|
Gundalow
A gundalow (also known in period accounts as a "gondola") is a type of flat-bottomed sailing barge once common in Maine and New Hampshire rivers, United States. It first appeared in the mid-1600s, reached maturity of design in the 1700 and 1800s, and lingered into the early 1900s before nearly vanishing as a commercial watercraft. Characteristics A form of sailing barge similar to a scow, gundalows characteristically employed tidal currents for propulsion, but shipped a single lateen sail brailed to a heavy yard to harness winds. The yard was attached to a stump mast and heavily counterweighted, pivoting down while still under sail to shoot under bridges while maintaining the boat's way. Up to long, gundalows were fitted with a pivoting leeboard in lieu of a fixed keel, giving them an exceptionally shallow draft and allowing them to "take the hard" (settle into sand, ledge, or mudflats) both for loading and unloading cargoes and maintenance. Cargoes Common cargoes were bricks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Valcour Island
The Battle of Valcour Island, also known as the Battle of Valcour Bay, was a naval engagement that took place on October 11, 1776, on Lake Champlain. The main action took place in Valcour Bay, a narrow strait between the Province of New York, New York mainland and Valcour Island. The battle is generally regarded as one of the first naval battles of the American Revolutionary War, and one of the first fought by the United States Navy. Most of the ships in the American fleet under the command of Benedict Arnold were captured or destroyed by a Kingdom of Great Britain, British force under the overall direction of General Guy Carleton, 1st Baron Dorchester, Guy Carleton. However, the American defense of Lake Champlain stalled British plans to reach the upper Hudson River valley. The Continental Army had retreated from Province of Quebec (1763-1791), Quebec to Fort Ticonderoga and Fort Crown Point in June 1776 after British forces were massively reinforced. They spent the summer of 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noble Train Of Artillery
The noble train of artillery, also known as the Knox Expedition, was an expedition led by Continental Army Colonel Henry Knox to transport heavy weaponry that had been Capture of Fort Ticonderoga, captured at Fort Ticonderoga to the Continental Army camps outside Boston during the winter of 1775–76. Knox went to Ticonderoga in November 1775 and moved 60 tons#Ware, Ware (2000), p. 18 of cannon and other armaments over the course of three winter months by boat, horse, ox-drawn sledges, and manpower along poor-quality roads, across two semi-frozen rivers, and through the forests and swamps of the lightly inhabited Berkshires to the Boston area,#Ware, Ware (2000), pp. 19–24#Brooks, N. Brooks (1900), p. 38 covering approximately . Historian Victor Brooks has called Knox's exploit "one of the most stupendous feats of logistics" of the American Revolutionary War.#VBrooks, V. Brooks (1999), p. 210 The route he took is now known as the Henry Knox Trail. Background The American Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leeboard
A leeboard is a form of pivoting keel used largely by sailboats, very often in lieu of a fixed keel. Typically mounted in pairs on each side of a hull, leeboards function much like a centreboard, allowing shallow-draft craft to ply waters inaccessible to fixed-keel boats. Only the leeward side leeboard is used at any time, as it submerges when the boat heels under the force of the wind. A disadvantage, where there is an inadequate fixed keel, is that leeboards typically ship (bear) little ballast, and being on the far ( lee) side delays the onset of unballasted craft's heeling, that is, inhibits the effect of putting up a good, constant resistance against the wind. The classical, archetypal definition of ballast is a low, central weight to optimise centre of mass, to reduce turning moment and therefore resistance to the boat keeling over; however, the centre of gravity tends to be higher in self-righting vessels. Modern developments allow leeboards to act as a speed-enh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gandelow
The gandelow is a traditional wooden fishing boat used on the River Shannon on the west coast of Ireland. The boat has been in use by fishing communities since at least the 17th century, mostly for catching salmon and cutting reeds. The gandelow is a flat-bottomed boat about 7 metres long constructed by local craftsmen following traditional designs. It has recently experienced a revival and is now in use for sport, exercise and recreational fishing. History The origins of the gandelow’s name are unknown - it may be connected with that of the Italian gondola ('small boat') or, possibly, be a version of the Viking name for their flat-bottomed boats. Most gandelows were around 7 metres (23 feet) along and were rowed by two or three fishermen whose main catch was salmon. The boats were also used for cutting thatching reeds and for transporting people and the occasional cow or sheep. In Limerick, some boats were used to take pilots out to the ocean-going vessels or acted as small lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateen Sail
A lateen (from French ''latine'', meaning "Latin") or latin-rig is a triangular sail set on a long yard mounted at an angle on the mast, and running in a fore-and-aft direction. The settee can be considered to be an associated type of the same overall category of sail. The lateen originated in the Mediterranean as early as the 2nd century AD, during Roman times, and became common there by the 5th century. The wider introduction of lateen rig at this time coincided with a reduction in the use of the Mediterranean square rig of the classical era. Since the performance of these two rigs is broadly similar, it is suggested that the change from one to the other was on cost grounds, since lateen rigs used fewer components and had less cordage to be replaced when it wore out. Arab seafarers adopted the lateen rig at a later datethere is some limited archaeological evidence of lateen rig in the Indian Ocean in the 13th century AD and iconographic evidence from the 16th century. It h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
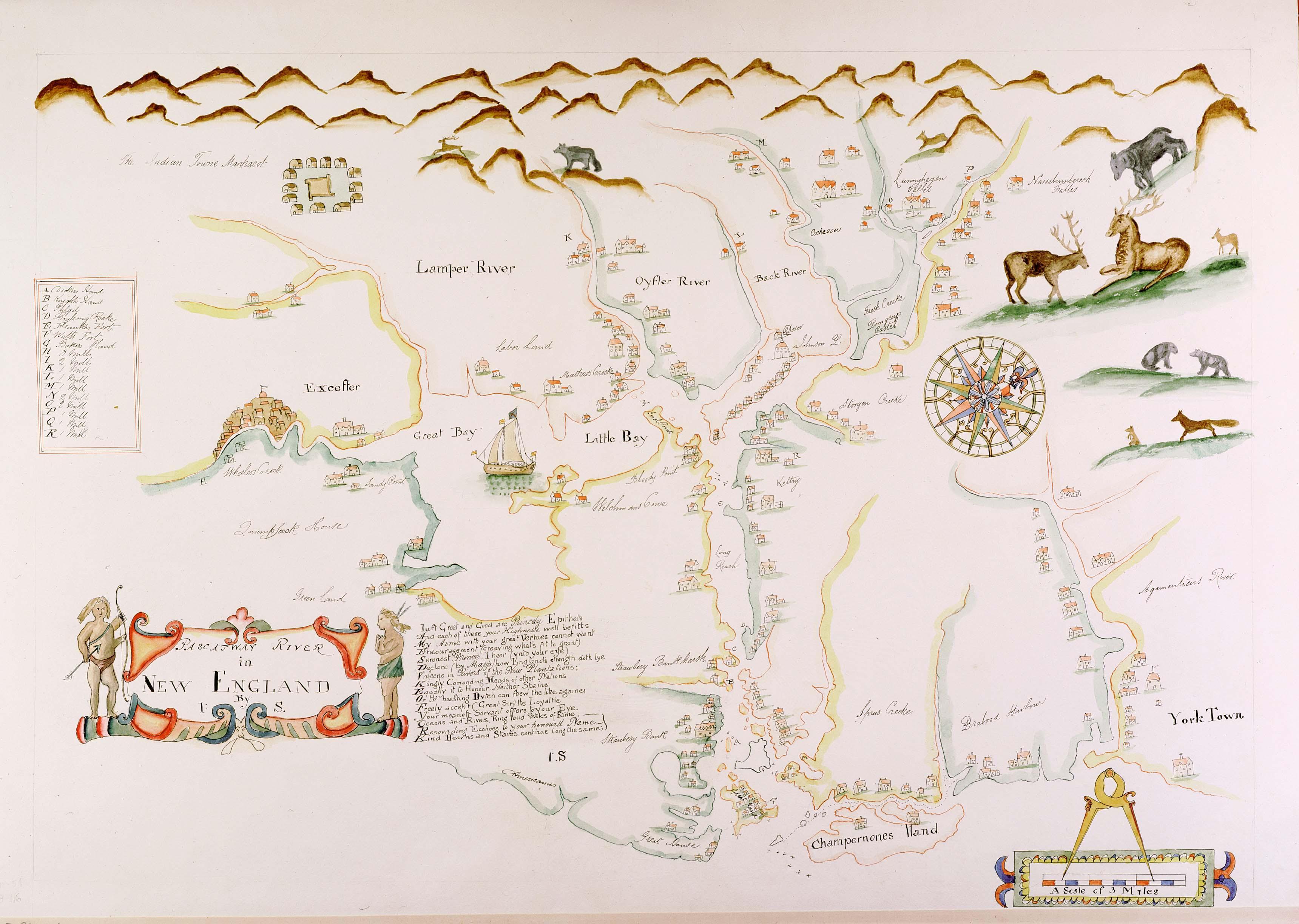
Piscataqua (ship)
Piscataqua, believed to be an Abenaki word meaning ''rapid waters'', may refer to: * Piscataqua River, a fast-moving estuarine river dividing coastal New Hampshire and Maine in the United States * Piscataqua River (Presumpscot River), a tributary of the Presumpscot River in Maine See also * Piscataquis County, Maine * Piscataquis River The Piscataquis River () is a major tributary of the Penobscot River, found in Piscataquis County, Maine, United States. It starts from the confluence of its East Branch and West Branch () in Blanchard. The river flows in a mostly eastern dir ..., a tributary of the Penobscot River in Maine * Piscataquog River, a tributary of the Merrimack River in New Hampshire * Piscataway (other) {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
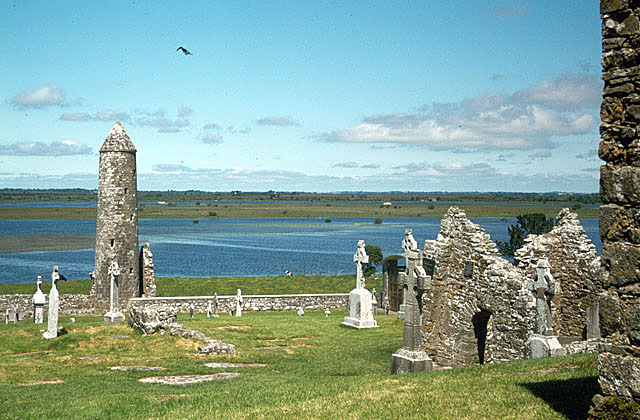
River Shannon
The River Shannon ( or archaic ') is the major river on the island of Ireland, and at in length, is the longest river in the British Isles. It drains the Shannon River Basin, which has an area of , – approximately one fifth of the area of Ireland. Known as an important waterway since antiquity, the Shannon first appeared in maps by the Graeco-Egyptian geographer Ptolemy ( 100 – 170 AD). The river flows generally southwards from the Shannon Pot in County Cavan before turning west and emptying into the Atlantic Ocean through the long Shannon Estuary. Limerick city stands at the point where the river water meets the sea water of the estuary. The Shannon is tidal east of Limerick as far as the base of the Ardnacrusha dam. The Shannon divides the west of Ireland (principally the province of Connacht) from the east and south (Leinster and most of Munster; County Clare, being west of the Shannon but part of the province of Munster, is the major exception.) The river rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piscataqua River
The Piscataqua River (Abenaki language, Abenaki: ''Pskehtekwis'') is a tidal river forming the boundary of the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Maine from its origin at the confluence of the Salmon Falls River and Cochecho River to the Atlantic Ocean. The drainage basin of the river is approximately , including the subwatersheds of the Great Works River and the five rivers flowing into Great Bay (New Hampshire), Great Bay: the Bellamy River, Bellamy, Oyster River (New Hampshire), Oyster, Lamprey River, Lamprey, Squamscott River, Squamscott, and Winnicut River, Winnicut. The river runs southeastward, with New Hampshire to the south and west and Maine to the north and east, and empties into the Gulf of Maine east of Portsmouth, New Hampshire. The last before the sea are known as Portsmouth Harbor and have a tidal current of around . Beyond the tidal currents, the river has a flood current speed of 12 knots, making it the fastest river on the eastern seaboard of the United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocheco River
The Cochecho River (incorrectly Cocheco River) is a tributary of the Piscataqua River, long, in the U.S. state of New Hampshire. It rises in northern Strafford County and runs southeastward, through the town of Farmington and the cities of Rochester and Dover, where it provides hydroelectric power. Below the center of Dover, the river is tidal and joins the Salmon Falls River at the Maine border to form the Piscataqua. Significant tributaries include the Ela River, the Mad River, and the Isinglass River. History of the name Cochecho is an Abenaki word meaning "rapid foaming water," referring to Cochecho Falls in downtown Dover. Settlers adopted the name for both the river and principal settlement, the village of Cochecho. One of the oldest place names in New Hampshire, and the original name of Dover, Cochecho is at risk of extinction because of bureaucratic corruption. In 1642, Richard Waldron was granted water privileges at Cochecho Falls, moving there from Dover Point to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dover, New Hampshire
Dover is a city in Strafford County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 32,741 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, making it the most populous city in the New Hampshire Seacoast Region (New Hampshire), Seacoast region and the List of municipalities in New Hampshire, fifth most populous city in New Hampshire. It is the county seat of Strafford County, and home to Wentworth-Douglass Hospital, the Woodman Institute Museum, and the Children's Museum of New Hampshire. Etymology The city is named for Dover, Kent, England. First recorded in its Latinised form of ''Portus Dubris'', the word "Dover" derives from the insular Celtic languages, Brythonic word for "waters" (''dwfr'' in Middle Welsh). The same element is present in the word's French language, French (''Douvres'') and Welsh Language, Modern Welsh (''Dofr'') forms. History Settlement The first known European to explore the region was Martin Pring from Bristol, England, in 1603. In 1623, brothers Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
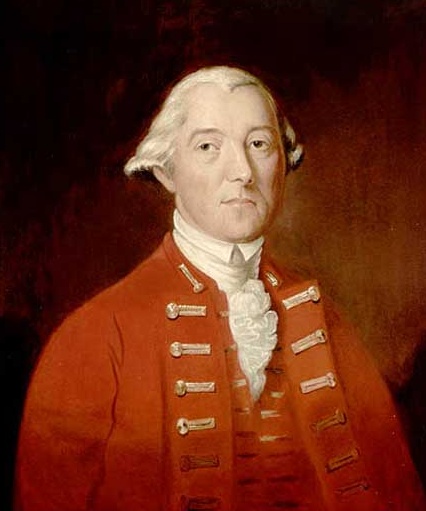
Captain Edward Adams
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader or highest rank officer of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, etc. In militaries, the captain is typically at the level of an officer commanding a company or battalion of infantry, a ship, or a battery of artillery, or another distinct unit. It can also be a rank of command in an air force. The term also may be used as an informal or honorary title for persons in similar commanding roles. Etymology The word "captain" derives from the Middle English "capitane", itself coming from the Latin "caput", meaning "head". It is considered cognate with the Greek word (, , or "the topmost"), which was used as title for a senior Byzantine military rank and office. The word was Latinized as . Both ultimately derive from the Proto-Indo-European "*kaput", also meaning head. Occupations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portsmouth, New Hampshire
Portsmouth is a city in Rockingham County, New Hampshire, Rockingham County, New Hampshire, United States. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 census it had a population of 21,956. A historic seaport and popular summer tourist destination on the Piscataqua River bordering the state of Maine, Portsmouth was formerly the home of the Strategic Air Command's Pease Air Force Base, since converted to Portsmouth International Airport at Pease. History Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American Indians of the Abenaki and other Algonquian languages-speaking nations, and their predecessors, inhabited the territory of coastal New Hampshire for thousands of years before European contact. The first known European to explore and write about the area was Martin Pring in 1603. The Piscataqua River is a tidal estuary with a swift current, but forms a good natural harbor. The west bank of the harbor was settled by European colonists in 1630 and named Strawbery Banke, after the many wild Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |