|
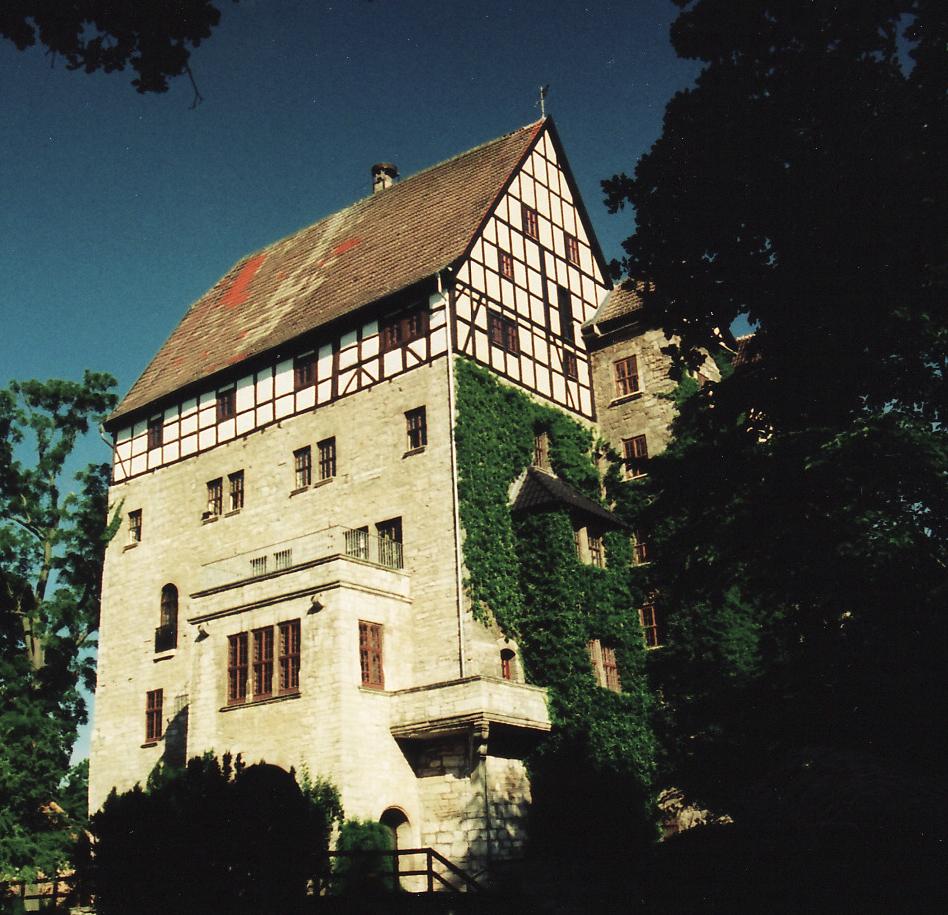
Großengottern
Großengottern is a village and a former Municipalities in Germany, municipality in the Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis Districts of Germany, district of Thuringia, Germany. Since 1 January 2019, it is part of the municipality of Unstrut-Hainich. Geography Großengottern is located in the northern Thuringian basin between the towns of Mühlhausen and Bad Langensalza. The village of Großengottern lies in the area of the Inner Thuringian hilly farmland, the north and the east of the village, the , in the Unstrut floodplain between Mühlhausen and Bad Langensalza. The highest elevation is above sea level (Normalnull, NN) at to the west of the village, the lowest at about above sea level (NN) on the Unstrut in the far east of the terrain. Other elevations are the two former undercut slope areas of the Unstrut, the ''Hopfenberg'' hill to the north-east and the ''Schalkenberg'' to the south-east of the village. The ''Gottern'' area is mainly used for agriculture, with arable farming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Martin's Church, Großengottern
St Martin's Church () in the lower part of the village of Großengottern in Thuringia, Germany, is a Late Gothic architecture, Late Gothic Church (building), church building. Today, it is a Lutheranism, Lutheran parish church. History Like St Walpurgis' Church, Großengottern, St Walpurgis' Church in the upper part of Großengottern, which is also Late Gothic architecture, Late Gothic in style, St Martin's Church is older than the written records indicate. A parish priest has been resident in Großengottern since 1280. St Martin's Church, the older church, is documented in 1318. Since 1500, both churches have hardly been changed structurally. The many similarities include the appearance which is applied to the church and village seals. The choir and tower were built around 1500, further alterations took place in 1617–1647, and the east window was changed in the 19th century. Architecture and interior The building is a rubble-stone construction with a three-si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Walpurgis' Church, Großengottern
St Walpurgis' Church () in the upper part of the village of Großengottern in Thuringia, Germany, is a Late Gothic church building dating from the 15th century. Today, it is a Lutheran parish church. St Walpurgis' Church is known for its large Baroque organ by the significant organ builder Tobias H. G. Trost. History and architecture Like St Martin's Church in the lower part of Großengottern, which is also Late Gothic and was first mentioned in a document in 1318, St Walpurgis' Church is older than the written records indicate. A priest has been resident in Großengottern since 1280. St Walpurgis' Church was first mentioned in a document in 1494 when it was reconstructed and extended. Since 1500, both churches have hardly been changed structurally. The many similarities include the appearance and are applied to the church and village seals. St Walpurgis' Church was built on pre-existing foundation walls and walls of a predecessor church. The vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seebach, Mühlhausen
Seebach () is a village and a rural quarter of the town of Mühlhausen in Thuringia, central Germany. It lies on the right side of the Unstrut river. Geography Location Seebach lies to the north of the ''Seebach'', a left-sided tributary of the Unstrut coming from Niederdorla, at an altitude of between and above Normalnull, NN. The highest elevations within the Seebach terrain are the ''Kobenberg'' ( above NN) in the south and the ''Kahler Berg'' ( above NN) in the southwest. Geology The near-surface geological subsoil of the hilly farmland around Seebach is characterised by the rocks of the Gypsum Keuper and the ''Bunte Mergel'' (Middle Keuper). The mostly clayey rocks are overlain by thick loess loam layers, especially on the hilltops. In the broad Unstrut valley in the east, alluvial loams are exposed. History Seebach was first mentioned as "Sebecke" in a deed of gift from Count Erpho to the Prince-Bishopric of Würzburg in 859 AD. The village was named after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unstrut-Hainich (Verwaltungsgemeinschaft)
Unstrut-Hainich is a former ''Verwaltungsgemeinschaft'' in the district of Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis in Thuringia, Germany. The seat of the ''Verwaltungsgemeinschaft'' was in Großengottern. It was disbanded in January 2019. The ''Verwaltungsgemeinschaft'' Unstrut-Hainich consisted of the following municipalities: # Altengottern # Flarchheim # Großengottern # Heroldishausen # Mülverstedt # Schönstedt Schönstedt is a village and a former municipality in the Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis district of Thuringia, Germany Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the Nort ... # Weberstedt References Former Verwaltungsgemeinschaften in Thuringia {{UnstrutHainich-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unstrut-Hainich
Unstrut-Hainich is a municipality in the district Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis, in Thuringia, Germany. It was created with effect from 1 January 2019 by the merger of the former municipalities of Altengottern, Flarchheim, Großengottern, Heroldishausen, Mülverstedt and Weberstedt. On 1 January 2024, it absorbed the former municipality Schönstedt. Gesetz- und Verordnungsblatt für den Freistaat Thüringen, 2023 Nr. 15, p. 349 The name refers to the river and the hill chain |
Early Modern Period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There is no exact date that marks the beginning or end of the period and its extent may vary depending on the area of history being studied. In general, the early modern period is considered to have lasted from around the start of the 16th century to the start of the 19th century (about 1500–1800). In a European context, it is defined as the period following the Middle Ages and preceding the advent of modernity; but the dates of these boundaries are far from universally agreed. In the context of World history (field), global history, the early modern period is often used even in contexts where there is no equivalent "medieval" period. Various events and historical transitions have been proposed as the start of the early modern period, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People's Commissars to oppose the military forces of the new nation's adversaries during the Russian Civil War, especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army. In February 1946, the Red Army (which embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces alongside the Soviet Navy) was renamed the "Soviet Army". Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union it was split between the post-Soviet states, with its bulk becoming the Russian Ground Forces, commonly considered to be the successor of the Soviet Army. The Red Army provided the largest land warfare, ground force in the Allies of World War II, Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its Soviet invasion of Manchuria, invasion of Manchuria assisted the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutheranism
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched the Reformation in 1517. The Lutheran Churches adhere to the Bible and the Ecumenical Creeds, with Lutheran doctrine being explicated in the Book of Concord. Lutherans hold themselves to be in continuity with the apostolic church and affirm the writings of the Church Fathers and the first four ecumenical councils. The schism between Roman Catholicism and Lutheranism, which was formalized in the Diet of Worms, Edict of Worms of 1521, centered around two points: the proper source of s:Augsburg Confession#Article XXVIII: Of Ecclesiastical Power., authority in the church, often called the formal principle of the Reformation, and the doctrine of s:Augsburg Confession#Article IV: Of Justification., justification, the material principle of Luther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schönstedt
Schönstedt is a village and a former municipality in the Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis district of Thuringia, Germany Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu .... On 1 January 2024 it became part of the municipality Unstrut-Hainich. Gesetz- und Verordnungsblatt für den Freistaat Thüringen, 2023 Nr. 15, p. 349 References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Germany
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on 3 October 1990. Until 1989, it was generally viewed as a communist state and described itself as a Socialist state, socialist "workers' and peasants' state". The Economy of East Germany, economy of the country was Central planning, centrally planned and government-owned corporation, state-owned. Although the GDR had to pay substantial war reparations to the Soviets, its economy became the most successful in the Eastern Bloc. Before its establishment, the country's territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the Berlin Declaration (1945), Berlin Declaration abolishing German sovereignty in World War II. The Potsdam Agreement established the Soviet occupation zone in Germany, Soviet-occupied zone, bounded on the east b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heroldishausen
Heroldishausen is a village and a former municipality in the Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis district of Thuringia, Germany. Since 1 January 2019, it is part of the municipality Unstrut-Hainich Unstrut-Hainich is a municipality in the district Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis, in Thuringia, Germany. It was created with effect from 1 January 2019 by the merger of the former municipalities of Altengottern, Flarchheim, Großengottern, Heroldishause .... References Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis Former municipalities in Thuringia {{UnstrutHainich-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin Airlift
The Berlin Blockade (24 June 1948 – 12 May 1949) was one of the first major international crises of the Cold War. During the multinational occupation of post–World War II Germany, the Soviet Union blocked the Western Allies' railway, road, and canal access to the sectors of Berlin under Western control. The Soviets offered to drop the blockade if the Western Allies withdrew the newly introduced Deutsche Mark from West Berlin. The Western Allies organised the Berlin Airlift (German: ''Berliner Luftbrücke'', lit. "Berlin Air Bridge") from 26 June 1948 to 30 September 1949 to carry supplies to the people of West Berlin, a difficult feat given the size of the city and the population. American and British air forces flew over Berlin more than 250,000 times, dropping necessities such as fuel and food, with the original plan being to lift 3,475 tons of supplies daily. By the spring of 1949, that number was often met twofold, with the peak daily delivery totalling 12,941 ton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |