|
Gubernaculum
The paired gubernacula (from Ancient Greek κυβερνάω = pilot, steer) also called the caudal genital ligament, are embryonic structures which begin as undifferentiated mesenchyme attaching to the caudal end of the gonads (testes in males and ovaries in females). Structure The gubernaculum is present only during the development of the reproductive system. It is later replaced by distinct vestiges in males and females.The gubernaculum arises in the upper abdomen from the lower end of the gonadal ridge and helps guide the testis in its descent to the inguinal region. Males * The upper part of the gubernaculum degenerates. * The lower part persists as the gubernaculum testis (" scrotal ligament"). This ligament secures the testis to the most inferior portion of the scrotum, tethering it in place and limiting the degree to which the testis can move within the scrotum. * Cryptorchidism (undescended testes) are observed in ''INSL3''-null male mice. This implicates INSL3 as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gubernaculum Testis
In the inguinal crest of a peculiar structure, the gubernaculum testis makes its appearance. This is at first a slender band, extending from that part of the skin of the groin which afterward forms the scrotum through the inguinal canal to the body and epididymis of the testis A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testoster .... External links Images Embryology {{developmental-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, aircraft, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (generally air or water). On an aircraft the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw and p-factor and is not the primary control used to turn the airplane. A rudder operates by redirecting the fluid past the hull or fuselage, thus imparting a turning or yawing motion to the craft. In basic form, a rudder is a flat plane or sheet of material attached with hinges to the craft's stern, tail, or after end. Often rudders are shaped so as to minimize hydrodynamic or aerodynamic drag. On simple watercraft, a tiller—essentially, a stick or pole acting as a lever arm—may be attached to the top of the rudder to allow it to be turned by a helmsman. In larger vessels, cables, pushrods, or hydraulics may be used to link rudders to steering wheels. In typical aircraft, the rudder is operated by pedals via mechanical linkages or hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate Mesoderm
Intermediate mesoderm or intermediate mesenchyme is a narrow section of the mesoderm (one of the three primary germ layers) located between the paraxial mesoderm and the lateral plate of the developing embryo. The intermediate mesoderm develops into vital parts of the urogenital system (kidneys, gonads and respective tracts). Early formation Factors regulating the formation of the intermediate mesoderm are not fully understood. It is believed that bone morphogenic proteins, or BMPs, specify regions of growth along the dorsal-ventral axis of the mesoderm and plays a central role in formation of the intermediate mesoderm. Vg1/ Nodal signalling is an identified regulator of intermediate mesoderm formation acting through BMP signalling. Excess Vg1/Nodal signalling during early gastrulation stages results in expansion of the intermediate mesoderm at the expense of the adjacent paraxial mesoderm, whereas inhibition of Vg1/Nodal signalling represses intermediate mesoderm formation. A li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canal Of Nuck
__NOTOC__ The canal of Nuck, first described by Anton Nuck ( de) in 1691, is an abnormal patent (open) pouch of peritoneum extending into the labia majora of women. It is analogous to a patent processus vaginalis in males (see hydrocele testis, inguinal hernia). In rare cases, it may give rise to a cyst or a hydrocele in women and has potential to develop into an indirect inguinal hernia. The pouch accompanies the gubernaculum during development of the urinary and reproductive organs, more specifically during the descent of the ovaries The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the bod ..., and normally obliterates. See also * List of homologues of the human reproductive system References Further reading * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Canal Of Nuck Mammal female reproductive syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hunter (surgeon)
John Hunter (13 February 1728 – 16 October 1793) was a British surgeon, one of the most distinguished scientists and surgeons of his day. He was an early advocate of careful observation and scientific method in medicine. He was a teacher of, and collaborator with, Edward Jenner, pioneer of the smallpox vaccine. He is alleged to have paid for the stolen body of Charles Byrne, and proceeded to study and exhibit it against the deceased's explicit wishes. His wife, Anne Hunter (''née'' Home), was a poet, some of whose poems were set to music by Joseph Haydn. He learned anatomy by assisting his elder brother William with dissections in William's anatomy school in Central London, starting in 1748, and quickly became an expert in anatomy. He spent some years as an Army surgeon, worked with the dentist James Spence conducting tooth transplants, and in 1764 set up his own anatomy school in London. He built up a collection of living animals whose skeletons and other organs he p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
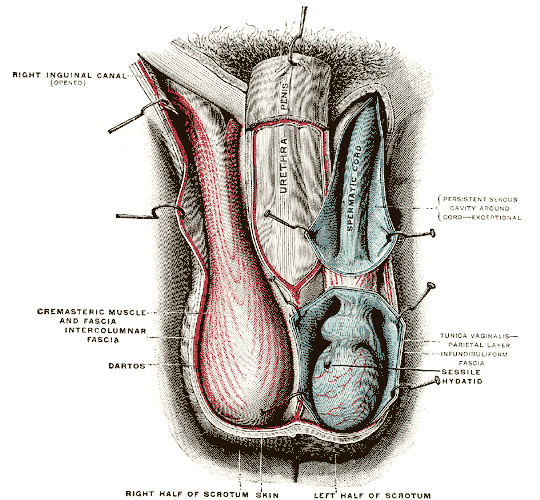
Inguinal Canal
The inguinal canals are the two passages in the anterior abdominal wall of humans and animals which in males convey the spermatic cords and in females the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males. There is one inguinal canal on each side of the midline. Structure The inguinal canals are situated just above the medial half of the inguinal ligament. In both sexes the canals transmit the ilioinguinal nerves. The canals are approximately 3.75 to 4 cm long. , angled anteroinferiorly and medially. In males, its diameter is normally 2 cm (±1 cm in standard deviation) at the deep inguinal ring.The diameter has been estimated to be ±2.2cm ±1.08cm in Africans, and 2.1 cm ±0.41cm in Europeans. A first-order approximation is to visualize each canal as a cylinder. Walls To help define the boundaries, these canals are often further approximated as boxes with six sides. Not including the two rings, the remaining four sides are usuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. The ovaries also secrete hormones that play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal period through menopause. It is also an endocrine gland because of the various hormones that it secretes. Structure The ovaries are considered the female gonads. Each ovary is whitish in color and located alongside the lateral wall of the uterus in a region called the ovarian fossa. The ovarian fossa is the region that is bounded by the external iliac artery and in front of the ureter and the internal iliac artery. This area is about 4 cm x 3 cm x 2 cm in size.Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
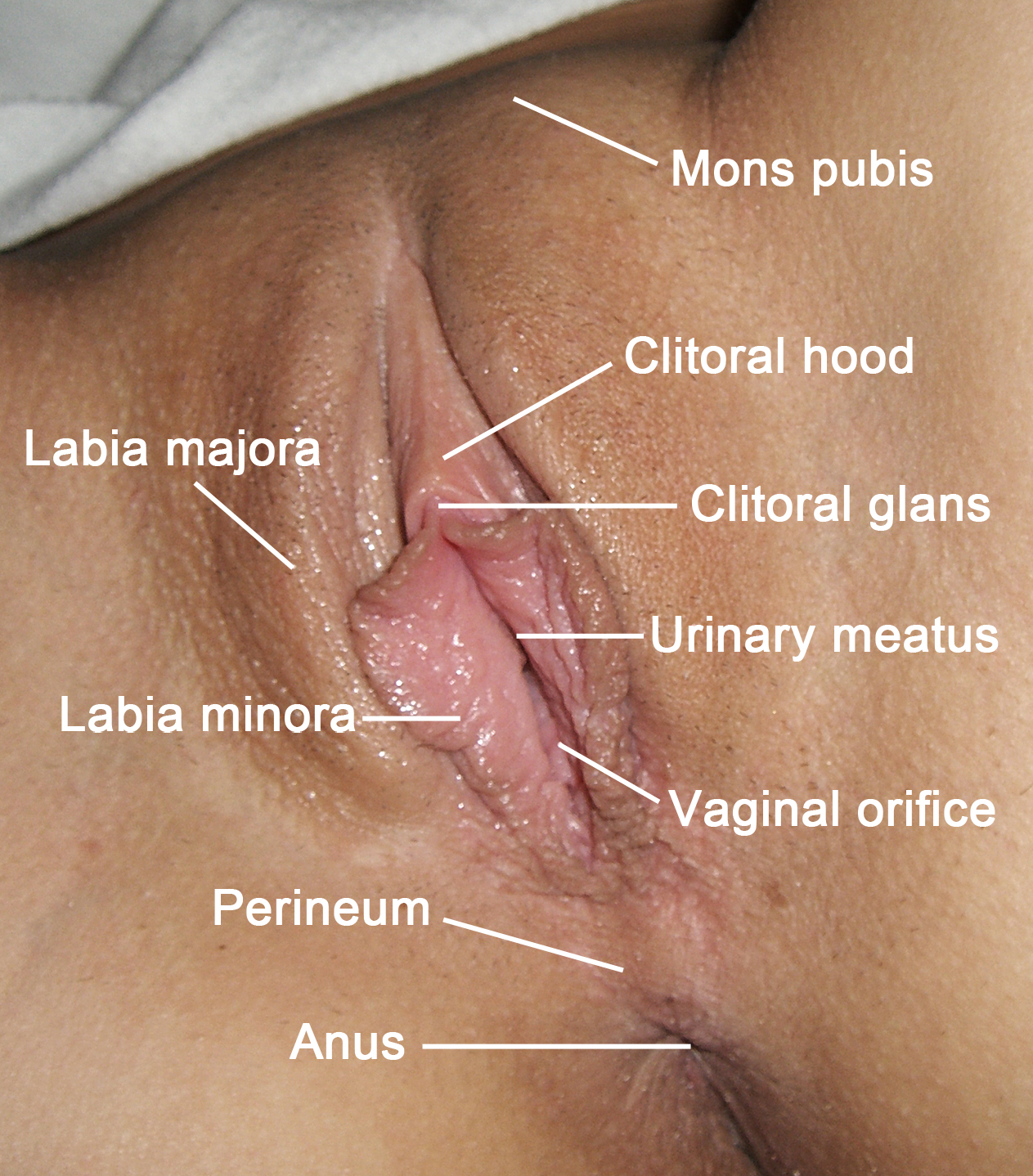
Labia Majora
The labia majora (singular: ''labium majus'') are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora they form the labia of the vulva. The labia majora are homologous to the male scrotum. Etymology ''Labia majora'' is the Latin plural for big ("major") lips; the singular is ''labium majus.'' The Latin term ''labium/labia'' is used in anatomy for a number of usually paired parallel structures, but in English it is mostly applied to two pairs of parts of female external genitals (vulva)—labia majora and labia minora. Labia majora are commonly known as the outer lips, while labia minora (Latin for ''small lips''), which run alongside between them, are referred to as the inner lips. Traditionally, to avoid confusion with other lip-like structures of the body, the labia of female genitals were termed by anatomists in Latin as ''labia majora (''or ''minora) pudendi.'' Embryology Embryolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrotum
The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum contains the external spermatic fascia, testes, epididymis, and ductus deferens. It is a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein, and pampiniform plexus. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical, slightly raised ridge of scrotal skin under which is found the scrotal septum. It appears as a thin longitudinal line that runs front to back over the entire scrotum. In humans and some other mammals the scrotum becomes covered with pubic hair at puberty. The scrotum will usually tighten during penile erection and when exposed to cold temperatures. One testis is typically lower than the other to avoid compression in the event of an impact. The scrotum is bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round Ligament Of The Uterus
The round ligament of the uterus is a ligament that connects the uterus to the labia majora. Structure The round ligament of the uterus originates at the uterine horns, in the parametrium. The round ligament exits the pelvis via the deep inguinal ring. It passes through the inguinal canal, and continues on to the labia majora. At the labia majora, its fibers spread and mix with the tissue of the mons pubis. Development The round ligament develops from the gubernaculum which attaches the gonad to the labioscrotal swellings in the embryo. Blood supply The round ligament is supplied by the artery of the round ligament of uterus, also known as ''Sampson's artery''. Function The function of the round ligament is maintenance of the anteversion of the uterus (a position where the fundus of the uterus is turned forward at the junction of cervix and vagina) during pregnancy. Normally, the cardinal ligament is what supports the uterine angle (angle of anteversion). When the uterus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |