|
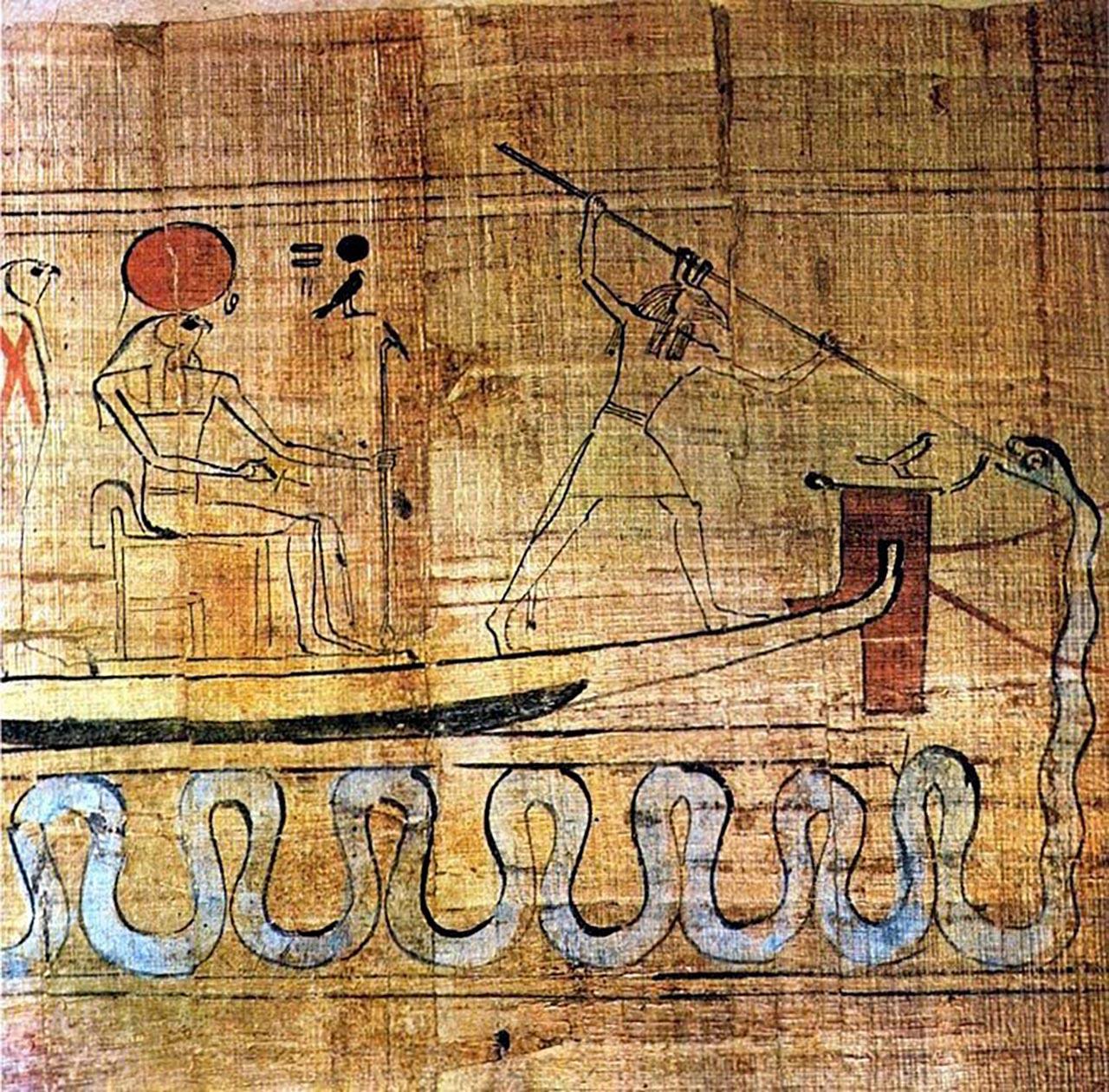
Guabancex
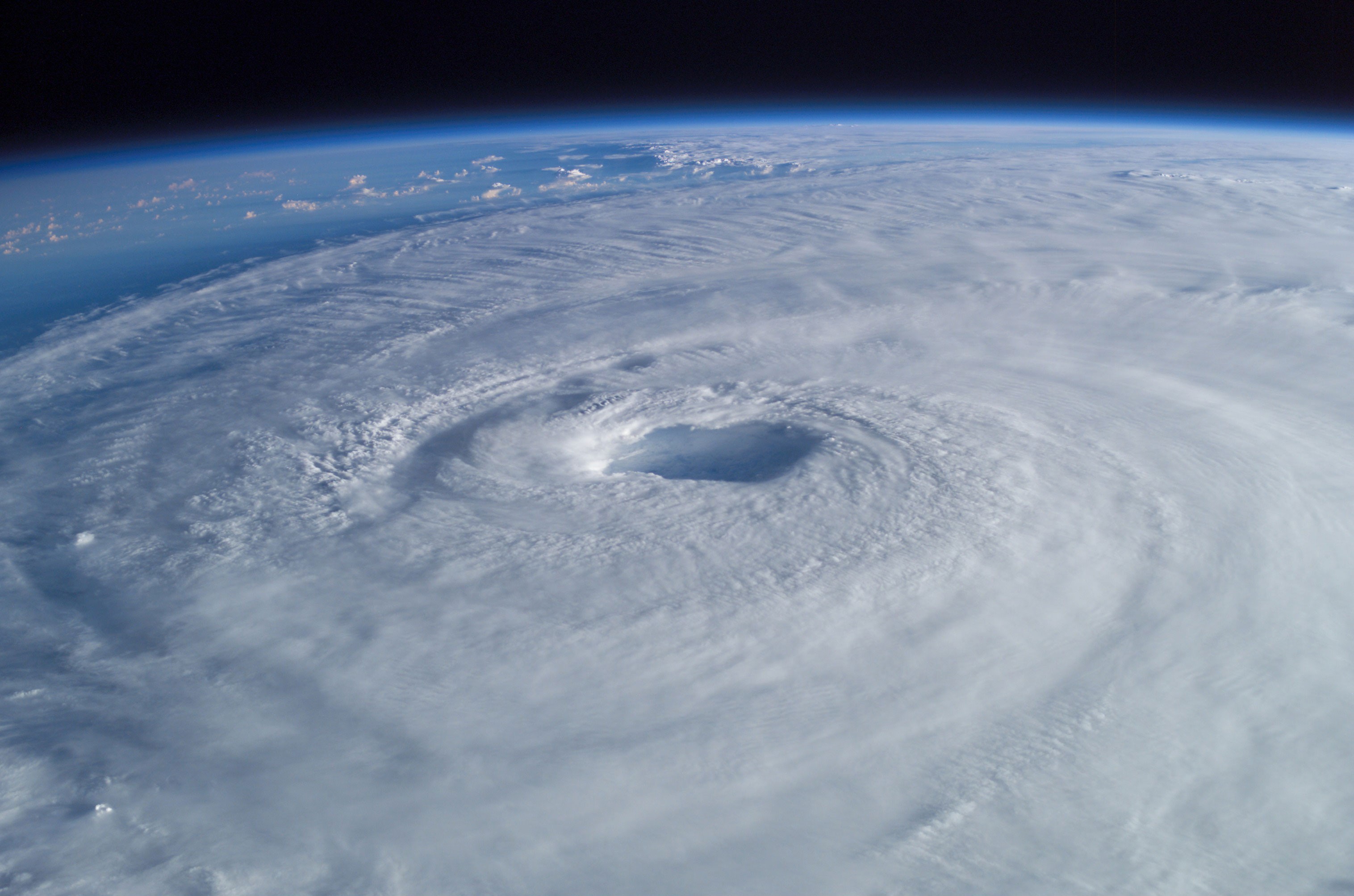
Guabancex is the zemi or deity of chaos and disorder in Taíno mythology and religion, which was practiced by the Taíno people in Puerto Rico, Hispaniola, Jamaica, and Cuba, as well as by Arawak natives elsewhere in the Caribbean. She was described as a mercurial goddess that controlled the weather, conjuring storms known as "juracán" when displeased. The latter term was later used to name the climatological phenomenon that is now known as a hurricane in the Western Hemisphere. The Taínos were aware of the spiraling wind pattern of hurricanes, a knowledge that they used when depicting the deity. Her zemi idol was said to depict a woman, but the most common depiction of Guabancex presents a furious face with her arms extended in a "~" pattern. Etymology From Juracán we derive the Spanish word ''huracán'' and eventually the English word ''hurricane''. As the pronunciation varied across indigenous groups, many of the alternative names, as mentioned in the OED, included furacan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atabey (goddess)
Atabey is an ancestral mother of the Taíno, one of two supreme ancestral spirits in Taíno mythology. She was worshipped as a zemi, which is an embodiment of nature and ancestral spirit, (not to be confused with a goddess, how she is commonly referred to in colonial terms to replace Taíno verbiage and culture) of fresh water and fertility; she is the female entity who represents the Spirit of all horizontal water, lakes, streams, the sea, and the marine tides. This spirit was one of the most important for the native tribes that inhabited the Caribbean islands of the Antilles, mostly in Puerto Rico (Borikén), Hispaniola, and Cuba. Atabey or Atabeira defines prime matter and all that is tangible or material and has several manifestations. One is the aforementioned nurturing maternal figure. Another is Caguana: the spirit of love. The last is Guabancex (also known as Gua Ban Ceh): the violent, Wild Mother of storms, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Alternate names for Atabey are I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taíno Mythology
Taíno mythology is the body or collection of myths of the Taíno in Cuba, Puerto Rico, Dominican Republic and the Greater Antilles. The Island Arawak-speaking Taino recorded their mythology in communal sacred performances called areitos which are mostly lost. Areitos involved complex elaborations in dance, music, oratory, fabric, and trance. They also performed areitos for important social events like harvest time and births, marriages, and deaths of chiefs. Taino religious practice was centered on veneration of zemis, ancestors, and mythic heroes within a perception that had no distinction between natural and supernatural. Zemis generally held away over specific natural domains, processes, rhythms, and resources. Yucahu, son of mother goddess Atabey, for example, was the god of cassava or yucca, the primary food source of the Taino. Opiyelguobiran, the soul dog, ferried dead souls between realms. Religion was administered by priests (behikes or bohikes), and chiefs or kasikes ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taíno
The Taíno are the Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, Indigenous peoples of the Greater Antilles and surrounding islands. At the time of European contact in the late 15th century, they were the principal inhabitants of most of what is now The Bahamas, Cuba, the Dominican Republic, Haiti, Jamaica, Puerto Rico, and the northern Lesser Antilles. The Lucayan people, Lucayan branch of the Taíno were the first New World peoples encountered by Christopher Columbus, in the Lucayan Archipelago, Bahama Archipelago on October 12, 1492. The Taíno historically spoke an Arawakan languages, Arawakan language. Granberry and Vescelius (2004) recognized two varieties of the Taino language: "Classical Taino", spoken in Puerto Rico and most of Hispaniola, and "Ciboney Taino", spoken in the Bahamas, most of Cuba, western Hispaniola, and Jamaica. They lived in agricultural societies ruled by caciques with fixed settlements and a Matrilineality, matrilineal system of kinship and inheritance. Taíno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yúcahu
YúcahuFray Ramón Pané 1999, p.4 —also written as Yucáhuguama Bagua Maórocoti, Yukajú, Yocajú, Yokahu or Yukiyú— was the masculine spirit of fertility in Taíno mythology.Stevens-Arroyo 2006, p.221 He was the supreme deity or zemi of the Pre-Columbian Taíno people along with his mother Atabey who was his feminine counterpart. Dominant in the Caribbean region at the time of Columbus’ First voyages of Discovery, the peoples associated with Taíno culture inhabited the islands of the Bahamas, the Greater Antilles, and the Lesser Antilles.Rouse 1993, p.13Rouse 1993, p.5 Mythology Yúcahu was the supreme deity of the Taíno people. "They call him Yúcahu Bagua Maórocoti" is the earliest mention of the zemí taken from the first page of Fray Ramón Pané's ''Account of the Antiquities of the Indians''. As the Taíno did not possess a written language, the name is the phonetic spelling as recorded by the Spanish missionaries, Ramón Pané, and Bartolomé de las Casas. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zemi
A zemi or cemi (Taíno: [sɛmi]) was a deity or ancestral spirit, and a sculptural object housing the spirit, among the Taíno people of the Caribbean.Bercht et al, 23 Cemi’no or Zemi’no is a plural word for the spirits. Theology Taíno religion, as recorded by late 15th and 16th century Spaniards, centered on a supreme creator god and a fertility goddess. The creator god is Yukiyu, Yúcahu Maórocoti and he governs the growth of the staple food, the cassava. The goddess is Atabey (goddess), Attabeira, who governs water, rivers, and seas. Lesser deities govern natural forces and are also zemis.Bercht et al, 23 Boinayel, the Rain Giver, is one such zemi, whose magical tears become rainfall."Deity Figure (Zemi) Dominican Republic; Taino (1979.206.380)" In Heilbrunn Timeline o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclones
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is called a hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean. A typhoon is the same thing which occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean and South Pacific, comparable storms are referred to as "tropical cyclones". In modern times, on average around 80 to 90 named tropical cyclones form each year around the world, over half of which develop hurricane-force winds of or more. Tropical cyclones typically form over large bodies of relatively warm water. They derive their energy through the evaporation of water from the ocean s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sky And Weather Goddesses
The sky is an unobstructed view upward from the surface of the Earth. It includes the atmosphere and outer space. It may also be considered a place between the ground and outer space, thus distinct from outer space. In the field of astronomy, the sky is also called the celestial sphere. This is an abstract sphere, concentric to the Earth, on which the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars appear to be drifting. The celestial sphere is conventionally divided into designated areas called constellations. Usually, the term ''sky'' informally refers to a perspective from the Earth's surface; however, the meaning and usage can vary. An observer on the surface of the Earth can see a small part of the sky, which resembles a dome (sometimes called the ''sky bowl'') appearing flatter during the day than at night. In some cases, such as in discussing the weather, the sky refers to only the lower, denser layers of the atmosphere. The daytime sky appears blue because air molecules scatter sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaos Gods
A chaos deity is a deity or more often a figure or spirit in mythology associated with or being a personification of primordial chaos. The following is a list of chaos deities in various mythologies. Africa and the Middle East Afroasiatic Middle East Arabian * Falak * Hinn and Binn Canaanite * Yam, god of the sea and primordial chaos * Tannin (monster) Egyptian * Apep the ultimate evil of Egyptian mythology in snake form * Isfet chaos, disorder, and injustice - opposed to Maat * Nu (mythology) primordial waters * Set (deity) Set (; Egyptian language#Egyptological pronunciation, Egyptological: ''Sutekh - swtẖ ~ stẖ'' or: Seth ) is a deity, god of deserts, storms, disorder, violence, and foreigners in ancient Egyptian religion. In Ancient Greek, the god's name is ... was not originally evil, but developed into a hated figure thanks to the invading Hyksos who identified him with their chief god, fights Apep. Hebrew * Leviathan (is referred to as a reptilian aquatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huracan
Huracán (; ; , "one legged"), often referred to as ''U Kʼux Kaj'', the "Heart of Sky", is a Kʼicheʼ people, Kʼicheʼ Maya mythology, Maya god of wind, storm, fire and one of the creator deities who participated in all three attempts at creating humanity. He also caused the Deluge (mythology), Great Flood after the second generation of humans angered the gods. He supposedly lived in the windy mists above the floodwaters and repeatedly invoked "earth" until land came up from the seas. His name, understood as 'One-Leg', suggests god K of Postclassic and Classic Maya iconography, a deity of lightning with one human leg, and one leg shaped like a serpent. God K is commonly referred to as Bolon Tzacab or Kʼawiil and was a god associated with power, creation, and lightning. The name may ultimately derive from ''huracan'', a Carib language, Carib word,Read & González 2000, p.200. and the source of the words ''hurricane'' and ''orcan'' (European windstorm). Related deities are T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Yunque, Puerto Rico
El Yunque or El Yunque Peak (Spanish: ''Pico El Yunque'') (Taíno: ''Yukiyu'') is a mountain located fully within the boundaries of the El Yunque National Forest, part of the U.S. Forest Service, which is the only tropical rainforest under the U.S. Forest Service jurisdiction. It is located in the municipality of Río Grande. Background The peak itself, standing at above sea level is not the highest in Puerto Rico or even the Sierra de Luquillo range where it is located. It is however the most famous peak due to its curious shape, its natural environment and history, and for its cultural importance to the Taino people. The peak is nearly always covered in thin mist and due to its high humidity, a quick shower develops during some afternoons. The hike to the top from the Mina Falls is not challenging yet it takes almost hours. This peak is located on the El Yunque massif which also contains other smaller peaks such as Mount Britton, Juan Diego Peak and the Roca del Yunque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainforest
Rainforests are forests characterized by a closed and continuous tree Canopy (biology), canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforests can be generally classified as tropical rainforests or temperate rainforests, but other types have been described. Estimates vary from 40% to 75% of all biotic community, biotic species being Indigenous (ecology), indigenous to the rainforests. There may be many millions of species of plants, insects and microorganisms still undiscovered in tropical rainforests. Tropical rainforests have been called the "jewels of the Earth" and the "medicine chest (idiom), world's largest pharmacy", because over one quarter of natural medicines have been discovered there. Rainforests as well as endemic rainforest species are rapidly disappearing due to #Deforestation, deforestation, the resulting habitat loss and air pollution, pollution of the atmosphere. Definition Rainforests are cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Antilles
The Greater Antilles is a grouping of the larger islands in the Caribbean Sea, including Cuba, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, and Jamaica, together with Navassa Island and the Cayman Islands. Seven island states share the region of the Greater Antilles, with Haiti and the Dominican Republic sharing the island of Hispaniola. Together with the Lesser Antilles, they make up the Antilles, which along with the Lucayan Archipelago, form the West Indies in the Caribbean region of the Americas. While most of the Greater Antilles consists of independent countries, Puerto Rico and Navassa Island are Territories of the United States, unincorporated territories of the United States, while the Cayman Islands are a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory. The largest island is Cuba, which extends to the western end of the island group. Puerto Rico lies on the eastern end, and the island of Hispaniola, the most populated island, is located in the middle. Jamaica lies to the south of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |