|
Gronausaurus
''Brancasaurus'' (meaning "Branca's lizard") is a genus of plesiosaur which lived in a freshwater lake in the Early Cretaceous of what is now North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a long neck possessing vertebrae bearing distinctively-shaped "shark fin"-shaped neural spines, and a relatively small and pointed head, ''Brancasaurus'' is superficially similar to ''Elasmosaurus'', albeit smaller in size at in length as a subadult. The type species of this genus is ''Brancasaurus brancai'', first named by Theodor Wegner in 1914 in honor of German paleontologist Wilhelm von Branca. Another plesiosaur named from the same region, ''Gronausaurus wegneri'', most likely represents a synonym of this genus. While traditionally considered as a basal member of the Elasmosauridae, ''Brancasaurus'' has more recently been recovered as a member, or close relative, of the Leptocleididae, a group containing many other freshwater plesiosaurs. Description ''Brancasaurus'' was a medium-sized plesiosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brancasaurus Skull
''Brancasaurus'' (meaning "Branca's lizard") is a genus of plesiosaur which lived in a freshwater lake in the Early Cretaceous of what is now North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a long neck possessing vertebrae bearing distinctively-shaped "shark fin"-shaped neural spines, and a relatively small and pointed head, ''Brancasaurus'' is superficially similar to ''Elasmosaurus'', albeit smaller in size at in length as a subadult. The type species of this genus is ''Brancasaurus brancai'', first named by Theodor Wegner in 1914 in honor of German paleontologist Wilhelm von Branca. Another plesiosaur named from the same region, ''Gronausaurus wegneri'', most likely represents a synonym of this genus. While traditionally considered as a basal member of the Elasmosauridae, ''Brancasaurus'' has more recently been recovered as a member, or close relative, of the Leptocleididae, a group containing many other freshwater plesiosaurs. Description ''Brancasaurus'' was a medium-sized plesios ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesiosaur
The Plesiosauria (; Greek: πλησίος, ''plesios'', meaning "near to" and ''sauros'', meaning "lizard") or plesiosaurs are an order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia. Plesiosaurs first appeared in the latest Triassic Period, possibly in the Rhaetian stage, about 203 million years ago. They became especially common during the Jurassic Period, thriving until their disappearance due to the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous Period, about 66 million years ago. They had a worldwide oceanic distribution, and some species at least partly inhabited freshwater environments. Plesiosaurs were among the first fossil reptiles discovered. In the beginning of the nineteenth century, scientists realised how distinctive their build was and they were named as a separate order in 1835. The first plesiosaurian genus, the eponymous '' Plesiosaurus'', was named in 1821. Since then, more than a hundred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and right vagus nerves—but they are typically referred to collectively as a single subsystem. The vagus is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system in the human body and comprises both sensory and motor fibers. The sensory fibers originate from neurons of the nodose ganglion, whereas the motor fibers come from neurons of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and the nucleus ambiguus. The vagus was also historically called the pneumogastric nerve. Structure Upon leaving the medulla oblongata between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle, the vagus nerve extends through the jugular foramen, then passes into the carotid sheath between the internal carotid artery and the internal jugular vein down to the neck, chest, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve (), also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior (closer to the nose) to the vagus nerve. Being a mixed nerve (sensorimotor), it carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, whereas the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest. Structure From the anterior portion of the medulla oblongata, the glossopharyngeal nerve passes laterally across or below the flocculus, and leaves the skull through the central part of the jugular foramen. From the superior and inferior ganglia in jugular foramen, it has its own sheath of dura mater. The inferior ganglion on the inferior surface of petrous part of temporal is related with a triangular depression into which the aqueduct of cochlea opens. On the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory Nerve
The accessory nerve, also known as the eleventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve XI, or simply CN XI, is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is classified as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerves because part of it was formerly believed to originate in the brain. The sternocleidomastoid muscle tilts and rotates the head, whereas the trapezius muscle, connecting to the scapula, acts to shrug the shoulder. Traditional descriptions of the accessory nerve divide it into a spinal part and a cranial part. The cranial component rapidly joins the vagus nerve, and there is ongoing debate about whether the cranial part should be considered part of the accessory nerve proper. Consequently, the term "accessory nerve" usually refers only to nerve supplying the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles, also called the spinal accessory nerve. Strength testing of these muscles can be measured during a neurological examination to assess funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
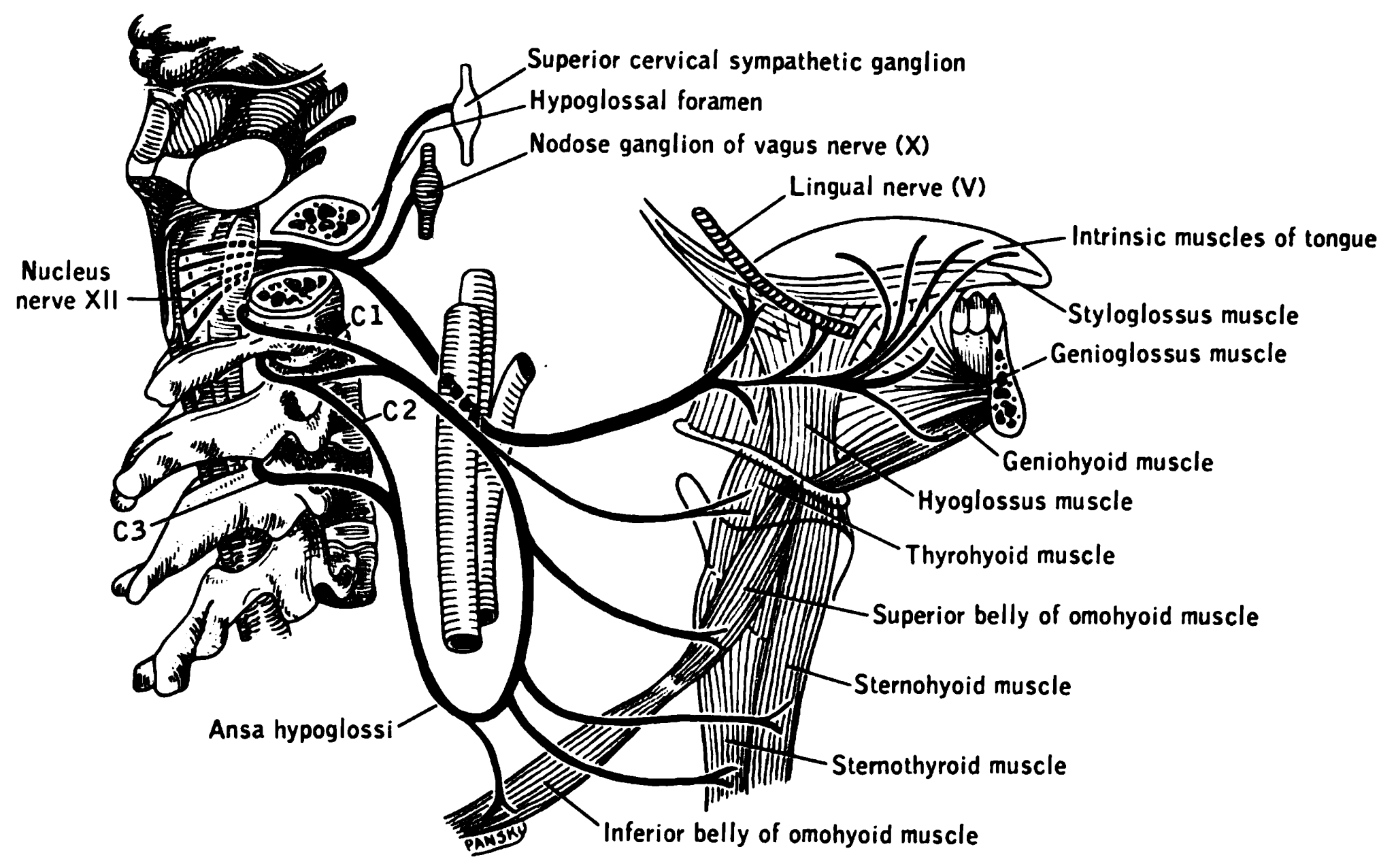
Hypoglossal Nerve
The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by the vagus nerve. CN XII is a nerve with a solely motor function. The nerve arises from the hypoglossal nucleus in the medulla as a number of small rootlets, passes through the hypoglossal canal and down through the neck, and eventually passes up again over the tongue muscles it supplies into the tongue. The nerve is involved in controlling tongue movements required for speech and swallowing, including sticking out the tongue and moving it from side to side. Damage to the nerve or the neural pathways which control it can affect the ability of the tongue to move and its appearance, with the most common sources of damage being injury from trauma or surgery, and motor neuron disease. The first recorded description of the nerve is by Her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semicircular Canals
The semicircular canals or semicircular ducts are three semicircular, interconnected tubes located in the innermost part of each ear, the inner ear. The three canals are the horizontal, superior and posterior semicircular canals. Structure The semicircular canals are a component of the bony labyrinth that are at right angles from each other. At one end of each of the semicircular canals is a dilated sac called an osseous ampulla, which is more than twice the diameter of the canal. Each ampulla contains an ampullary crest, the crista ampullaris which consists of a thick gelatinous cap called a cupula and many hair cells. The superior and posterior semicircular canals are oriented vertically at right angles to each other. The lateral semicircular canal is about a 30-degree angle from the horizontal plane. The orientations of the canals cause a different canal to be stimulated by movement of the head in different planes, and more than one canal is stimulated at once if the movem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurocranium
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skullcap. The remainder of the skull is the facial skeleton. In comparative anatomy, neurocranium is sometimes used synonymously with endocranium or chondrocranium. Structure The neurocranium is divided into two portions: * the membranous part, consisting of flat bones, which surround the brain; and * the cartilaginous part, or chondrocranium, which forms bones of the base of the skull. In humans, the neurocranium is usually considered to include the following eight bones: * 1 ethmoid bone * 1 frontal bone * 1 occipital bone * 2 parietal bones * 1 sphenoid bone * 2 temporal bones The ossicles (three on each side) are usually not included as bones of the neurocranium. There may variably also be extra sutural bones present. Below the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamosal Bone
The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone. In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestral component of the dermal roof and is typically thin compared to other skull bones. The squamosal bone lies ventral to the temporal series and otic notch, and is bordered anteriorly by the postorbital. Posteriorly, the squamosal articulates with the quadrate and pterygoid bones. The squamosal is bordered anteroventrally by the jugal and ventrally by the quadratojugal. Function in reptiles In reptiles, the quadrate and articular bones of the skull articulate to form the jaw joint. The squamosal bone lies anterior to the quadrate bone. Anatomy in synapsids Non-mammalian synapsids In non-mammalian synapsids, the jaw is composed of four bony elements and referred to as a quadro-articular jaw because the joint is between the articular an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Structure In humans, the maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla * Four processes ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process of maxilla ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process * three surfaces – anterior, posterior, medial * the Infraorbital foramen * the maxillary sinus * the incisive foramen Articulations Each maxilla articulates with nine bones: * two of the cranium: the frontal and ethmoid * seven of the face: the nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |