|
Gurpurab
Gurpurab (Punjabi: ਗੁਰਪੁਰਬ ) in Sikh tradition is a celebration of an anniversary of a Guru's birth marked by the holding of a festival. There are indications in the old chronicles that the gurus who succeeded Guru Nanak celebrated his birthday. Such importance was attached to the anniversaries that dates of the deaths of the first four gurus were recorded on a leaf in the first recension of the Scripture prepared by the Fifth Guru, Guru Arjan. The term ''gurpurab'' first appeared in the time of the gurus. It is a compound of the word ''purab'' (or ''parva'' in Sanskrit), mean a birth day with the word ''guru''. It occurs in at least five places in the writings of Bhai Gurdas (1551–1636), written in the time of Guru Arjan Dev Ji (5th Guru of the Sikhs). Among the more important gurpurbs in the Nanakshahi calendar are the birth anniversaries of Guru Nanak and Guru Gobind Singh, the martyrdom days of Guru Arjan and Guru Tegh Bahadur, and of the installation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanakshahi Calendar
The Nanakshahi calendar (Punjabi: ਨਾਨਕਸ਼ਾਹੀ ਜੰਤਰੀ ) is a tropical solar calendar used in Sikhism. It is based on the "Barah Maha" (Twelve Months), a composition composed by the Sikh gurus reflecting the changes in nature conveyed in the twelve-month cycle of the year. The year begins with the month of Chet, with 1 Chet corresponding to 14 March. The reference epoch of the Nanakshahi calendar is the birth of Guru Nanak Dev, corresponding to the year 1469 CE. Etymology The Nanakshahi Calendar is named after the founder of the Sikh religion, Guru Nanak Dev Ji.J. Gordon Melton, Martin Baumann (2010) Religions of the World: A Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Beliefs and Practices, 2nd Edition volumes ABC-Cli/ref> History Sikhs have traditionally recognised two eras and luni-solar calendars: the Nanakshahi and Khalsa. Traditionally, both these calendars closely followed the Bikrami calendar with the Nanakshahi year beginning on Katak Pooranmashi (full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also referred to as ('father Nānak'), was the founder of Sikhism and is the first of the ten Sikh Gurus. His birth is celebrated worldwide as Guru Nanak Gurpurab on '' Katak Pooranmashi'' ('full-moon of Kattak'), i.e. October–November. Nanak is said to have travelled far and wide across Asia teaching people the message of '' ik onkar'' (), who dwells in every one of his creations and constitutes the eternal Truth. With this concept, he would set up a unique spiritual, social, and political platform based on equality, fraternal love, goodness, and virtue. Nanak's words are registered in the form of 974 poetic hymn A hymn is a type of song, and partially synonymous with devotional song, specifically written for the purpose of adoration or prayer, and typically addressed to a deity or deities, or to a prominent figure or personification. The word ''hymn . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punjabi Language
Punjabi (; ; , ), sometimes spelled Panjabi, is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language of the Punjab, Punjab region of Pakistan and India. It has approximately 113 million native speakers. Punjabi is the most widely-spoken first language in Pakistan, with 80.5 million native speakers as per the 2017 Census of Pakistan, 2017 census, and the 11th most widely-spoken in India, with 31.1 million native speakers, as per the 2011 Census of India, 2011 census. The language is spoken among a Punjabi diaspora, significant overseas diaspora, particularly in Canada, the United States, and the United Kingdom. In Pakistan, Punjabi is written using the Shahmukhi alphabet, based on the Persian alphabet, Perso-Arabic script; in India, it is written using the Gurmukhi, Gurmukhi alphabet, based on the Brahmic scripts, Indic scripts. Punjabi is unusual among the Indo-Aryan languages and the broader Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family in its usage of Tone (linguistics) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurdwara
A gurdwara (sometimes written as gurudwara) ( Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰਦੁਆਰਾ ''guradu'ārā'', meaning "Door to the Guru") is a place of assembly and worship for Sikhs. Sikhs also refer to gurdwaras as ''Gurdwara Sahib''. People from all faiths are welcomed in gurdwaras. Each gurdwara has a '' Darbar Sahib'' where the current and everlasting guru of the Sikhs, the scripture Guru Granth Sahib, is placed on a (an elevated throne) in a prominent central position. Any congregant (sometimes with specialized training, in which case they can be known by the term granthi) may recite, sing, and explain the verses from the Guru Granth Sahib, in the presence of the rest of the congregation. All gurdwaras have a hall, where people can eat free vegetarian food served by volunteers at the gurdwara. They may also have a medical facility room, library, nursery, classroom, meeting rooms, playground, sports ground, a gift shop, and finally a repair shop. A gurdwara can be identified from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirtan
Kirtana ( sa, कीर्तन; ), also rendered as Kirtan, is a Sanskrit word that means "narrating, reciting, telling, describing" of an idea or story, specifically in Indian religions. It also refers to a genre of religious performance arts, connoting a musical form of narration or shared recitation, particularly of spiritual or religious ideas, native to the Indian subcontinent. With roots in the Vedic ''anukirtana'' tradition, a kirtan is a call-and-response style song or chant, set to music, wherein multiple singers recite or describe a legend, or express loving devotion to a deity, or discuss spiritual ideas. It may include dancing or direct expression of ''bhavas'' (emotive states) by the singer. Many kirtan performances are structured to engage the audience where they either repeat the chant,Sara Brown (2012), ''Every Word Is a Song, Every Step Is a Dance'', PhD Thesis, Florida State University (Advisor: Michael Bakan), pages 25-26, 87-88, 277 or reply to the call o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rehras
Rehras Sahib ( pa, ਰਹਰਾਸਿ ਸਾਹਿਬ), commonly known as So dar Rehras, is the daily evening prayer of the Sikhs and is part of Nitnem. It includes hymns from Guru Granth Sahib Ji and Dasam Granth Ji. It contains hymns of So Dar, So Purakh, Chaupai Sahib, Anand Sahib and Mundhavani, among which Chaupai Sahib is from the Dasam Granth Ji. This Bani is a collection of hymns of five Sikh Gurus: Guru Nanak Dev Ji, Guru Amar Das Ji, Guru Ram Das Ji, Guru Arjan Dev Ji and Guru Gobind Singh Ji. See also * Guru Granth Sahib Ji * SGPC The Shiromani Gurdwara Parbandhak Committee ( SGPC; "Supreme Gurdwara Management Committee") is an organization in India responsible for the management of Gurdwaras, Sikh places of worship in states of Punjab and Himachal Pradesh and the union ... * Dasam Granth Ji References External links * Complete Rehras Sahib (PDF)' * Rehras Sahib Bani in Punjabi' * Rehras Sahib Bani in Hindi' Adi Granth Sikh terminology Sik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karah Parsad
Karah ( fa, كراه, also Romanized as Karāh) is a village in Dalfard Rural District, Sarduiyeh District, Jiroft County, Kerman Province, Iran Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm .... At the 2006 census, its population was 58, in 12 families. References Populated places in Jiroft County {{Jiroft-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katha (storytelling Format)
Katha (or Kathya) is an Indian style of religious storytelling, performances of which are a ritual event in Hinduism. It often involves ''priest- narrators'' (kathavachak or vyas) who recite stories from Hindu religious texts, such as the Puranas, the Ramayana or Bhagavata Purana, followed by a commentary (''Pravachan''). Kathas sometimes take place in households, involving smaller stories related to the '' Vrat'' Katha genre. The didactic Satyanarayan and Ramayana kathas instill moral values by revealing the consequences of human action (karma). Claus, p. 331 History Each region of India has developed its own style and tradition of storytelling in local languages. Epics and puranas, ancient stories of wisdom told in Sanskrit, are the story material common to most regions. Performances are given in temples and at weddings and other religious (or social) functions. The single performer should be versatile in exposition and able to interestingly narrate humorous anecdotes. The sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
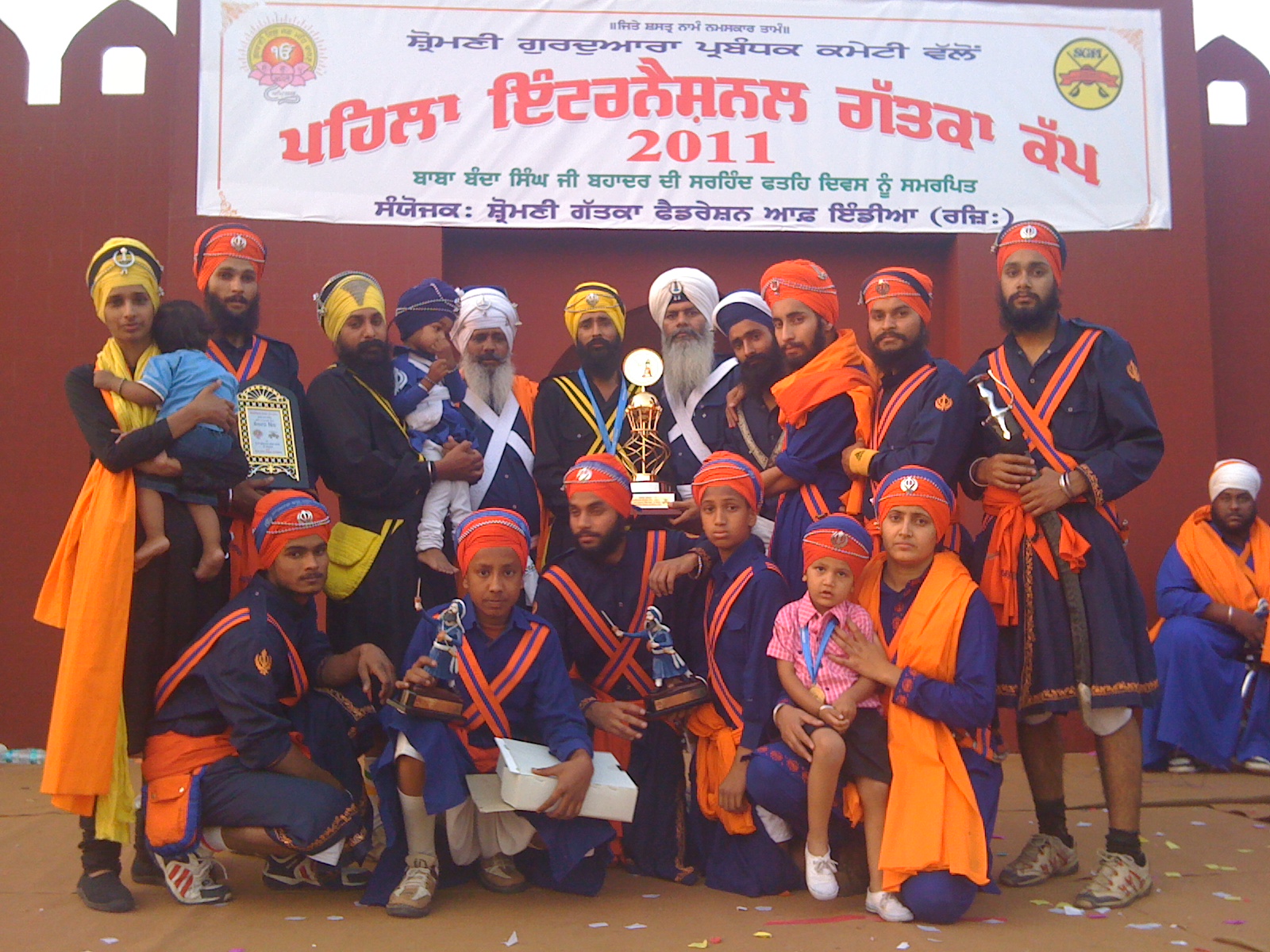
Gatka
Gatka (; ; hi, गतका; ur, ) is a form of martial art associated primarily with the Sikhs of the Punjab and other related ethnic groups, such as Hindkowans. It is a style of stick-fighting, with wooden sticks intended to simulate swords. The Punjabi name, , refers to the wooden stick used and this term might have originated as a diminutive of a Sanskrit word, , meaning "mace". The stick used in Gatka is made of wood and is usually long, with a thickness of around . It comes with a fitted leather hilt, and is often decorated with Punjabi-style multi-coloured threads. The other weapon used in the sport is a shield, natively known as . It is round in shape, measuring , and is made of dry leather. It is filled with either cotton or dry grass to protect the hand of player in case of full contact hit by an opponent. Gatka originated in the Punjab in the 15th century. There has been a revival during the later 20th century, with an International Gatka Federation was fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panj Piare
Panj Pyare ( pa, ਪੰਜ ਪਿਆਰੇ, ', the five beloved ones) is the collective name given to five men − Daya Singh, Dharam Singh, Himmat Singh, Mohkam Singh and Sahib Singh – by the tenth Sikh guru, Guru Gobind Singh during the historic and monumental divan at Anandpur Sahib in the Punjab region of India on March 30, 1699. (The Gregorian calendar skipped 11 days in 1752. So, in present times, Vaisakhi occurs near 13 April every year.) They formed the nucleus of the Khalsa: the first five persons to receive Khanda di Pahul initiation and rites (baptism) of the two-edged sword. They were the inaugural Panj Pyare. However, the term is not limited only to this inaugural group. After them, any group of five baptized Sikhs are also referred to as the Panj Pyare. Until the Vaisakhi of AD 1699, the Sikh initiation ceremony was known as ''Charan Pahul''. Story of Vasakhi Gobind Rai was 33 years old when he had Divine inspiration to actuate his designs and make an undying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |