|
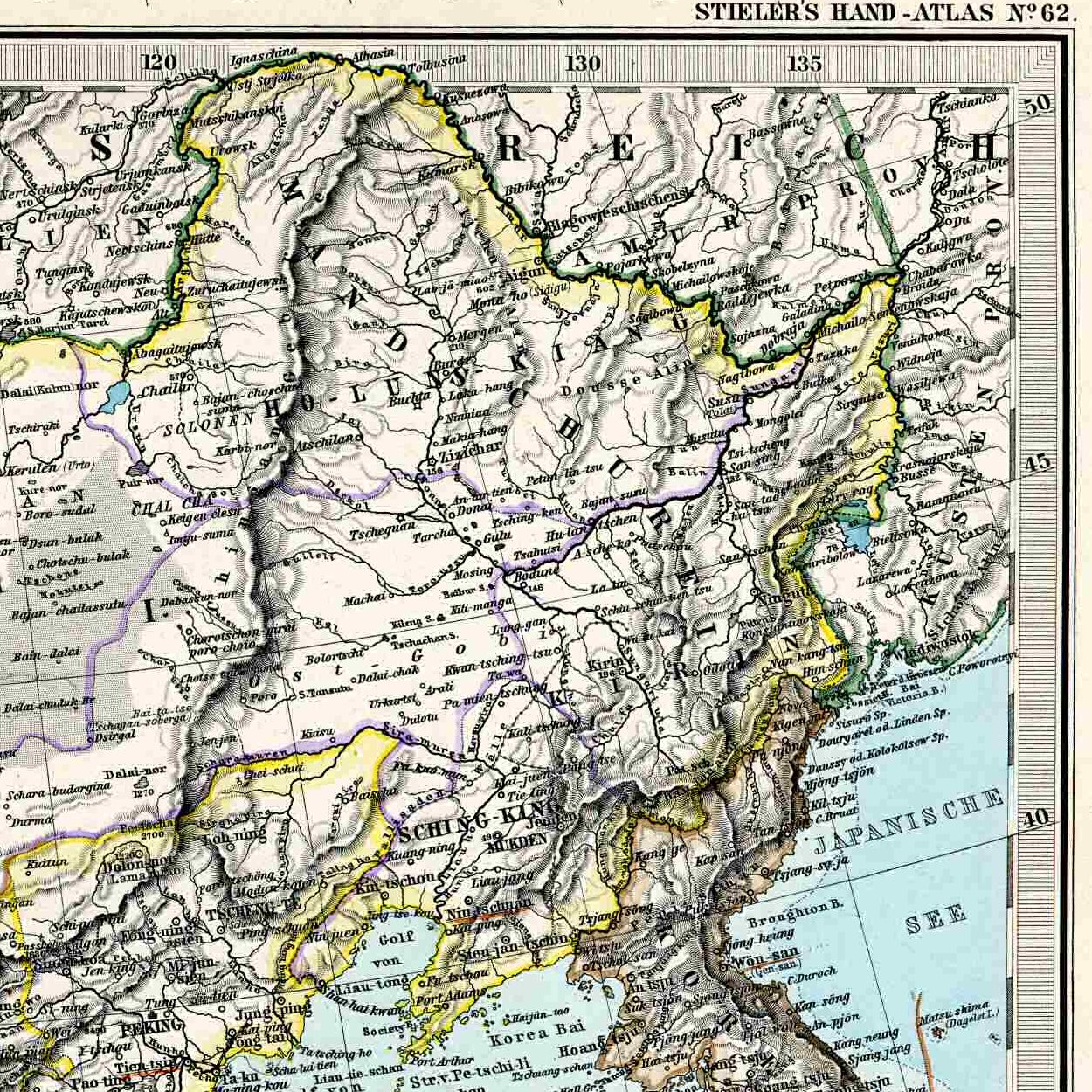
Greater Khingan Range
The Greater Khingan Range or Da Hinggan Range ( zh, s=大兴安岭, t=大興安嶺, p=Dà Xīng'ān Lǐng; IPA: ) is a volcanic mountain range in the Inner Mongolia region of Northeast China. It was originally called the Xianbei Mountains, which later became the name of the northern branch of the Donghu, the Xianbei. Geography The range extends from north to south. It is the watershed between the Nen and Songhua river systems to the east, and the Amur and its tributaries to the northwest. Population Its slopes are a relatively rich grazing area. The Khitan people lived on the eastern slopes before establishing the Liao Dynasty in the tenth century. Oroqen, a Tungusic people, live along the Greater and Lesser Khingan range in northeastern China and belong to the oldest autochthonous populations of the region. On the western slopes lived the nomadic people, who raised sheep and camels and used the Mongolian plateau for their pastoralist economy. In fiction The Greater K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genhe
Genhe City or Gegengol (; zh, c=根河市), formerly Ergun Left Banner ( zh, s=额尔古纳左旗), is a county-level city in the far northeast of Inner Mongolia, China, under the administration of Hulunbuir City. The city spans an area of , and has a total population of 130,722 as of 2019. Geography and climate Genhe has a monsoon-influenced subarctic climate (Köppen ''Dwc''), making it one of the coldest locations nationally, with an annual mean temperature of . Winters are long, severely cold, and very dry in terms of total precipitation, while summers are short and warm; the normal monthly mean temperature ranges from in January to in July. Over two-thirds of the annual precipitation of is distributed from June through August. Administrative divisions Genhe is divided into 4 subdistricts, 4 towns, and 1 ethnic township. Demographics As of 2019, Genhe is home to 130,722 inhabitants, the 72nd most of Inner Mongolia's 103 county-level divisions. As of 2017, 64,4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oroqen People
The Oroqen or Orochen people ( Oroqen:; ; Mongolian: ) are an ethnic group in northern China. They form one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China. The Oroqen people are largely concentrated in the northern Chinese provinces of Heilongjiang and Inner Mongolia, which are home to 45.54% and 41.94% of the 8,259 Oroqen people living in China. The Oroqen Autonomous Banner is also located in Inner Mongolia. The Oroqens are mainly hunters, and customarily use animal fur and skins for clothing. Many of them have given up hunting and adhered to laws that aimed to protect wildlife in the People's Republic of China. The government has provided modern dwellings for those who have left behind the traditional way of life. The Oroqen are represented in the People's Congress by their own delegate and are a recognized ethnic minority. In the Russian Empire, various peoples in various places were called Orochen (; orthography before Soviet reform), in sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges Of China
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountains t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xing'an (other)
Xing'an ( t, s, ''Xīng'ān'') is the atonal pinyin romanization of various Chinese words and names. It may refer to: * Xing'an County in Guangxi * Xing'an Province Xing'an (; or Hsingan) refers to a former province, which once occupied western Heilongjiang and part of northwest Jilin provinces of China. The name is related to that of the Greater Khingan Mountains. Another name used for this land was Barga, w ..., a former division of Manchuria * Xing'an District in Hegang, Heilongjiang * Xing'an, Hebei, a town in Gaocheng District * Xing'an, Heilongjiang, a town in Mohe See also * Khingan (other), various mountain ranges in northern China and in Mongolia * Hinggan (other), the Manchu form of the same name {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Khingan
Lesser Khingan ( zh, c=小兴安岭, p=Xiǎo Xīng'ān Lǐng; , ''Maly Khingan'') is a mountain range in China's Heilongjiang province and the adjacent parts of Russia's Amur Oblast and Jewish Autonomous Oblast.Малый Хинган '' Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (GSE; , ''BSE'') is one of the largest Russian-language encyclopedias, published in the Soviet Union from 1926 to 1990. After 2002, the encyclopedia's data was partially included into the later ''Great Russian Enc ... '' in 30 volumes — Ch. ed. A.M. Prokhorov. - 3rd ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daxing'anling Prefecture
Daxing'anling (), also known as Da Hinggan Ling, is the northernmost Chinese prefecture-level division, located in northwestern Heilongjiang Province. It covers and had a population of 520,000, as of 2004. It is named after the Greater Khingan Range (Daxing'anling; ; Amba Hinggan Dabagan) Mountains. In 2007, it had a GDP of RMB 6.1 billion and a growth rate of 11.1%. In 2015, Daxing'anling Prefecture had a GDP of RMB 13.49 billion, and a GDP of RMB 15.39 billion in the year 2014. Administrative divisions Daxing'anling Prefecture administrates 1 county-level city, 2 counties, and 4 administration zones. These counties and management districts contain 6 urban subdistricts, 24 towns, 11 townships, 2 ethnic townships, 41 residential communities, and 80 villages. Forestry divisions Administered by the State Forestry Administration's Heilongjiang Daxing'anling Forestry Group Corporation () with 10 Forestry Bureaus and 61 Woodlands. Administered by Daxing'anling Prefectur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Cixin
Liu Cixin (, pronounced ; born 23 June 1963) is a Chinese computer engineer and science fiction writer. In English translations of his works, his name is given as Cixin Liu. He is sometimes called "''Da'' Liu" ("Big Liu") by his fellow science fiction writers in China. He is a nine-time winner of China's Galaxy Award (China), Galaxy Award, and has also received the 2015 Hugo Award for his novel ''The Three-Body Problem (novel), The Three-Body Problem'', as well as the 2017 Locus Award for ''Death's End''. He is also a winner of the Chinese Nebula Awards (China), Nebula Award. He is a member of the China Science Writers Association and the vice president of the Shanxi Writers Association. Life and career Liu was born on 23 June 1963 in Beijing. He grew up in Yangquan, Shanxi, where his parents had been sent to work in the mines. Due to the violence of the Cultural Revolution he was sent to live in his ancestral home in Luoshan County, Henan. Liu graduated from the North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Three-Body Problem (novel)
''The Three-Body Problem'' () is a 2008 novel by the Chinese hard science fiction author Liu Cixin. It is the first novel in the ''Remembrance of Earth's Past'' trilogy. The series portrays a fictional past, present, and future wherein Earth encounters an alien civilization from a nearby system of three Sun-like stars orbiting one another, a representative example of the three-body problem in orbital mechanics. The story was originally serialized in ''Science Fiction World'' in 2006 before it was published as a standalone book in 2008. In 2006, it received the Galaxy Award for Chinese science fiction.Clute, John"Yinhe Award", Science Fiction Encyclopedia, 3rd edition. Accessed November 21, 2017 In 2012, it was described as one of China's most successful full-length novels of the past two decades. The English translation by Ken Liu was published by Tor Books in 2014. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Fiction
Science fiction (often shortened to sci-fi or abbreviated SF) is a genre of speculative fiction that deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts. These concepts may include information technology and robotics, biological manipulations, space exploration, time travel, Parallel universes in fiction, parallel universes, and extraterrestrials in fiction, extraterrestrial life. The genre often explores human responses to the consequences of projected or imagined scientific advances. Science fiction is related to fantasy (together abbreviated wikt:SF&F, SF&F), Horror fiction, horror, and superhero fiction, and it contains many #Subgenres, subgenres. The genre's precise Definitions of science fiction, definition has long been disputed among authors, critics, scholars, and readers. Major subgenres include hard science fiction, ''hard'' science fiction, which emphasizes scientific accuracy, and soft science fiction, ''soft'' science fiction, which focuses on social sciences. Other no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
900–1800
9 (nine) is the natural number following and preceding . Evolution of the Hindu–Arabic digit Circa 300 BC, as part of the Brahmi numerals, various Indians wrote a digit 9 similar in shape to the modern closing question mark without the bottom dot. The Kshatrapa, Andhra and Gupta started curving the bottom vertical line coming up with a -look-alike. How the numbers got to their Gupta form is open to considerable debate. The Nagari continued the bottom stroke to make a circle and enclose the 3-look-alike, in much the same way that the sign @ encircles a lowercase ''a''. As time went on, the enclosing circle became bigger and its line continued beyond the circle downwards, as the 3-look-alike became smaller. Soon, all that was left of the 3-look-alike was a squiggle. The Arabs simply connected that squiggle to the downward stroke at the middle and subsequent European change was purely cosmetic. While the shape of the glyph for the digit 9 has an ascender in most modern typefa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |