|
Gumma (pathology)
A gumma (plural gummata or gummas) is a soft, non-cancerous growth resulting from the tertiary stage of syphilis (and yaws). It is a form of granuloma. Gummas are most commonly found in the liver (''gumma hepatis''), but can also be found in brain, heart, skin, bone, testis, and other tissues, leading to a variety of potential problems including neurological disorders or heart valve disease. Presentation Gummas have a firm, necrotic center surrounded by inflamed tissue, which forms an amorphous proteinaceous mass. The center may become partly hyalinized. These central regions begin to die through coagulative necrosis, though they also retain some of the structural characteristics of previously normal tissues, enabling a distinction from the granulomas of tuberculosis where caseous necrosis obliterates preexisting structures. Other histological features of gummas include an ''intervening zone'' containing epithelioid cells with indistinct borders and multinucleated giant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gummata Hepatis
A gumma (plural gummata or gummas) is a soft, non-cancerous growth resulting from the tertiary stage of syphilis (and yaws). It is a form of granuloma. Gummas are most commonly found in the liver (''gumma hepatis''), but can also be found in brain, heart, skin, bone, testis, and other tissues, leading to a variety of potential problems including neurological disorders or heart valve disease. Presentation Gummas have a firm, necrotic center surrounded by inflamed tissue, which forms an amorphous proteinaceous mass. The center may become partly hyalinized. These central regions begin to die through coagulative necrosis, though they also retain some of the structural characteristics of previously normal tissues, enabling a distinction from the granulomas of tuberculosis where caseous necrosis obliterates preexisting structures. Other histological features of gummas include an ''intervening zone'' containing epithelioid cells with indistinct borders and multinucleated giant c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many internal organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either simple squamous, simple columnar, or simple cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexually Transmitted Diseases And Infections
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, oral sex, or sometimes manual sex. STIs often do not initially cause symptoms, which results in a risk of transmitting them to others. The term ''sexually transmitted infection'' is generally preferred over ''sexually transmitted disease'' or ''venereal disease'', as it includes cases with no symptomatic disease. Symptoms and signs of STIs may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge, ulcers on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain. Some STIs can cause infertility. Bacterial STIs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Viral STIs include genital warts, genital herpes, and HIV/AIDS. Parasitic STIs include trichomoniasis. Most STIs are treatable and curable; of the most common infections, syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: 'tissue', 'suffering', and '' -logia'' 'study of') is the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks "). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as phosphate buffered saline). Preparation for h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirochaete
A spirochaete () or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetota (also called Spirochaetes ), which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) Gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled (corkscrew-shaped or spiraled, hence the name) cells. Spirochaetes are chemoheterotrophic in nature, with lengths between 3 and 500 μm and diameters around 0.09 to at least 3 μm. Spirochaetes are distinguished from other bacterial phyla by the location of their flagella, called endoflagella, or periplasmic flagella, which are sometimes called ''axial filaments''. Endoflagella are anchored at each end (pole) of the bacterium within the periplasmic space (between the inner and outer membranes) where they project backwards to extend the length of the cell. These cause a twisting motion which allows the spirochaete to move. When reproducing, a spirochaete will undergo asexual transverse binary fission. Most spirochaetes are free-living and anaero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who is often regarded as one of the founders of modern pathology. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components. In contrast, ''apoptosis'' is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal. Cellular death due to necrosis does not follow the apoptotic signal transduction pathway, but rather various receptors are activated and result in the loss of cell membrane integrity and an uncontrolled release of products of cell death into the extracellular space. This initiates an inflammatory response in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Cell
Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells or effector B cells, are white blood cells that originate in the lymphoid organs as B cells and secrete large quantities of proteins called antibodies in response to being presented specific substances called antigens. These antibodies are transported from the plasma cells by the blood plasma and the lymphatic system to the site of the target antigen (foreign substance), where they initiate its neutralization or destruction. B cells differentiate into plasma cells that produce antibody molecules closely modeled after the receptors of the precursor B cell. Structure Plasma cells are large lymphocytes with abundant cytoplasm and a characteristic appearance on light microscopy. They have basophilic cytoplasm and an eccentric nucleus with heterochromatin in a characteristic cartwheel or clock face arrangement. Their cytoplasm also contains a pale zone that on electron microscopy contains an extensive Golgi apparatus and centrioles. Abundan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and innate lymphoid cells (ILCs; "innate T cell-like" cells involved in mucosal immunity and homeostasis), of which natural killer cells are an important subtype (which functions in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity). They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte" (with ''cyte'' meaning cell). Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells. Types The three major types of lymphocyte are T cells, B cells and natural killer (NK) cells. They can also be classified as small lymphocytes and large lymphocytes based on their size and appearance. Lymphocytes can be identified by their large nucleus. T cells and B cells T cells (thymus cells) and B cells ( bone marrow- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
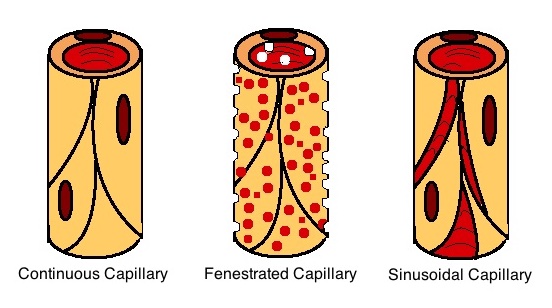
Capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell typically with a spindle shape that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells of connective tissue in animals. Structure Fibroblasts have a branched cytoplasm surrounding an elliptical, speckled cell nucleus, nucleus having two or more nucleoli. Active fibroblasts can be recognized by their abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). Inactive fibroblasts, called 'fibrocytes', are smaller, spindle-shaped, and have less RER. Although disjointed and scattered when covering large spaces, fibroblasts often locally align in parallel clusters when crowded together. Unlike the epithelial cells lining the body structures, fibroblasts do not form flat monolayers and are not restricted by a polarizing attachment to a basal lamina on one side, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Cell
A giant cell (also known as a multinucleated giant cell, or multinucleate giant cell) is a mass formed by the union of several distinct cells (usually histiocytes), often forming a granuloma. Although there is typically a focus on the pathological aspects of multinucleate giant cells (MGCs), they also play many important physiological roles. Osteoclasts are a type of MGC that are critical for the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bone and are present normally in a healthy human body. Osteoclasts are frequently classified and discussed separately from other MGCs which are more closely linked with disease. Non-osteoclast MGCs can arise in response to an infection, such as tuberculosis, herpes, or HIV, or as part of a foreign body reaction. These MGCs are cells of monocyte or macrophage lineage fused together. Similar to their monocyte precursors, they can phagocytose foreign materials. However, their large size and extensive membrane ruffling make them better equipped t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caseous Necrosis
Caseous necrosis or caseous degeneration () is a unique form of cell death in which the tissue maintains a cheese-like appearance.Robbins and Cotran: Pathologic Basis of Disease, 8th Ed. 2010. Pg. 16 Unlike with coagulative necrosis, tissue structure is destroyed. Caseous necrosis is enclosed within a granuloma. Caseous necrosis is most notably associated with tuberculoma. The dead tissue appears as a soft and white proteinaceous dead cell mass. The term ''caseous'' means 'pertaining or related to cheese', and comes from the Latin word 'cheese'. Histology In caseous necrosis no histological architecture is preserved (unlike with coagulative necrosis). On microscopic examination with H&E staining, the area is acellular, characterised by amorphous, roughly granular eosinophilic debris of now dead cells, also containing interspearsed haematoxyphilic remnants of cell nucleus contents. This caseus necrotic center is enclosed within a granuloma. Causes Frequently caseous necrosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |