|
Guangdong Fleet
The Guangdong Fleet () was the smallest of China's four regional fleets during the second half of the nineteenth century. The fleet played virtually no part in the Sino-French War (August 1884–April 1885), but several of its ships saw action in the Sino-Japanese War (1894–5). Leadership In the summer of 1882, when China began to challenge French expansion in Tonkin, the Guangdong Fleet was commanded by Wu Quanmei (吳全美). Composition The composition of the Guangdong Fleet during the 1870s and early 1880s is difficult to establish. British sources record about fifteen small war vessels built and stationed at Canton between 1865 and 1885, and the fleet also contained at least seven vessels purchased from overseas. Seven steamers built in Britain or France were purchased in 1867 and 1868 by Jui Lin (瑞麟), the governor-general of the Two Guangs, for use against pirates. Although the identity of these vessels is not entirely certain, they seem to have included the woo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The Qing Dynasty
The flag of the Qing dynasty was an emblem adopted in the late 19th century (1889) featuring the Azure Dragon on a plain yellow field with the red flaming pearl in the upper left corner. It became the first national flag of China and is usually referred to as the "Yellow Dragon Flag" (). Ruling China from 1644 until the overthrow of the monarchy during the Xinhai Revolution, the Qing dynasty was the last Imperial dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty in Chinese history. Between 1862 and 1912, the dynasty represented itself with the dragon flag. On January 10, 1912, the Yellow Dragon Flag was replaced by the Five Races Under One Union, Five-Colored Flag, and on February 12 Emperor Pu Yi abdicated, ending the rule of the Qing Dynasty. Designs Since the Ming dynasty, yellow was considered the royal color of successive Chinese emperors. Members of the imperial family of China at that time were the only ones allowed to display the color yellow in buildings and on garments. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hainan Island
Hainan is an island province and the southernmost province of China. It consists of the eponymous Hainan Island and various smaller islands in the South China Sea under the province's administration. The name literally means "South of the Sea". The province has a land area of , of which Hainan Island is and the rest is over 200 islands scattered across three archipelagos: Zhongsha, Xisha and Nansha. It was part of Guangdong from 1950 to 1988, after which it was made a province of its own and was designated as a special economic zone by Deng Xiaoping, as part of the Chinese economic reform program. The Han Chinese population, who compose a majority of the population at 82%, speak a wide variety of languages including Standard Chinese, Hainam Min, Yue Chinese, Cantonese, Hakka Chinese, etc. Indigenous peoples such as the Hlai, a Kra–Dai-speaking ethnic group, are native to the island and compose 15% of the population. Their native languages include the Hlai langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Of The Qing Dynasty
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a distinct military uniform. They may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of a military is usually defined as defence of their state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms "armed forces" and "military" are often synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include other paramilitary forces such as armed police. Beyond warfare, the military may be employed in additional sanctioned and non-sanctioned functions within the state, including internal security threats, crowd control, promotion of political agendas, emergency services and reconstruction, prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Fleets
Chinese may refer to: * Something related to China * Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity **Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China. **''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation ** List of ethnic groups in China, people of various ethnicities in contemporary China ** Ethnic minorities in China, people of non-Han Chinese ethnicities in modern China ** Ethnic groups in Chinese history, people of various ethnicities in historical China ** Nationals of the People's Republic of China ** Nationals of the Republic of China ** Overseas Chinese, Chinese people residing outside the territories of mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan * Sinitic languages, the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family ** Chinese language, a group of related languages spoken predominantly in China, sharing a written script (Chinese characters in traditional and simplified forms) *** Standard Chines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Corvette Kwan Chia
''Kwan Chia'' (), often called ''Guangjia'', was a 1,296-ton composite cruiser, often called a corvette, in service with the Imperial Chinese Guangdong Fleet. Total officers and crew were 180. The ship's maximum speed was . Design ''Kwan Chia'' was built at the Foochow Navy Yard in 1887. Her hull was composite-built, with wooden planking over an iron frame. She displaced 1,296 tons and had a length of . She had a single screw that pushed her through the water at . By the time she was completed she was obsolete, but her armament was fairly modern, consisting of four 4.7-inch (120 mm) and one 5.9-inch (150 mm) Krupp breech-loading guns. Two of her 4.7-inch guns were on sponsons on either side of the ship near the bow, the other two were further aft on pivot mounts inboard, and the 5.9-inch gun was on the stern. Naval service She was built for the Guangdong Fleet, one of the Imperial Chinese Navy's four regional fleets. Nothing is known of her early career, but she along with se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
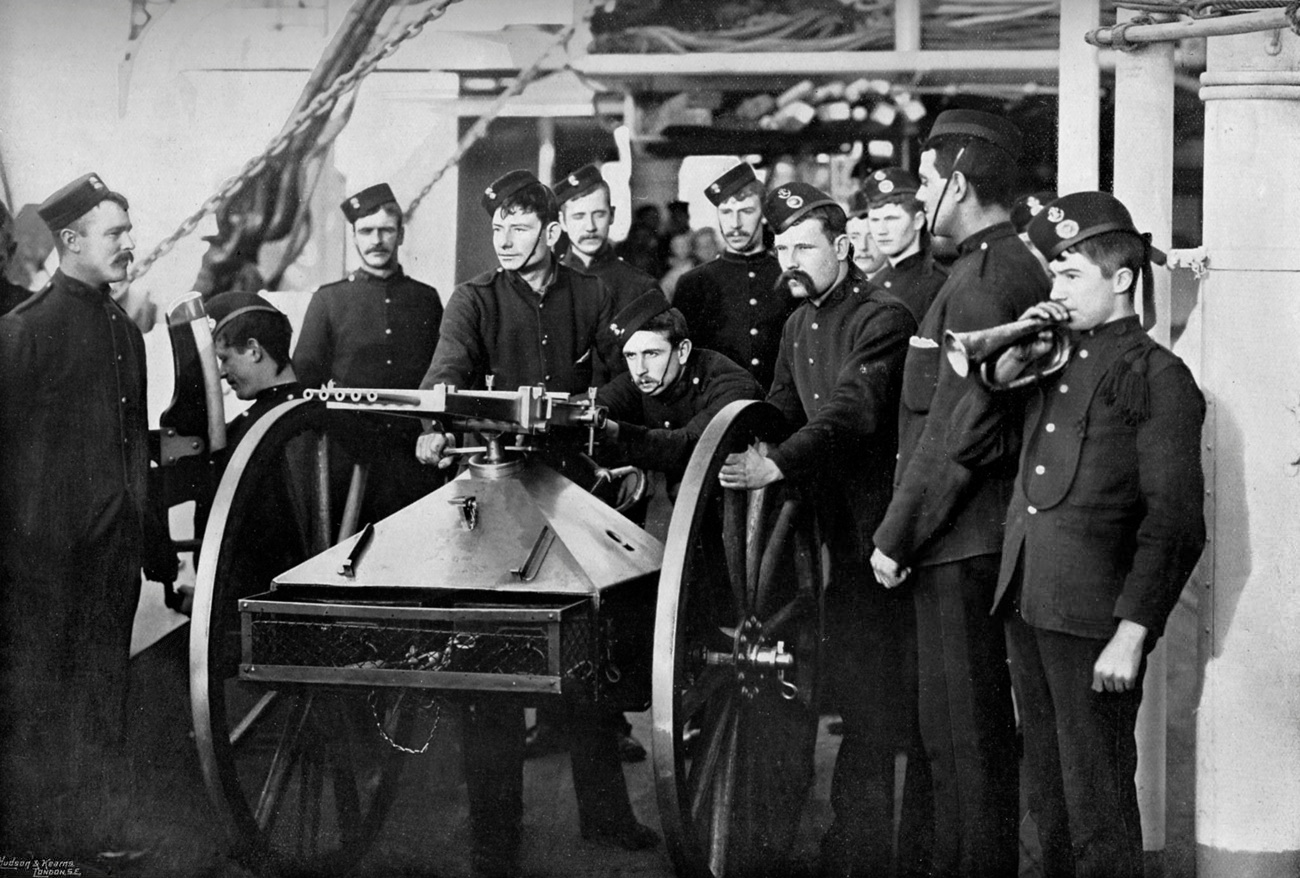
Nordenfeldt
The Nordenfelt gun was a multiple-barrel organ gun that had a row of up to twelve barrels. It was fired by pulling a lever back and forth and ammunition was gravity fed through chutes for each barrel. It was produced in a number of different calibres up to . Larger calibres were also used, but for these calibres the design simply permitted rapid manual loading rather than true automatic fire. This article covers the anti-personnel rifle-calibre (typically ) gun. Development The weapon was designed by a Swedish engineer, Helge Palmcrantz. He created a mechanism to load and fire a multiple barreled gun by simply moving a single lever backwards and forwards. It was patented in 1873. Production of the weapon was funded by a Swedish steel producer and banker (later weapons maker) named Thorsten Nordenfelt, who was working in London. The name of the weapon was changed to the Nordenfelt gun. A plant producing the weapon was set up in England with sales offices in London and long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krupp
Friedrich Krupp AG Hoesch-Krupp (formerly Fried. Krupp AG and Friedrich Krupp GmbH), trade name, trading as Krupp, was the largest company in Europe at the beginning of the 20th century as well as Germany's premier weapons manufacturer during both world war, world wars. It produced battleship, battleships, U-boats, tanks, howitzers, guns, utilities, and hundreds of other commodities. The company also produced steel used to build railroads in the United States and to cap the Chrysler Building. After the Nazi Germany, Nazis seized power in Germany, Krupp supported the regime and was one of many German businesses that profited from forced labour under German rule during World War II, slave labor during World War II. Upon the war's end, the head of the company, Alfried Krupp, was tried and convicted as a war criminal for employing prisoners of war, foreign civilians and concentration camp inmates under inhumane conditions in support of the Nazi war effort. Despite being senten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Fuzhou
The Battle of Fuzhou, or Battle of Foochow, also known as the Battle of the Pagoda Anchorage (French: Combat naval de Fou-Tchéou, Chinese: , 馬江之役 or 馬尾海戰, literally Battle of Mawei), was the opening engagement of the 16-month Sino-French War (December 1883 – April 1885). The battle was fought on 23 August 1884 off the Pagoda Anchorage in Mawei () harbour, to the southeast of the city of Fuzhou (Foochow). During the battle Admiral Amédée Courbet's Far East Squadron virtually destroyed the Fujian Fleet, one of China's four regional fleets. Background On 11 May 1884 French and Chinese negotiators concluded the Tientsin Accord, an agreement designed to end several months of undeclared hostilities between France and China in Tonkin. On 23 June 1884, French troops advancing to occupy Lạng Sơn, in accordance with the terms of this agreement, clashed near the small town of Bắc Lệ with a detachment of the Chinese Guangxi Army. The Chinese opened fire o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Peilun
Zhang Peilun () (1848–1903) was a Chinese government official of the late Qing dynasty, who served as a naval commander during the Sino-French War (August 1884–April 1885). He is the grandfather of novelist Eileen Chang. Early life Zhang Peilun was born in Hangzhou on November 24, 1848. His father, Zhang Yintang (張印塘, 1797–1854), was a mid-level government official who died in office as Supervision Commissioner of Anhui when Zhang Peilun was 6, which left the family in genteel poverty. Zhang was, by all reports, a bright and studious child. After passing the provincial imperial examination at age 23 and the metropolitan one at 24, he came under the tutelage of Li Hongzao and quickly rose to prominence. Political Views Zhang was one of the foremost members of the so-called Purist Party ( 清流黨) led by Zhang Zhidong, an extremist group which urged resistance to French encroachment in north Vietnam in the early 1880s, even at the cost of war with France, in opposi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fujian Fleet
The Fujian Fleet ( or ) founded in 1678 as the Fujian Marine Fleet was one of China's four regional fleets during the closing decades of the nineteenth century. The fleet was almost annihilated on 23 August 1884 by Admiral Amédée Courbet's Far East Squadron at the Battle of Fuzhou, the opening engagement of the Sino-French War (August 1884 – April 1885). Composition The Fujian Fleet, which would be the main target of the French attack in August 1884, was considerably weaker than the Beiyang Fleet and the Nanyang Fleet, though slightly stronger than the Guangdong Fleet. Nearly all of its ships were elderly products of the Foochow Navy Yard. Its flagship, the wooden corvette ''Yangwu'', was built in 1872. The other Chinese-built ships included the wooden gunboats ''Fuxing'' and ''Zhenwei'' (1870 and 1872), the wooden transports ''Fupo'', ''Feiyun'', ''Ji'an'', ''Yongbao'' and ''Chenhang'' (all built in 1874 or earlier), and the despatch vessel ''Yixin''. The fleet als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
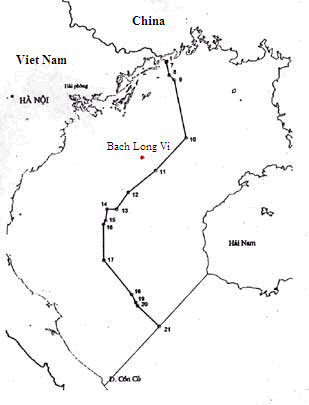
Gulf Of Tonkin
The Gulf of Tonkin is a gulf at the northwestern portion of the South China Sea, located off the coasts of Tonkin ( northern Vietnam) and South China. It has a total surface area of . It is defined in the west and northwest by the northern coastline of Vietnam down to the Cồn Cỏ district, in the north by China's Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, and to the east by the Leizhou Peninsula and Hainan Island. English sources from the People's Republic of China refer to the Gulf of Tonkin as Beibu Wan. Description and etymology The name ''Tonkin'', written "" in chữ Hán characters and in the Vietnamese alphabet, means "eastern capital", and is the former toponym for Hanoi, the present capital of Vietnam. It is not to be confused with Tokyo, which is also written "" and also means "eastern capital". During the French colonial era, the northern region of today’s Vietnam was called ''Tonkin''. ''Bắc Bộ'' is the native Vietnamese name of Tonkin, which is the nowad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Rivière (naval Officer)
Henri Laurent Rivière (1827–1883) was a French naval officer and a writer who is chiefly remembered today for advancing the French conquest of Tonkin (northern Vietnam) in the 1880s. Rivière's seizure of the citadel of Hanoi in April 1882 inaugurated a period of undeclared hostilities between France and Dai Nam (as Vietnam was known then) that culminated one year later in the Tonkin campaign (1883–1886). Early career Born in Paris on 12 July 1827, Rivière entered the École Navale in October 1842. He passed out as a midshipman (second class) in August 1845, and saw his first naval service in the Pacific Ocean on ''Brillante''. In February 1847 he was posted to the South Seas, South Seas naval division, to ''Virginie''. He was promoted to midshipman (first class) in September 1847 and to ''Ensign (rank), enseigne de vaisseau'' in September 1849. During the next five years he served in the Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean (France), Mediterranean squadron aboard French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |