|
Guianan Moist Forests
The Guianan moist forests (NT0125) is an ecoregion in the east of Venezuela, north of Brazil and the Guyanas (Guyana, Suriname and French Guiana). It is in the Amazon biome. The climate is hot and humid, with two rainy seasons each year. As of 1996 the tropical rainforest habitat was relatively intact, although there were mounting threats from illegal logging and gold mining. Location The Guianan moist forests ecoregion covers most of Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana. It covers part of eastern Venezuela and parts of the north of the Brazilian states of Pará and Amapá. It has a total area of . Along the Atlantic coast to the east and northeast the ecoregion adjoins strips of Guianan freshwater swamp forests, Amazon-Orinoco-Southern Caribbean mangroves and Orinoco Delta swamp forests. To the northwest it adjoins the Llanos ecoregion, the Guianan piedmont and lowland moist forests and Guianan Highlands moist forest. Scattered patches of this last ecoregion are found on higher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramakatoi
Paramakatoi is an Amerindian community in the Potaro-Siparuni Region of Guyana, located in the Pacaraima Mountains. With an altitude of , it is east of Kurukabaru. History The Akawaio and Patamona people are the most prominent groups in the area. Their communities had a deep connection with the land for their reliance on hunting, fishing, and subsistence farming. The village name comes from the name of the nearby creek, which is surrounded by Palamaka plants, and "toi" means savannah in the Patamona language. "Palamakatoi" became "Paramakatoi" when missionaries arrived in the area. The colonial period saw the influence of the Dutch and later the British in the area, but much of the region's interior, including places like Paramakatoi, remained relatively isolated from European settlement. Paramakatoi's development as a more established settlement is closely tied to the expansion of government and infrastructure in the 20th century. The community saw the establishment of roa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guianan Piedmont And Lowland Moist Forests
The Guianan piedmont and lowland moist forests (NT0182) is an ecoregion in the south of Venezuela and the north of Brazil. It is in the Amazon biome. The ecoregion is relatively intact, largely protected by conservation units or indigenous territories, and less threatened by global warming than flatter and more deforested regions. Location The Guianan piedmont and lowland moist forests ecoregion is in the south of Venezuela and the north of the Brazilian states of Amazonas and Roraima. It surrounds sections of the Guayanan Highlands moist forests, which in turn surround areas of tepui. It includes or adjoins patches of Rio Negro campinarana. To the north the ecoregion adjoins the Llanos, and to the east it adjoins the Guianan moist forests and the Guianan savanna. To the southeast it adjoins the Uatuma–Trombetas moist forests, and to the south and southwest it adjoins the Negro–Branco moist forests. Ecology The Guianan piedmont and lowland moist forests ecoregion is in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tepui
A tepui , or tepuy (), is a member of a family of table-top mountains or mesas found in northern South America, especially in Venezuela, western Guyana, and northern Brazil. The word tepui means "house of the gods" in the native tongue of the Pemon, the indigenous people who inhabit the Gran Sabana. Tepuis tend to be found as isolated entities rather than in connected ranges, which makes them the host of a unique array of endemic plant and animal species. Notable tepuis include Auyantepui, Autana, Neblina, and Mount Roraima. They are typically composed of sheer blocks of Precambrian quartz arenite sandstone that rise abruptly from the jungle. Auyantepui is the source of Angel Falls, the world's tallest waterfall. Morphology These table-top mountains are the remains of a large sandstone plateau that once covered the granite basement complex between the north border of the Amazon Basin and the Orinoco, between the Atlantic coast and the Rio Negro. This area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oyapock
The Oyapock or Oiapoque ( ; ; ) is a long river in South America that forms most of the border between the French overseas department of French Guiana and the Brazilian state of Amapá. Course The Oyapock runs through the Guianan moist forests ecoregion. It rises in the Tumuk Humak () mountain range and flows into the Atlantic Ocean, where its estuary forms a large bay bordering on Cape Orange. The mouth of the Oyapock is the northern ''end'' of Brazil's coastline, as it is where the border between Brazil and French Guiana meets the ocean, but nearby Cape Orange, which separates the Bay of Oyapock from the Atlantic Ocean, is the northernmost ''point'' of the Brazilian coast. In Brazil, both the cape and the mouth of the Oyapock are often mistaken for the whole country's northernmost point (rather than just of its coastline), and in the past this information could even be found in geography schoolbooks. Yet the true northernmost point in Brazil is actually far inland, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maroni (river)
The Maroni () or Marowijne (; ) is a river in South America that forms the border between French Guiana and Suriname. Course The Maroni runs through the Guianan moist forests ecoregion. It originates in the Tumuk Humak Mountains and forms the (disputed) border between France (region of French Guiana) and Suriname. In its upper reaches, it is also known as the Lawa, and close to its source it is known as the Litani. The total length of Litani, Lawa and Maroni is . There are two nature preserves located in the estuary region on the Surinamese side of the river, near the village of Galibi. They provide protection for the birds and the leatherback sea turtles that hatch there. Territorial dispute In 1860, the question was posed from the French side, which of the two tributary rivers was the headwater, and thus the border. A joint French-Dutch commission was appointed to review the issue. The Dutch side of the commission consisted of J.H. Baron van Heerdt tot Eversberg, J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courantyne River
The Courantyne River ( ), also known as Corentyne and Corantijn (), is a river in northern South America in Suriname and Guyana. It is the longest List of rivers of Suriname, river in the country and creates the border between Suriname and the East Berbice-Corentyne region of Guyana. Its tributaries include Kutari River, Coeroeni River, New River (South America), New River, and Zombie Creek. In Suriname; Kabalebo River, Lucie River, Sipaliwini River, Kutari River. Course The river runs through the Guianan moist forests ecoregion. It originates in the Acarai Mountains and flows northward via the Boven (Upper) Courantyne which is the source river for approximately between Guyana and Suriname, emptying into the Atlantic Ocean near Corriverton, Guyana and Nieuw Nickerie, Suriname. A ferry service operates between these two towns. A bridge is to be built by China Road and Bridge Corporation. Small ocean-going vessels are able to navigate the river for about to Apura, Suriname. Wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essequibo River
The Essequibo River (; originally called by Alonso de Ojeda; ) is the largest river in Guyana, and the largest river between the Orinoco and Amazon River, Amazon. Rising in the Acarai Mountains near the Brazil–Guyana border, the Essequibo flows to the north for through forest and savanna into the Atlantic Ocean. It has a total drainage basin of and an average discharge of . Territory near the river is argued over by Venezuela and Guyana. The river is administered by Guyana after being previously colonized by the British Guiana, British. Historically, Venezuela has claimed the Essequibo River as their most eastern border, though in practice it was under Dutch colonization of the Guianas, Dutch control. Geography The river runs through the Guianan moist forests ecoregion. The average annual rainfall in the catchment area is 2,174 mm. There are many rapids and waterfalls (e.g., Kaieteur Falls on the Potaro River) along the route of the Essequibo, and its wide estuary is dotted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
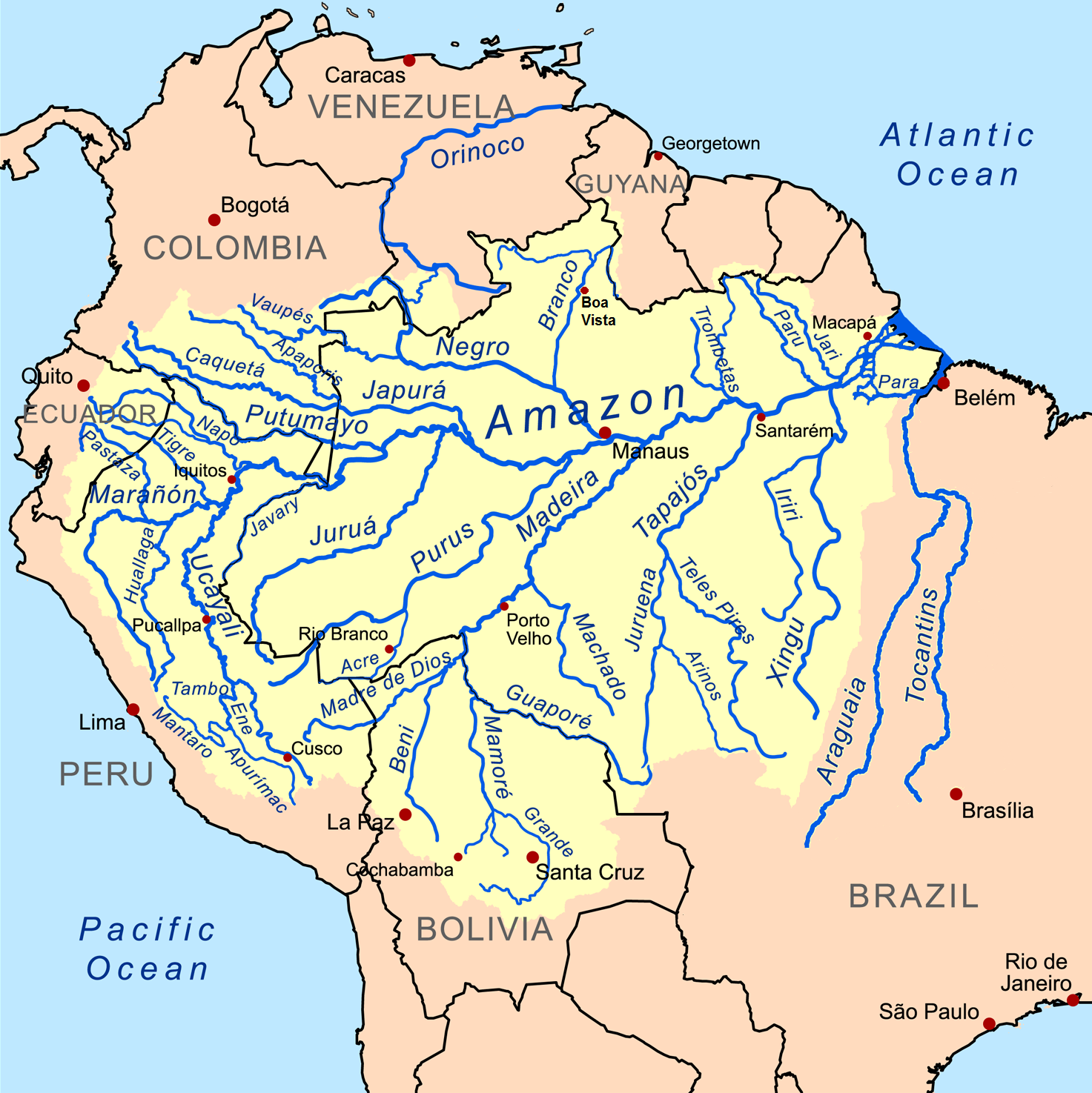
Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributary, tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela, as well as the territory of French Guiana. Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest, also known as Amazon rainforest, Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest, it is the largest rainforest in the world. Geography The Amazon River begins in the Andes, Andes Mountains at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurímac River, Apurimac River in Peru. The highest point in the Drainage divide, watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá at . The Amazon River Basin occupies the entire central and eastern area of South America, lying to the east of the Andes mountain range and extending from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumuk Humak Mountains
The Tumuk Humak Mountains (, , ) are a mountain range in South America, stretching about east–west in the border area between Brazil in the south and Suriname and French Guiana in the north. In the language of the Apalam and Wayana peoples, ''Tumucumaque'' means "the mountain rock symbolizing the struggle between the shaman and the spirits". The range is very remote and almost inaccessible. Both the Maroni and Oyapock rivers rise in the Tumuk Humak Mountains. The Maroni () forms the entire (disputed) border between Suriname and French Guiana, and the Oyapock () most of the border between French Guiana and Brazil. The Tumuk Humak Mountains are part of the Tumucumaque Uplands of the Guiana Shield. They are geographically important because they form the divide between the biogeographical system of the Amazon Basin and that of the Atlantic coastal area of the Guianas. The Tumuk Humak plateau is covered primarily with lowland and plateau forests. Brazil's Tumucumaque Mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acarai Mountains
The Acarai Mountains (also, Akarai Mountains) (; ) are a wet, forested highland region of low mountains located in the southern part of Guyana. This range lies along the common border between Guyana and Brazil. The Acarai Mountains is one of four mountain ranges in Guyana, the others being the Imataka, Kanuku and Pakaraima mountains. The headwaters of the Essequibo River, the longest river in Guyana, and the Courantyne River, have their sources in this range. The actual source of the Essequibo was discovered in 2013 by a Guyanese-German team. The mountain range was first mentioned in 1821 by A.H. Brué as Sierra do Acaray. This range is home to a single village of Wai-Wais, the descendants of surviving tribes that were once believed extinct. The village was first mentioned around 1837. The unnamed high point of this range is located at , and has an altitude of . This range extends to the east, where it becomes the Tumuk Humak Mountains along the border of Suriname and French Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guiana Shield
The Guiana Shield (; ; ; ) is one of the three cratons of the South American Plate. It is a 1.7 billion-year-old Precambrian geological formation in northeast South America that forms a portion of the northern coast. The higher elevations on the shield are called the Guiana Highlands, which is where the table-like mountains called tepuis are found. The Guiana Highlands are also the source of some of the world's most well-known waterfalls such as Angel Falls, Kaieteur Falls and Cuquenan Falls. The Guiana Shield underlies Guyana (previously ''British Guiana''), Suriname (previously ''Dutch Guiana''), and French Guiana (or ''Guyane''), much of southern Venezuela, as well as parts of Colombia and Brazil. The rocks of the Guiana Shield consist of metasediments and metavolcanics ( greenstones) overlain by sub-horizontal layers of sandstones, quartzites, shales and conglomerates intruded by sills of younger mafic intrusives such as gabbros. Geology The oldest rocks in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orinoco
The Orinoco () is one of the longest rivers in South America at . Its drainage basin, sometimes known as the Orinoquia, covers approximately 1 million km2, with 65% of it in Venezuela and 35% in Colombia. It is the List of rivers by discharge, fourth largest river in the world by Discharge (hydrology), discharge volume of water (39,000 m3/s at Orinoco Delta, delta) due to the high precipitation throughout its catchment area (ca 2,300 mm/a). The Orinoco River and its tributaries are the major transportation system for eastern and interior Venezuela and the Llanos of Colombia. The environment and wildlife in the Orinoco's basin are extremely diverse. Etymology The river's name is derived from the Warao language, Warao term for "a place to paddle", itself derived from the terms ''güiri'' (paddle) and ''noko'' (place) i.e. a navigable place. History The mouth of the Orinoco River at the Atlantic Ocean was documented by Christopher Columbus on 1 August 1498, during his Christo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |