipalities constitute Metropolitan Białystok. The city has a warm summer continental climate, characterized by warm summers and long frosty winters. Forests are an important part of Białystok's character and occupy around (18% of the administrative area of the city) which places it as the fifth-most forested city in Poland. The first settlers arrived in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |