|
Guerrero (ship)
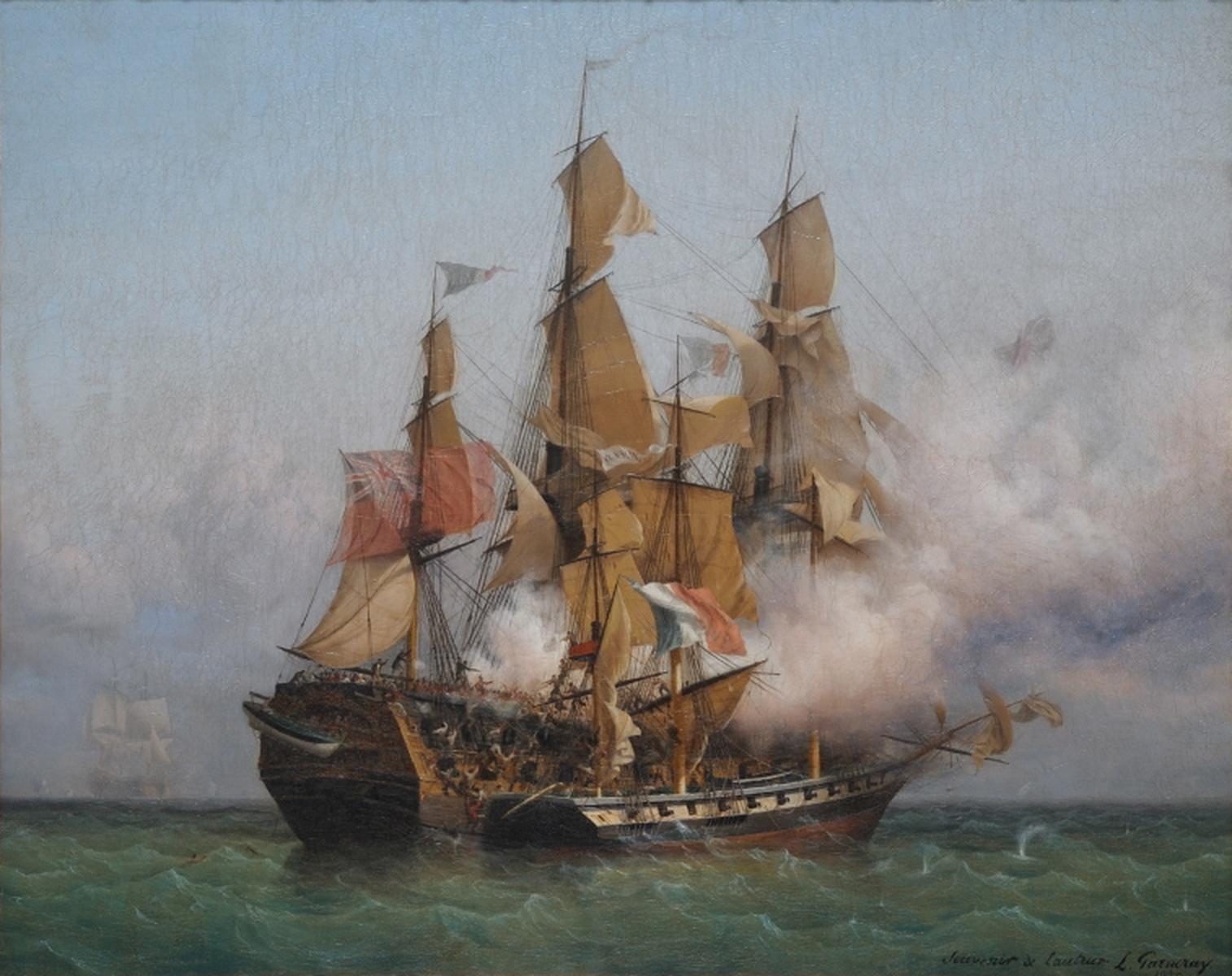
''Guerrero'' was a Spanish slave ship that wrecked in 1827 on a reef near the Florida Keys with 561 Africans aboard. Forty-one of the Africans drowned in the wreck. ''Guerrero'' had been engaged in a battle with a British anti-slavery patrol ship, , stationed on the northern approaches to Cuba. ''Nimble'' also ran onto the reef, but was refloated and returned to service. The two ships were attended by wreckers, who rescued the Spanish crew and surviving Africans from their ship and helped refloat ''Nimble.'' Spanish crew members hijacked two of the wrecking vessels and took almost 400 Africans to Cuba, where they were sold as slaves. Most of the remaining Africans were eventually returned to Africa. History The history of the ship is unclear. Because the slave trade to Cuba was illegal in the 1820s, ships that successfully delivered a cargo of captives from Africa to Cuba were often destroyed or registered under a new name to avoid confiscation by the Spanish authorities. The Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privateer
A privateer is a private person or vessel which engages in commerce raiding under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or delegated authority issued commissions, also referred to as letters of marque, during wartime. The commission empowered the holder to carry on all forms of hostility permissible at sea by the usages of war. This included attacking foreign vessels and taking them as prizes and taking crews prisoner for exchange. Captured ships were subject to condemnation and sale under prize law, with the proceeds divided by percentage between the privateer's sponsors, shipowners, captains and crew. A percentage share usually went to the issuer of the commission (i.e. the sovereign). Most colonial powers, as well as other countries, engaged in privateering. Privateering allowed sovereigns to multiply their naval forces at relatively low cost by mobilizi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberia
Liberia, officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to Guinea–Liberia border, its north, Ivory Coast to Ivory Coast–Liberia border, its east, and the Atlantic Ocean to its south and southwest. It has a population of around 5.5million and covers an area of . The official language is English. Languages of Liberia, Over 20 indigenous languages are spoken, reflecting the country's ethnic and cultural diversity. The capital and largest List of cities in Liberia, city is Monrovia. Liberia began in the early 19th century as a project of the American Colonization Society (ACS), which believed that black people would face better chances for freedom and prosperity in Africa than in the United States. Between 1822 and the outbreak of the American Civil War in 1861, more than 15,000 freed and free-born African Americans, along with 3,198 Afro-Caribbeans, relocated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biscayne Bay
Biscayne Bay is a lagoon with characteristics of an estuary located on the Atlantic coast of South Florida. The northern end of the lagoon is surrounded by the densely developed heart of the Miami metropolitan area while the southern end is largely undeveloped with a large portion of the lagoon included in Biscayne National Park. The part of the lagoon that is traditionally called "Biscayne Bay" is approximately long and up to wide, with a surface area of . Various definitions may include Dumfoundling Bay, Card Sound, and Barnes Sound in a larger "Biscayne Bay", which is long with a surface area of about . Etymology Hernando de Escalante Fontaneda related in the 16th century that a sailor from the Bay of Biscay called the ''Viscayno'' or ''Biscayno'' had lived on the lower east coast of Florida for a while after being shipwrecked, and a 17th-century map shows a ''Cayo de Biscainhos'', the probable origin of the name for Key Biscayne. The lagoon was known as "Key Biscayne Bay" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Caesar (pirate)
Caesar, later known as “Black Caesar” (fl. 1718), was a West African pirate who operated during the Golden Age of Piracy. He served aboard the ''Queen Anne's Revenge'' of Edward Teach (Blackbeard) and was one of the surviving members of that crew following Blackbeard’s death at the hands of Lieutenant Robert Maynard in 1718. Myths surrounding his life - that he was African royalty and terrorized the Florida Keys for years before joining Blackbeard - have been intermixed with legends and fictional accounts as well as with other pirates. The legend Black Caesar, according to traditional accounts, was a prominent African tribal war chieftain. Widely known for his "huge size, immense strength and keen intelligence," he evaded capture from many different slave traders. Caesar was finally captured when he and twenty of his warriors were lured onto a ship by a slave trader. Showing him a watch, the trader promised to show him and his warriors more objects, which were "too heavy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar's Rock
Caesar's Rock is a small island north of the upper Florida Keys in Biscayne National Park. It is in Miami-Dade County, Florida. It is located in southern Biscayne Bay, just north of Old Rhodes Key and Totten Key, just southeast off the southern tip of Elliott Key, and due south of Adams Key. It is in the middle of Caesar Creek, the creek that separates Elliott and Old Rhodes Keys. History The island is named after Black Caesar (pirate), Black Caesar, a pirate. Munroe, writing in "The Commodore's Story" (1930) states: "Caesar's Rock a small island about the middle of the creek, was reputed to be the dwelling place and ship yard of the pirate (Black Caesar)." This is apparently the small key due north of Meig's Key. It is unnamed on current charts. References Uninhabit ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schooner
A schooner ( ) is a type of sailing ship, sailing vessel defined by its Rig (sailing), rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more Mast (sailing), masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schooner also has a square topsail on the foremast, to which may be added a Topgallant sail, topgallant. Differing definitions leave uncertain whether the addition of a Course (sail), fore course would make such a vessel a brigantine. Many schooners are Gaff rig, gaff-rigged, but other examples include Bermuda rig and the staysail schooner. Etymology The term "schooner" first appeared in eastern North America in the early 1700s. The term may be related to a Scots language, Scots word meaning to skip over water, or to skip stones. History The exact origins of schooner rigged vessels are obscure, but by early 17th century they appear in paintings by Dutch marine artists. The earliest known il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot (unit)
The knot () is a unit of speed equal to one nautical mile per hour, exactly (approximately or ). The ISO standard symbol for the knot is kn. The same symbol is preferred by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers ( IEEE), while kt is also common, especially in aviation, where it is the form recommended by the International Civil Aviation Organization ( ICAO). The knot is a non- SI unit. The knot is used in meteorology, and in maritime and air navigation. A vessel travelling at 1 knot along a meridian travels approximately one minute of geographic latitude in one hour. Definitions ;1 international knot = :1 nautical mile per hour (by definition), : (exactly), : (approximately), : (approximately), : (approximately) : (approximately). The length of the internationally agreed nautical mile is . The US adopted the international definition in 1954, having previously used the US nautical mile (). The UK adopted the international nautical mile defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Largo
Key Largo () is an island in the upper Florida Keys archipelago and is the largest section of the keys, at long. It is one of the northernmost of the Florida Keys in Monroe County, and the northernmost of the keys connected by U.S. Highway 1 (the Overseas Highway). Three census-designated places (CDPs) are on the island of Key Largo: North Key Largo (near the Card Sound Bridge), Key Largo (roughly from the island's southernmost point) and Tavernier (at the island's south end). As of 2010, these three CDPs have a combined population of 13,850. None of Key Largo is an incorporated municipality; it is governed, at the local level, by Monroe County. Key Largo is connected to the mainland of Miami-Dade County by two routes, the first being the Overseas Highway—the southernmost portion of U.S. Highway 1—which enters Key Largo at Jewfish Creek (near the middle of the island) before turning southwest. The second route is via Card Sound Road, which connects to the norther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carysfort Reef
Carysfort is a coral reef located within the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. It lies to the east of Key Largo, within the Key Largo Existing Management Area, which is immediately to the east of John Pennekamp Coral Reef State Park. This reef is within a Sanctuary Preservation Area (SPA). The reef is northeast of The Elbow. The Carysfort Reef Light is near the center of the SPA. The reef is named after , which ran aground there (but did not sink) in 1770. Several charts and other publications of the late 18th and early 19th centuries spelled the name of the reef as "Carysford", with some sources giving the ship's name as ''Carysford'', but "Carysfort" was standard for the reef by the middle of the 19th century. The reef is one of the most dangerous on the Florida Reef tract which parallels the Florida Keys. Of the 324 ships that were known to have wrecked on the Florida Reef from the beginning of 1833 through 1841, 63 did so on Carysfort Reef. The United States Lightho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carysfort Reef Light
Carysfort Reef Light is located on Carysfort Reef east of Key Largo, Florida. The lighthouse has an iron-pile foundation with a platform, and a skeletal, octagonal, pyramidal tower, which is painted red. The light was above the water. It was the oldest functioning lighthouse of its type in the United States until it was decommissioned in 2015, having been completed in 1852. The light last installed was a xenon flashtube beacon. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1984. The reef Carysfort Reef is named for , a 28-gun Royal Navy post ship that ran aground on the reef in 1770. The reef is one of the most dangerous on the Florida Reef tract which parallels the Florida Keys. Of the 324 ships that were known to have wrecked on the Florida Reef from 1833 through 1841 (during the period the lightship ''Florida'' was stationed at the reef), 63 did so on Carysfort Reef. The United States Lighthouse Board reported that "Carysfort Reef picks up twenty percent of al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Bahama Bank
The Bahama Banks are the submerged carbonate platforms located in the archipelago of The Bahamas within the Lucayan Archipelago. The term is usually applied in referring to either the Great Bahama Bank around Andros Island, or the Little Bahama Bank of Grand Bahama Island and Great Abaco, which are the largest of the platforms, and the Cay Sal Bank. The three banks of the Turks and Caicos Islands, namely the Caicos Bank of the Caicos island group, the Turks Bank of the Turks island group, and the submerged Mouchoir Bank, and the two banks north of the Dominican Republic in Hispaniola, namely the submerged Silver Bank and Navidad Bank, are geographically and geologically part of the Lucayan Archipleago, which entire carbonate platform is often generally referred to as the ''Bahamas platform''. Geologic history and structure The limestone that comprises the Banks has been accumulating since at least the Cretaceous period, and perhaps as early as the Jurassic; today the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |