|
Greensleeves Records Artists
"Greensleeves" is a traditional English folk song. A broadside ballad by the name "A Newe Northen Dittye of ye Ladye Greene Sleves" was registered by Richard Jones at the London Stationers' Company in September 1580,Frank Kidson, ''English Folk-Song and Dance''. READ BOOKS, 2008, p.26. John M. Ward, "'And Who But Ladie Greensleeues?'", in ''The Well Enchanting Skill: Music, Poetry, and Drama in the Culture of the Renaissance: Essays in Honour of F. W. Sternfeld'', edited by John Caldwell, Edward Olleson, and Susan Wollenberg, 181–211 (Oxford:Clarendon Press; New York: Oxford University Press, 1990): 181. . and the tune is found in several late 16th-century and early 17th-century sources, such as ''Ballet's MS Lute Book'' and '' Het Luitboek van Thysius'', as well as various manuscripts preserved in the Seeley Historical Library in the University of Cambridge. Origin A broadside ballad by this name was registered at the London Stationer's Company in September 1580, by Richard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dante Gabriel Rossetti
Gabriel Charles Dante Rossetti (12 May 1828 – 9 April 1882), generally known as Dante Gabriel Rossetti ( ; ), was an English poet, illustrator, painter, translator, and member of the Rossetti family. He founded the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood in 1848 with William Holman Hunt and John Everett Millais. Rossetti inspired the next generation of artists and writers, William Morris and Edward Burne-Jones in particular. His work also influenced the European Symbolism (movement), Symbolists and was a major precursor of the Aesthetic movement. Rossetti's art was characterised by its sensuality and its medieval revivalism. His early poetry was influenced by John Keats and William Blake. His later poetry was characterised by the complex interlinking of thought and feeling, especially in his sonnet sequence ''The House of Life''. Poetry and image are closely entwined in Rossetti's work. He frequently wrote sonnets to accompany his pictures, spanning from ''The Girlhood of Mary Virgin' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer ( ; – 25 October 1400) was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for ''The Canterbury Tales''. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He was the first writer to be buried in what has since come to be called Poets' Corner, in Westminster Abbey. Chaucer also gained fame as a philosopher and astronomer, composing the scientific ''A Treatise on the Astrolabe'' for his 10-year-old son, Lewis. He maintained a career in public service as a bureaucrat, courtier, diplomat, and member of parliament, having been elected as Knight of the shire, shire knight for Kent. Among Chaucer's many other works are ''The Book of the Duchess'', ''The House of Fame'', ''The Legend of Good Women'', ''Troilus and Criseyde'', and ''Parlement of Foules''. He is seen as crucial in legitimising the literary use of Middle English when the dominant literary languages in England were still Anglo-Norman Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord (music)
In Western music theory, a chord is a group of notes played together for their harmony, harmonic Consonance and dissonance, consonance or dissonance. The most basic type of chord is a Triad (music), triad, so called because it consists of three distinct notes: the Root (chord), root note along with Interval (music), intervals of a Third (chord), third and a Fifth (chord), fifth above the root note. Chords with more than three notes include added tone chords, extended chords and tone clusters, which are used in contemporary classical music, jazz, and other genres. Chords are the building blocks of harmony and form the harmonic foundation of a piece of music. They provide the harmonic support and coloration that accompany melodies and contribute to the overall sound and mood of a musical composition. The factor (chord), factors, or component notes, of a chord are often sounded simultaneously but can instead be sounded consecutively, as in an arpeggio. A succession of chords is ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Music Score Library Project
The International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP), also known as the Petrucci Music Library after publisher Ottaviano Petrucci, is a subscription-based digital library of public-domain music scores. The project uses MediaWiki software, and has uploaded more than 736,000 scores and 80,700 recordings by 1,900 performers of more than 226,000 works by 27,400 composers. IMSLP has both an iOS app and an Android app. History Overview The site was launched on February 16, 2006. The library consists mainly of scans of old musical editions out of copyright. In addition, it admits scores by contemporary composers who wish to share their music with the world by releasing it under a Creative Commons license. One of the main projects of the IMSLP was the sorting and uploading of the complete works of Johann Sebastian Bach in the Bach-Gesellschaft Ausgabe (1851–99), a task that was completed on November 3, 2008. Besides J.S. Bach's complete public domain works, many or all availab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andalusian Progression
The Andalusian cadence (diatonic phrygian tetrachord) is a term adopted from flamenco music for a chord progression comprising four chords descending stepwise: iv–III–II–I progression with respect to the Phrygian mode or i–VII–VI–V progression with respect to the Aeolian mode (minor).Mojácar Flamenco , a website about basics in Flamenco music It is otherwise known as the minor . Traceable back to the , its effective sonorities made it one of the most popular progressions in |
Passamezzo Antico
The passamezzo antico is a ground bass or chord progression that was popular during the Italian Renaissance and known throughout Europe in the 16th century.Peter van der Merwe (musicologist), van der Merwe, Peter. 1989. ''Origins of the Popular Style: The Antecedents of Twentieth-Century Popular Music'', p.207. Oxford: Clarendon Press. . The progression is a variant of the double tonic: its major mode variant is known as the passamezzo moderno. The sequence consists of two phrase (music), phrases as follows: ''(For an explanation of this notation see Chord progression)'' Though usually in the key of G minor, in the key of A minor this gives: The romanesca is a variant of the passamezzo antico, where the first chord is the III (e.g., a C major chord in A minor). A famous example is "Greensleeves". The passamezzo antico chord changes are found, knowingly or not, in modern popular music culture: Carrie Underwood's debut album ''Some Hearts (Carrie Underwood album), Some Hearts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanesca
Romanesca is a melodic-harmonic formula popular from the mid–16th to early–17th centuries that was used as an aria formula for singing poetry and as a subject for instrumental variation. The pattern, which is found in an endless collection of compositions labeled ''romanesca'', perhaps from northern-central Italy, is a descending descant formula within a chordal progression that has a bass which moves by 4ths. The formula was not to be viewed as a fixed tune, but as a framework over which elaborate ornamentation can occur.Gerbino, Giuseppe. (2001). Romanesca. In John Tyrrell and Stanley Sadie (Eds.), The New Grove Dictionary of music and musicians (2nd ed., Vol. 21, pp. 577-578). New York: Grove It was most popular with Italian and Spanish composers of the Renaissance and early Baroque period. It was also used by vihuelistas including Luis de Narváez, Alonso Mudarra, Enríquez de Valderrábano, and Diego Pisador. Origins Scholars are uncertain of the precise origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostinato
In music, an ostinato (; derived from the Italian word for ''stubborn'', compare English ''obstinate'') is a motif or phrase that persistently repeats in the same musical voice, frequently in the same pitch. Well-known ostinato-based pieces include classical compositions such as Ravel's ''Boléro'' and the '' Carol of the Bells'', and popular songs such as John Lennon’s “Mind Games” (1973), Donna Summer and Giorgio Moroder's " I Feel Love" (1977), Henry Mancini's theme from ''Peter Gunn'' (1959), The Who's " Baba O'Riley" (1971), The Verve's " Bitter Sweet Symphony" (1997), and Flo Rida's " Low" (2007). Both ''ostinatos'' and ''ostinati'' are accepted English plural forms, the latter reflecting the word's Italian etymology. The repeating idea may be a rhythmic pattern, part of a tune, or a complete melody in itself. Kamien, Roger (1258). ''Music: An Appreciation'', p. 611. . Strictly speaking, ostinati should have exact repetition, but in common usage, the term cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
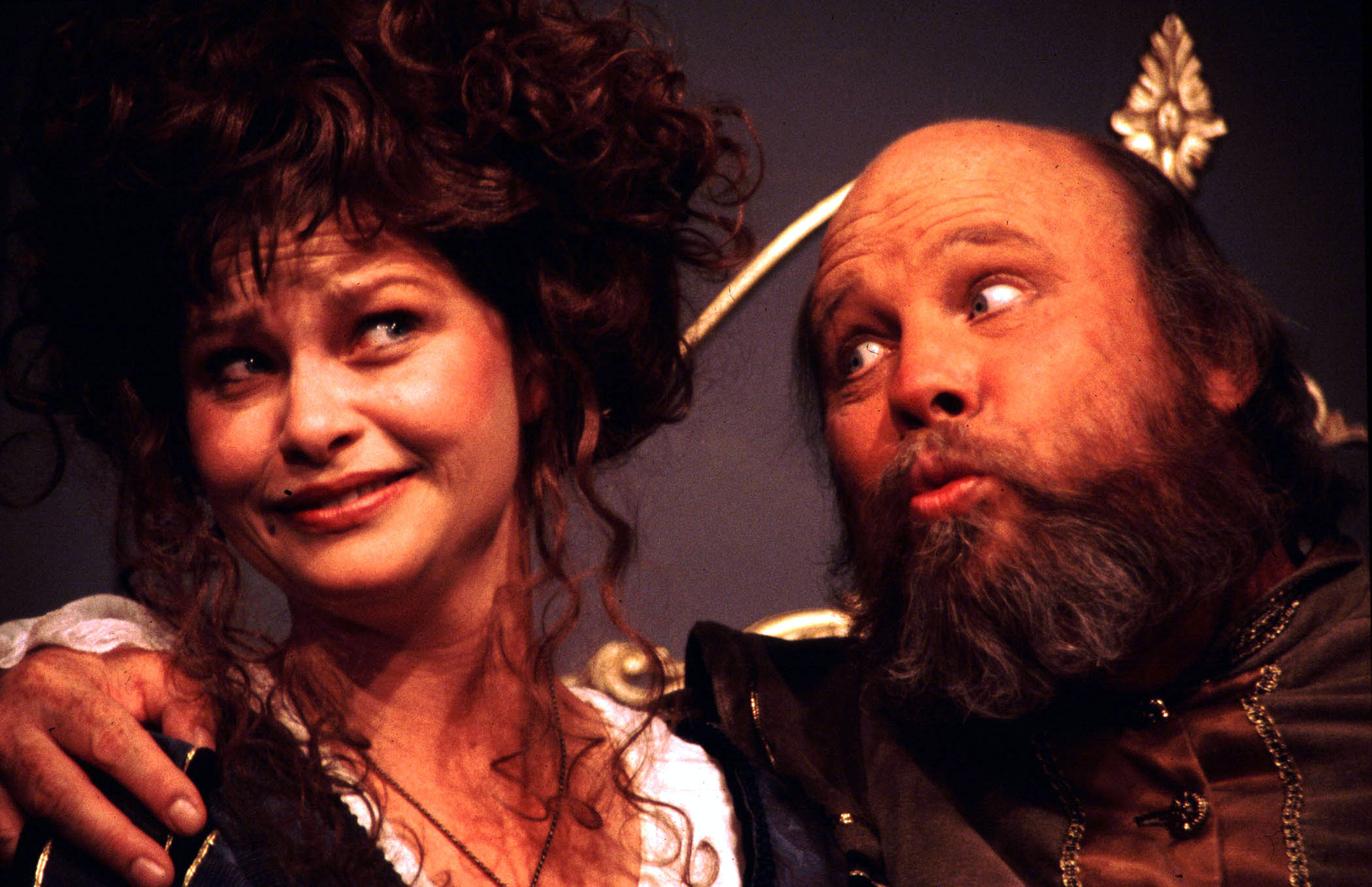
Falstaff
Sir John Falstaff is a fictional character who appears in three plays by William Shakespeare and is eulogised in a fourth. His significance as a fully developed character is primarily formed in the plays ''Henry IV, Part 1'' and '' Part 2'', where he is a companion to Prince Hal, the future King Henry V of England. Falstaff is also featured as the buffoonish suitor of two married women in ''The Merry Wives of Windsor''. Though primarily a comic figure, he embodies a depth common to Shakespeare's major characters. A fat, vain, and boastful knight, he spends most of his time drinking at the Boar's Head Inn with petty criminals, living on stolen or borrowed money. Falstaff leads the apparently wayward Prince Hal into trouble, and is repudiated when Hal becomes king. Falstaff has appeared in other works, including operas by Giuseppe Verdi, Ralph Vaughan Williams, and Otto Nicolai, a "symphonic study" by Edward Elgar, and in Orson Welles's 1966 film ''Chimes at Midnight''. The op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Merry Wives Of Windsor
''The Merry Wives of Windsor'' or ''Sir John Falstaff and the Merry Wives of Windsor'' is a comedy by William Shakespeare first published in 1602, though believed to have been written in or before 1597. The Windsor of the play's title is a reference to the town of Windsor, also the location of Windsor Castle in Berkshire, England. Though nominally set in the reign of Henry IV or early in the reign of Henry V, the play makes no pretence to exist outside contemporary Elizabethan-era English middle-class life. It features the character Sir John Falstaff, the fat knight who had previously been featured in ''Henry IV, Part 1'' and '' Part 2''. It has been adapted for the opera at least ten times. The play is one of Shakespeare's lesser-regarded works among literary critics. Tradition has it that ''The Merry Wives of Windsor'' was written at the request of Queen Elizabeth I. After watching ''Henry IV, Part 1'', she asked Shakespeare to write a play depicting Falstaff in love. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dante Gabriel Rossetti - My Lady Greensleeves (1859)
Dante Alighieri (; most likely baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri; – September 14, 1321), widely known mononymously as Dante, was an Italian poet, writer, and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', originally called (modern Italian: ) and later christened by Giovanni Boccaccio, is widely considered one of the most important poems of the Middle Ages and the greatest literary work in the Italian language. Dante chose to write in the vernacular, specifically, his own Tuscan dialect, at a time when much literature was still written in Latin, which was accessible only to educated readers, and many of his fellow Italian poets wrote in French or Provençal. His ' (''On Eloquence in the Vernacular'') was one of the first scholarly defenses of the vernacular. His use of the Florentine dialect for works such as '' The New Life'' (1295) and ''Divine Comedy'' helped establish the modern-day standardized Italian language. His work set a precedent that important Italian writers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Chatterton Dix
William Chatterton Dix (14 June 1837 – 9 September 1898) was an English writer of hymns and Carol (music), carols. He was born in Bristol, the son of John Ross Dix, John Dix, a local surgeon, who wrote ''The Life of Chatterton'' the poet, a book of ''Pen Pictures of Popular English Preachers'' and other works.James Moffatt, ''Handbook to the Church Hymnary'', Oxford University Press, 1927 His father gave him his middle name in honour of Thomas Chatterton, a poet about whom he had written a biography. He was educated at the Grammar School, Bristol, for a mercantile career, and became manager of a maritime insurance company in Glasgow where he spent most of his life.James Moffatt, ''Handbook to the Church Hymnary'', Oxford University Press, 1927, p. 318 His original hymns are found in most modern hymn-books. He wrote also felicitous renderings in metrical form of Richard Frederick Littledale's translations from the Greek in his ''Offices of the Holy Eastern Church''; and of John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |