|
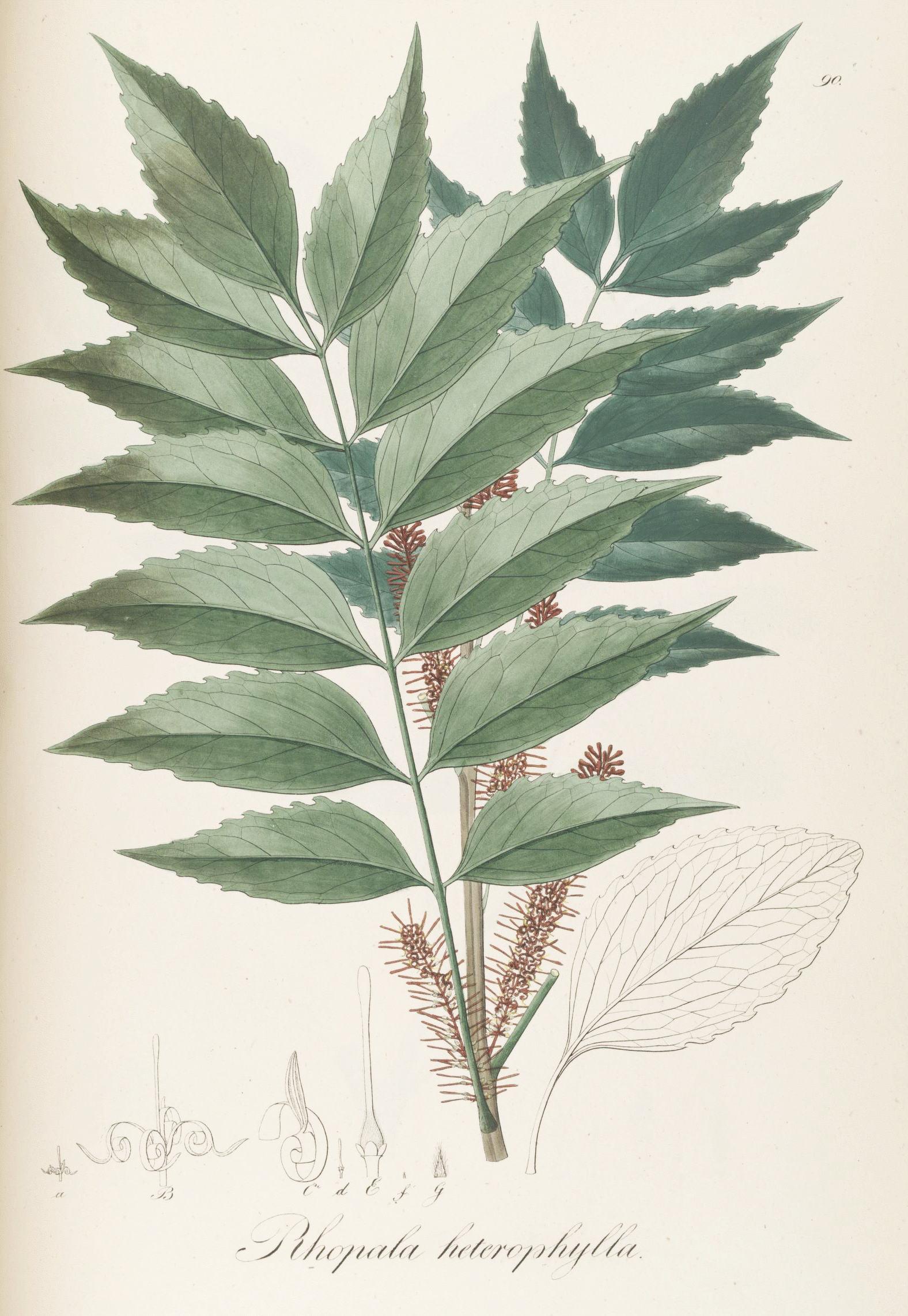
Grevillea Papuana
''Grevillea papuana'' is a tree species in the family Proteaceae. It is endemic to New Guinea. The species was formally described in 1916 by German botanist Ludwig Diels Dr. Friedrich Ludwig Emil Diels (24 September 1874 – 30 November 1945) was a German botanist. Diels was born in Hamburg, the son of the classical scholar Hermann Alexander Diels. From 1900 to 1902 he traveled together with Ernst Georg Pr .... References papuana Flora of New Guinea Plants described in 1916 Endemic flora of New Guinea {{proteaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Diels
Dr. Friedrich Ludwig Emil Diels (24 September 1874 – 30 November 1945) was a German botanist. Diels was born in Hamburg, the son of the classical scholar Hermann Alexander Diels. From 1900 to 1902 he traveled together with Ernst Georg Pritzel through South Africa, Java, Australia and New Zealand. Shortly before the First World War he travelled New Guinea and in the 1930s in Ecuador. Especially his collections of plants from Australia and Ecuador, which contained numerous holotypes, enriched the knowledge of the concerning floras. His monography on the Droseraceae from 1906 is still a standard. The majority of his collections were stored at the botanical garden in Berlin-Dahlem, whose vicedirector he had been since 1913, becoming its director in 1921 until 1945. His collections were destroyed there during an air raid in 1943. He died in Berlin on 30 November 1945. Honours Several genus of plants have been named after him including; ''Dielsantha'' (from ''Campanulace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteaceae
The Proteaceae form a family of flowering plants predominantly distributed in the Southern Hemisphere. The family comprises 83 genera with about 1,660 known species. Together with the Platanaceae and Nelumbonaceae, they make up the order Proteales. Well-known genera include '' Protea'', '' Banksia'', '' Embothrium'', '' Grevillea'', '' Hakea'' and '' Macadamia''. Species such as the New South Wales waratah ('' Telopea speciosissima''), king protea ('' Protea cynaroides''), and various species of ''Banksia'', ''soman'', and ''Leucadendron'' are popular cut flowers. The nuts of '' Macadamia integrifolia'' are widely grown commercially and consumed, as are those of Gevuina avellana on a smaller scale. Australia and South Africa have the greatest concentrations of diversity. Etymology The name Proteaceae was adapted by Robert Brown from the name Proteae coined in 1789 for the family by Antoine Laurent de Jussieu, based on the genus ''Protea'', which in 1767 Carl Linnaeus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua. The largest cities on the island are Jayapura (capital of Papua, Indonesia) and Port Moresby (capital of Papua New Guinea). Names The island has been known by various names: The name ''Papua'' was used to refer to parts of the island before contact with the West. Its etymology is unclear; one theory states that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grevillea
''Grevillea'', commonly known as spider flowers, is a genus of about 360 species of evergreen flowering plants in the family Proteaceae. Plants in the genus ''Grevillea'' are shrubs, rarely trees, with the leaves arranged alternately along the branches, the flowers zygomorphic, arranged in racemes at the ends of branchlets, and the fruit a follicle that splits down one side only, releasing one or two seeds. Description Plants in the genus ''Grevillea'' are shrubs, rarely small trees with simple or compound leaves arranged alternately along the branchlets. The flowers are zygomorphic and typically arranged in pairs along a sometimes branched raceme at the ends of branchlets. The flowers are bisexual, usually with four tepals in a single whorl. There are four stamens and the gynoecium has a single carpel. The fruit is a thin-walled follicle that splits down only one side, releasing one or two seeds before the next growing season. Taxonomy The genus ''Grevillea'' was first for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of New Guinea
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring ( indigenous) native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora as in the terms ''gut flora'' or ''skin flora''. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) was first made by Jules Thurma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plants Described In 1916
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have los ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |