|
Growth Hormone Receptor
Growth hormone receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GHR'' gene. GHR orthologs have been identified in most mammals. Structure Growth hormone receptor (GHR) is a transmembrane protein consisting of 620 amino acids. The receptor is part of the Type I cytokine receptor family of receptors. GHR exists in two forms as a full length membrane-bound receptor and as a soluble GH binding protein (GHBP). GHR contains two fibronectin type III β domains in its extracellular domain, whereas the intracellular domain contains tyrosine Kinase JAK2 binding sites for SH2 proteins. JAK2 is the primary signal transducer for growth hormone. Function This gene encodes a protein that is a transmembrane receptor for growth hormone. Binding of growth hormone to the receptor leads to reorientation of a pre-assembled receptor dimer dimerization (the receptor may however also exist as monomers on the cell surface ) and the activation of an intra- and intercellular signal transdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear DNA
Nuclear DNA (nDNA), or nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid, is the DNA contained within each cell nucleus of a eukaryotic organism. It encodes for the majority of the genome in eukaryotes, with mitochondrial DNA and plastid DNA coding for the rest. It adheres to Mendelian inheritance, with information coming from two parents, one male and one female—rather than matrilineally (through the mother) as in mitochondrial DNA. Structure Nuclear DNA is a nucleic acid, a polymeric biomolecule or biopolymer, found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Its structure is a double helix, with two strands wound around each other, a structure first described by Francis Crick and James D. Watson (1953) using data collected by Rosalind Franklin. Each strand is a long polymer chain of repeating nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a five-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and an organic base. Nucleotides are distinguished by their bases: purines, large bases that include adenine and gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatostatin
Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by #Nomenclature, several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the release of numerous secondary hormones. Somatostatin inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion. Somatostatin has two active forms produced by the alternative cleavage of a single preproprotein: one consisting of 14 amino acids (shown in infobox to right), the other consisting of 28 amino acids. Among the vertebrates, there exist six different somatostatin genes that have been named: ''SS1'', ''SS2'', ''SS3'', ''SS4'', ''SS5'' and ''SS6''. Zebrafish have all six. The six different genes, along with the five different somatostatin receptors, allow somatostatin to possess a large range of functions. Humans have only one somatostatin gene, ''SST''. Nomenclature Synonyms of "somatost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
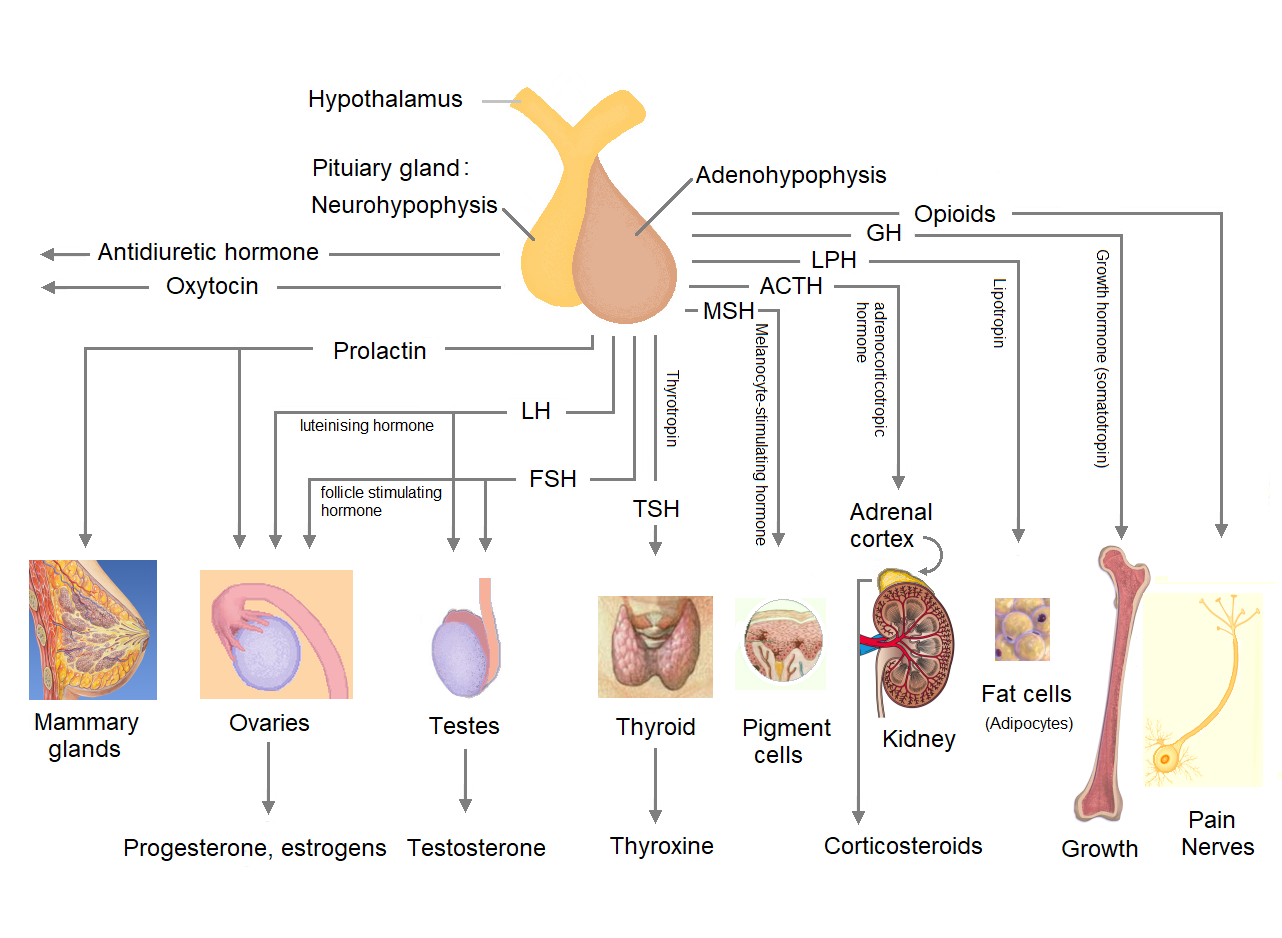
Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus control much of the body's endocrine system. It is seated in part of the sella turcica a fossa (anatomy), depression in the sphenoid bone, known as the hypophyseal fossa. The human pituitary gland is ovoid, oval shaped, about 1 cm in diameter, in weight on average, and about the size of a kidney bean. Digital version. There are two main lobes of the pituitary, an anterior pituitary, anterior lobe, and a posterior pituitary, posterior lobe joined and separated by a small intermediate lobe. The anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) is the glandular part that produces and secretes several hormones. The posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) secretes neurohypophysial hormones produced in the hypothalamus. Both lobes have different origins and they are both co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acromegaly
Acromegaly is a disorder that results in excess growth of certain parts of the human body. It is caused by excess growth hormone (GH) after the growth plates have closed. The initial symptom is typically enlargement of the hands and feet. There may also be an enlargement of the forehead, jaw, and nose. Other symptoms may include joint pain, thicker skin, deepening of the voice, headaches, and Visual impairment, problems with vision. Complications of the disease may include type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and high blood pressure. Signs and symptoms Features that may result from a high level of GH or expanding tumor include: * Headaches * Enlargement of the hands, feet, nose, lips, and ears, and a general thickening of the skin * Soft tissue swelling of internal organs, notably the heart with the attendant weakening of its muscularity, and the kidneys, also the vocal cords resulting in a characteristic thick, deep voice and slowing of speech * Generalized expansion of the skull at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pegvisomant
Pegvisomant, sold under the brand name Somavert, is a growth hormone receptor antagonist used in the treatment of acromegaly. It is primarily used if the pituitary gland tumor causing the acromegaly cannot be controlled with surgery or radiation, and the use of somatostatin analogues is unsuccessful, but is also effective as a monotherapy. It is delivered as a powder that is mixed with water and injected under the skin. Medical uses Pegvisomant is indicated for the treatment of adults with acromegaly. Side effects Side effects of pegvisomant include reactions at the injection site, swelling of the limbs, chest pain, hypoglycemia, nausea and hepatitis. Discovery Pegvisomant was discovered at Ohio University in 1987 by Distinguished Professor John Kopchick and graduate student Wen Chen at the Edison Biotechnology Institute. After completing clinical trials, it was approved for the treatment of acromegaly by the FDA in 2003 and marketed by Pfizer. Structure Pegvisomant is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves ." '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, beta b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnivores
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose nutrition and energy requirements are met by consumption of animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other soft tissues) as food, whether through predation or scavenging. Nomenclature Mammal order The technical term for mammals in the order Carnivora is ''carnivoran'', and they are so-named because most member species in the group have a carnivorous diet, but the similarity of the name of the order and the name of the diet causes confusion. Many but not all carnivorans are meat eaters; a few, such as the large and small cats (Felidae) are ''obligate'' carnivores (see below). Other classes of carnivore are highly variable. The ursids (bears), for example: while the Arctic polar bear eats meat almost exclusively (more than 90% of its diet is meat), almost all other bear species are omnivorous, and one species, the giant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mustelid
The Mustelidae (; from Latin , weasel) are a diverse family of carnivoran mammals, including weasels, badgers, otters, polecats, martens, grisons, and wolverines. Otherwise known as mustelids (), they form the largest family in the suborder Caniformia of the order Carnivora with about 66 to 70 species in nine subfamilies. Variety Mustelids vary greatly in size and behaviour. The smaller variants of the least weasel can be under in length, while the giant otter of Amazonian South America can measure up to and sea otters can exceed in weight. Wolverines can crush bones as thick as the femur of a moose to get at the marrow, and have been seen attempting to drive bears away from their kills. The sea otter uses rocks to break open shellfish to eat. Martens are largely arboreal, while European badgers dig extensive tunnel networks, called setts. Only one mustelid has been domesticated; the ferret. Tayra are also kept as pets (although they require a Dangerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermoptera
Colugos (), flying lemurs, or cobegos (), are arboreal gliding euarchontogliran mammals that are native to Southeast Asia. Their closest evolutionary relatives are primates. There are just two living species of colugos: the Sunda flying lemur (''Galeopterus variegatus'') and the Philippine flying lemur (''Cynocephalus volans''). These two species make up the entire family Cynocephalidae () and order Dermoptera, from Ancient Greek δέρμα (''dérma'') "skin" and πτερόν (''pterón'') "wing". Characteristics Colugos are nocturnal, tree-dwelling mammals. Appearance and anatomy They reach lengths of and weigh . They have long, slender front and rear limbs, a medium-length tail, and a relatively light build. The head is small, with large, front-focused eyes for excellent binocular vision, and small rounded ears. The incisor teeth of colugos are highly distinctive; they are comb-like in shape with up to 20 tines on each tooth. The incisors are analogous in app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felid
Felidae ( ) is the Family (biology), family of mammals in the Order (biology), order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats. A member of this family is also called a felid ( ). The 41 extant taxon, extant Felidae species exhibit the greatest diversity in fur patterns of all terrestrial carnivores. Cats have retractile claws, slender muscular bodies and strong flexible forelimbs. Their teeth and facial muscles allow for a powerful bite. They are all obligate carnivores, and most are solitary predators ambushing or stalking their prey. Wild cats occur in Africa, Europe, Asia and the Americas. Some wild cat species are adapted to forest and savanna habitats, some to arid environments, and a few also to wetlands and mountainous terrain. Their activity patterns range from nocturnal and crepuscular to Diurnality, diurnal, depending on their preferred prey species. Reginald Innes Pocock divided the extant Felidae into three subfamilies: the Pantherinae, the Felinae and the Acin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy (biology)
In biology, taxonomy () is the science, scientific study of naming, defining (Circumscription (taxonomy), circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxon, taxa (singular: taxon), and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain (biology), domain, kingdom (biology), kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class (biology), class, order (biology), order, family (biology), family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, having developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |