|
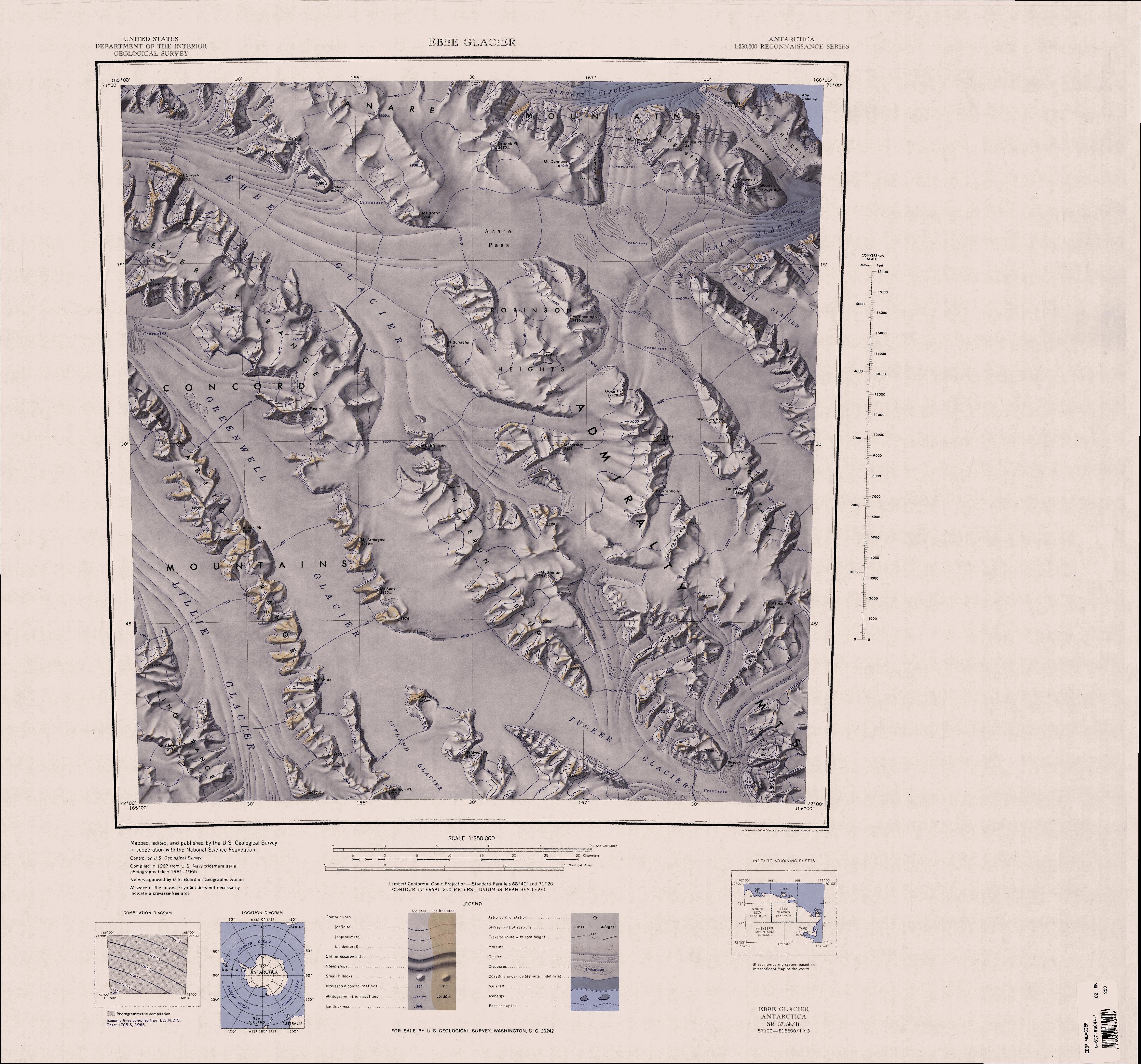
Grigg Peak
Robinson Heights in Antarctica () are the mainly ice-covered heights , elliptical in plan and long, which rise south of Anare Pass and form the northwest end of the Admiralty Mountains, Antarctica. Exploration and naming The Robinson Heights were mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy photography, 1960–63. They were named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Edwin S. Robinson, a United States Antarctic Research Program (USARP) geophysicist at McMurdo Sound in 1960. He participated in a number of geophysical traverses, including his leadership of the South Pole Station Traverse, 1962–63. Location The Robinson Heights are in the Admiraly Mountains to the south of the Anare Pass, which lies between the Ebbe Glacier and the Dennistoun Glacier to the south of the Anare Mountains. The Ebbe Glacier flow past its southwest side, separating it from the Homerun Range. The Lyttelton Range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78th parallel south, 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Victoria of the United Kingdom, Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. History Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 Meteorite, meteorites in Antarctica, some of which were found near the Allan Hills in Victoria Land. The meteorites appeared to have undergone little change since they were formed at what scientists believe was the birth of the Solar System. In 1981, Lichen, lichens fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dennistoun Glacier
The Dennistoun Glacier () is a glacier, long, draining the northern slopes of Mount Black Prince, Mount Royalist and Mount Adam in the Admiralty Mountains of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It flows northwest between the Lyttelton Range and Dunedin Range, turning east on rounding the latter range to enter the sea south of Cape Scott. Exploration and naming The coastal extremity of the Dennistoun Glacier was charted in 1911–12 by the Northern Party, led by Victor Campbell, of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13 (BrAE). The glacier is named after Jim Dennistoun, a New Zealand alpinist who was in charge of the mules on board the '' Terra Nova'' on her way to Antarctica. The entire extent of the glacier was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and United States Navy aerial photography, 1960–63. The name Fowlie Glacier, which in fact refers to a tributary glacier, has sometimes been inadvertently misapplied to this feature. Location The Denni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallett Station
Cape Hallett is a snow-free area (Antarctic oasis) on the northern tip of the Hallett Peninsula on the Ross Sea coast of Victoria Land, East Antarctica. Cape Adare lies to the north. History In 1956, during Operation Deep Freeze II, was damaged by an ice floe at Cape Hallett. On 16 October 1958, a Douglas C-124C Globemaster II (52-1017) of the USAF crashed into a 3200-foot mountain near Cape Hallett Bay while maneuvering, killing 7 of the 13 occupants. The Globemaster was on an airdrop flight from Christchurch to McMurdo Station and other navigational errors had occurred prior to the crash. Hallett Station The cape was the location of a joint scientific base, Hallett Station, between the United States and New Zealand during the International Geophysical Year of 1957, and was manned permanently until 1964, when there was a major fire. It was then used as a summer only base until 1973. The site is currently being remediated by removing hazardous materials: fuel, and oi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMurdo Station
McMurdo Station is an American Antarctic research station on the southern tip of Ross Island. It is operated by the United States through the United States Antarctic Program (USAP), a branch of the National Science Foundation. The station is the largest community in Antarctica, capable of supporting up to 1,500 residents, though the population fluctuates seasonally; during the antarctic night, there are fewer than two hundred people. It serves as one of three year-round United States Antarctic science facilities. Personnel and cargo going to or coming from Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station usually first pass through McMurdo, either by flight or by the McMurdo to South Pole Traverse; it is a hub for activities and science projects in Antarctica. McMurdo, Amundsen-Scott, and Palmer are the three non-seasonal United States stations on the continent, though by the Antarctic Treaty System the bases are not a legal claim (though the right is not forfeited); they are dedicated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunedin Range
The Dunedin Range () is a northwest-trending mountain range, long and wide. It is located east of Lyttelton Range in the Admiralty Mountains of Victoria Land, Antarctica. Name The Dunedin Range was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos, 1960–63. It was named by United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for the city of Dunedin, New Zealand which over the years has had a close association with Antarctic expeditions; also in recognition of the friendship and cooperation of its citizens with American participation in the U.S. Antarctic Research Program. Location The Dunedin Range is in the north of the Admiralty Mountains. It extended in the northwest-southeast direction from the Dennystoun Glacier, which flows along the west side, then turns past the northern tip of the range and runs east to the Southern Ocean The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyttelton Range
The Lyttelton Range () is a narrow northwest-trending mountain range located south of Dunedin Range in the Admiralty Mountains of Antarctica. The range is long and forms the western wall of the upper part of the Dennistoun Glacier. Exploration and naming The Lyttelton Range was mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos, 1960-63. It was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) after the port of Lyttelton, New Zealand, where over the years, many expedition ships refueled and replenished supplies en route to Antarctica; also in recognition of the friendship and cooperation of its citizens with American participation in the U.S. Antarctic Research Program. Location Lyttelton Range lies between Findlay Range, which extends southeast from Robinson Heights, to the west, and the Dunedin Range to the east. The upper Dennistoun Glacier flows past its east side. The Atkinson Glacier flows between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homerun Range
The Homerun Range () is a northwest-trending range, long and wide, east of Everett Range at the heads of the Ebbe Glacier and Tucker Glacier in Victoria Land, Antarctica. Exploration and naming The name of the Homerun Range derives from "Homerun Bluff," a field name of the southern party of the New Zealand Federated Mountain Clubs Antarctic Expedition (NZFMCAE), 1962–63, used to denote a turning point in their traverse at this range to the airlift point and return to Scott Base. The entire range was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos from 1960 to 1963. Location The Homerun Range is in the Admiralty Mountains, southeast of the Everett Range of the Concord Mountains. Robinson Heights and the Findlay Range are to the north and east. The McGregor Range is to the southeast. The Homerun Range runs from northwest to southeast, from Mount LeResche at the head of the Ebbe Glacier, past Mount Shelton to the poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anare Mountains
The Anare Mountains () are a large group of mainly snow-covered peaks and ridges along the northern coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica. The group is bounded on the north and east by the Pacific Ocean, on the west by Lillie Glacier, and on the south by Ebbe Glacier and Dennistoun Glacier. They are north of the Concord Mountains and east of the Bowers Mountains. Exploration and naming Mountains in this area were first sighted by Captain James Clark Ross in 1841. They were photographed during United States Navy Operation Highjump (1946–1947) and were surveyed by United States Geological Survey (USGS) helicopter teams, 1962–63. The Anare Mountains were named by the northern party of the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1963–64, for the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE), 1962, under Phillip Law, which performed survey work along the coast. Location In the northwest the Anare Mountains extend along the Pacific coast to the east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebbe Glacier
Lillie Glacier () is a large glacier in Antarctica, about long and wide. It lies between the Bowers Mountains on the west and the Concord Mountains and Anare Mountains on the east, flowing to Ob' Bay on the coast and forming the Lillie Glacier Tongue. Discovery and naming The glacier tongue was discovered by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, and was named by the expedition for Dennis G. Lillie, a biologist on the ''Terra Nova''. The name Lillie has since been extended to the entire glacier. The lower half of the glacier was plotted by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expedition (ANARE) (''Thala Dan'') in 1962, which explored the area and utilized air photos taken by United States Navy Operation Highjump, 1946–47. The whole feature was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos, 1960–62. On 22 October 1964 a United States Navy ski-equipped LC-47 airplane flew from Hallett Station to establish a cac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anare Pass
The Anare Mountains () are a large group of mainly snow-covered peaks and ridges along the northern coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica. The group is bounded on the north and east by the Pacific Ocean, on the west by Lillie Glacier, and on the south by Ebbe Glacier and Dennistoun Glacier. They are north of the Concord Mountains and east of the Bowers Mountains. Exploration and naming Mountains in this area were first sighted by Captain James Clark Ross in 1841. They were photographed during United States Navy Operation Highjump (1946–1947) and were surveyed by United States Geological Survey (USGS) helicopter teams, 1962–63. The Anare Mountains were named by the northern party of the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1963–64, for the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE), 1962, under Phillip Law, which performed survey work along the coast. Location In the northwest the Anare Mountains extend along the Pacific coast to the east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMurdo Sound
The McMurdo Sound is a sound in Antarctica, known as the southernmost passable body of water in the world, located approximately from the South Pole. Captain James Clark Ross discovered the sound in February 1841 and named it after Lieutenant Archibald McMurdo of HMS ''Terror''. The sound serves as a resupply route for cargo ships and airplanes that land on floating ice airstrips near McMurdo Station. The McMurdo seasonal Ice Runway was operated from October to December from the 1950s to the 2010s, then in December the ice breaks up and McMurdo port is opened by an Icebreaker ship and ships can resupply the Antarctic bases. Physical characteristics Boundary and extents The sound extends approximately 55 kilometers (34 mi) in length and width, and opens into the larger Ross Sea to the north. To the south, the sound is bounded by the Ross Ice Shelf cavity, to the west lies the Royal Society Range, and to the east is Ross Island. McMurdo Sound is separated from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |