|
Guobiao Standards
The National Standards of the People's Republic of China (), coded as , are the standards issued by the Standardization Administration of China under the authorization of Article 10 of the Standardization Law of the People's Republic of China. According to Article 2 of the Standardization Law, national standards are divided into mandatory national standards and recommended national standards. Mandatory national standards are prefixed "GB". Recommended national standards are prefixed "". Guidance technical documents are prefixed with "GB/Z", but are not legally part of the national standard system. Mandatory national standards are the basis for the product testing which products must undergo during the China Compulsory Certificate (CCC or 3C) certification. If there is no corresponding mandatory national standard, CCC is not required. Nomenclature A Chinese standard code has three parts: the prefix, the sequential number, and the year number. For example, GB 2312-1980 refers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GB Logo SVG
GB, or Gb may refer to: Places * United Kingdom (ISO 3166-1 code), a sovereign country situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe ** Great Britain, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800), a predecessor country of the United Kingdom * Gilgit-Baltistan, a region in northern Pakistan * Guinea-Bissau, a sovereign state in West Africa * Green Bay, Wisconsin, United States * Great Barrington, Massachusetts, United States Businesses and organisations * GB Airways, a British airline * Gardner Bender, a manufacturer of professional electrician's tools and supplies * Girls' Brigade, a Christian organization for girls * Grande Bibliothèque, a large public library in Montreal * University of Wisconsin–Green Bay, an American university * ABX Air (IATA airline designator GB), a cargo airline * GB Glace, a Swedish ice cream company * Griesedieck Brothers beer, an American beer brand * GB Supermarkets, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GB 12052
GB 12052-89, entitled ''Korean character coded character set for information interchange'' ( zh, s=信息交换用朝鲜文字编码字符集), is a character set standard established by China for the Korean language in China. It consists of a total of 5,979 characters, and has no relationship nor compatibility with South Korea's KS X 1001 and North Korea's KPS 9566. Characters Characters in GB 12052 are arranged in a 94×94 grid (as in ISO/IEC 2022), and the two-byte code point of each character is expressed in the ''qu''-''wei'' form, which specifies a row (''qu'' ) and the position of the character within the row (cell, ''wei'' ). The rows (numbered from 1 to 94) contain characters as follows: * 01–09: identical to GB 2312, except 03-04 ( in GB 2312, in GB 12052) * 16–37: modern Hangul syllables and ''jamo'', level 1 (2,017 syllables and 51 ''jamo'') * 38–52: modern Hangul syllables, level 2 (1,356 characters) * 53–72: archaic Hangul syllables and ''jamo'' (1,683 sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 639
ISO 639 is a international standard, standard by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) concerned with representation of languages and language groups. It currently consists of four sets (1-3, 5) of code, named after each part which formerly described respective set (part 4 was guidelines without its own coding system); a part 6 was published but withdrawn. It was first approved in 1967 as a single-part ISO Recommendation, ISO/R 639, superseded in 2002 by part 1 of the new series, ISO 639-1, followed by additional parts. All existing parts of the series were consolidated into a single standard in 2023, largely based on the text of ISO 639-4. Use of ISO 639 codes The language codes defined in the several sections of ISO 639 are used for bibliographic purposes and, in computing and internet environments, as a key element of Locale (computer software), locale data. The codes also find use in various applications, such as Wikipedia URLs for its different language edi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 3166-1
ISO 3166-1 (''Codes for the representation of names of countries and their subdivisions – Part 1: Country code'') is a standard defining codes for the names of countries, dependent territories, and special areas of geographical interest. It is the first part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization. It defines three sets of country codes: * ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 – two-letter country codes which are used most prominently for the Internet's country code top-level domains (with a few exceptions). * ISO 3166-1 alpha-3 – three-letter country codes which allow a better visual association between the codes and the country names than the alpha-2 codes. * ISO 3166-1 numeric – three-digit country codes which are identical to those developed and maintained by the United Nations Statistics Division, with the advantage of script (writing system) independence, and hence useful for people or systems using non-Latin scripts. The alphabetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 5218
ISO/IEC 5218 ''Information technology — Codes for the representation of human sexes'' is an international standard that defines a representation of human sexes through a language-neutral single-digit code. It can be used in information systems such as database applications. The four codes specified in ISO/IEC 5218 are: * 0 = Not known; * 1 = Male; * 2 = Female; * 9 = Not applicable. The standard specifies that its use may be referred to by the designator "SEX". The standard explicitly states that no significance is to be placed on the encoding of ''male'' as 1 and ''female'' as 2; the encoding merely reflects existing practice in the countries that initiated this standard. The standard also explains that it "meets the requirements of most applications that need to code human sexes. It does not provide codes for sexes that may be required in specific medical and scientific applications or in applications that need to code sex information other than for human beings." Since its 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Division Codes Of The People's Republic Of China
The administrative division codes of the People's Republic of China identify the administrative divisions of China at county level and above. They are published by the National Bureau of Statistics of China with the latest version issued on September 30, 2015. Coding scheme Reading from left to right, administrative division codes contain the following information: * The first and second digits identify the highest level administrative division, which may be a province, autonomous region, municipality or Special Administrative Region (SAR). * Digits three and four show summary data for the associated prefecture-level city, prefecture (地区 ''dìqū''), autonomous prefecture, Mongolian league, municipal city district or county. Codes 01 – 20 and 51 – 70 identify provincial level cities, codes 21 – 50 represent prefectures, autonomous prefectures and Mongolian leagues. *The fifth and sixth digits represent the county-level division – city district, county-level ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 2022
ISO/IEC 2022 ''Information technology—Character code structure and extension techniques'', is an ISO/IEC standard in the field of character encoding. It is equivalent to the ECMA standard ECMA-35, the ANSI standard ANSI X3.41 and the Japanese Industrial Standard JIS X 0202. Originating in 1971, it was most recently revised in 1994. ISO 2022 specifies a general structure which character encodings can conform to, dedicating particular ranges of bytes ( 0x00–1F and 0x7F–9F) to be used for non-printing control codes for formatting and in-band instructions (such as line breaks or formatting instructions for text terminals), rather than graphical characters. It also specifies a syntax for escape sequences, multiple-byte sequences beginning with the control code, which can likewise be used for in-band instructions. Specific sets of control codes and escape sequences designed to be used with ISO 2022 include ISO/IEC 6429, portions of which are implemented by ANSI.SYS and te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 646
ISO/IEC 646 ''Information technology — ISO 7-bit coded character set for information interchange'', is an International Organization for Standardization, ISO/International Electrotechnical Commission, IEC standard in the field of character encoding. It is equivalent to the Ecma International, ECMA standard ECMA-6 and developed in cooperation with ASCII at least since 1964. The first version of ECMA-6 had been published in 1965, based on work the ECMA's Technical Committee TC1 had carried out since December 1960. The first edition of ISO/IEC 646 was published in 1973, and the most recent, third, edition in 1991. ISO/IEC 646 specifies a 7-bit character code from which several national standards are derived. It allocates a set of 82 unique graphic characters to 7-bit code points, known as the ''invariant'' (INV) or ''basic character set'', including letters of the ISO basic Latin alphabet, Numerical digit, digits, and some common English language, English pun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, Textile, rags, poaceae, grasses, Feces#Other uses, herbivore dung, or other vegetable sources in water. Once the water is drained through a fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distributed on the surface, it can be pressed and dried. The papermaking process developed in east Asia, probably China, at least as early as 105 Common Era, CE, by the Han Dynasty, Han court eunuch Cai Lun, although the earliest archaeological fragments of paper derive from the 2nd century BCE in China. Although paper was originally made in single sheets by hand, today it is mass-produced on large machines—some making reels 10 metres wide, running at 2,000 metres per minute and up to 600,000 tonnes a year. It is a versatile material with many uses, including printing, painting, graphics, signage, design, packaging, decorating, writing, and Housekeeping, cleaning. It may also be used a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
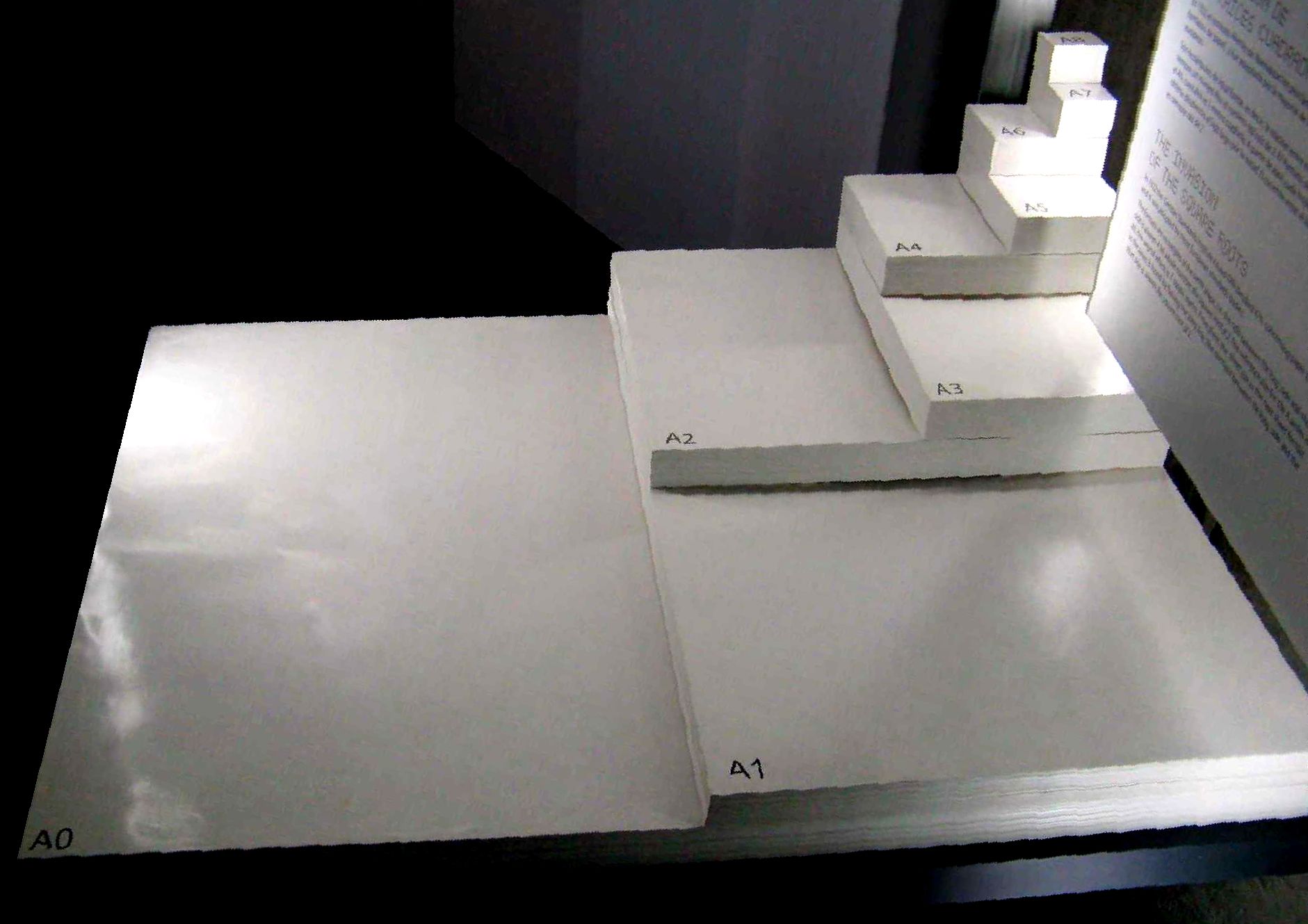
ISO 216
ISO 216 is an international standard for paper sizes, used around the world except in North America and parts of Latin America. The standard defines the "A", "B" and "C" series of paper sizes, which includes the A4, the most commonly available paper size worldwide. Two supplementary standards, ISO 217 and ISO 269, define related paper sizes; the ISO 269 "C" series is commonly listed alongside the A and B sizes. All ISO 216, ISO 217 and ISO 269 paper sizes (except some envelopes) have the same aspect ratio, , within rounding to millimetres. This ratio has the unique property that when cut or folded in half widthways, the halves also have the same aspect ratio. Each ISO paper size is one half of the area of the next larger size in the same series. Dimensions of A, B and C series History The oldest known mention of the advantages of basing a paper size on an aspect ratio of \sqrt is found in a letter written on 25 October 1786 by the German scientist Georg Christoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Housing And Urban-Rural Development
The Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development is a ministry of the People's Republic of China which provides housing and regulates the state construction activities in mainland China. History It was formerly known as the Ministry of Construction (). As part of US$586 billion economic stimulus package of November 2008, the government plans to: *Housing: increase the construction of more affordable and low-rent housing and the speeding up of slum demolition, to initiate a pilot program to rebuild rural homes, and a program to encourage nomads to move into permanent housing. *Rural infrastructure: improve roads and power grids in the countryside, and drinking water, including a huge project to divert water from the South to the North of China. Also, poverty relief initiatives will be strengthened. In November 2012, the Ministry established its smart cities pilot program, which became the start of a nationwide smart cities movement. From 2013 to 2015, 277 Chinese cities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Administration Of Quality Supervision, Inspection, And Quarantine
The General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China ( zh, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, abbreviated AQSIQ) was a ministerial-level department under the State Council of the People's Republic of China that was in charge of national quality, metrology, entry-exit commodity inspection, entry-exit health quarantine, entry-exit animal and plant quarantine, import-export food safety, certification and accreditation, standardization, as well as administrative law enforcement. AQSIQ directly administers provincial Entry-Exit Inspection and Quarantine Bureaus and Bureaus of Quality and Technical Supervision. For example, the Beijing Entry-Exit Inspection and Quarantine Bureau is responsible for collecting health declaration forms, and used thermal imaging to spot passengers with fever due to the 2009 flu pandemic prior to July 16, 2009. History AQSIQ was formed as the successor government body to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |