|
Great Ireland
Great Ireland (Old Norse: ''Írland hit mikla'' or ''Írland it mikla''), also known as White Men's Land (''Hvítramannaland''), and in Latin similarly as ''Hibernia Major'' and ''Albania'', was a land said by various Norsemen to be located near Vinland.Barnes, 2001, p. 31. In one report, in the ''Saga of Eric the Red'', some skrælingar captured in Markland described the people in what was supposedly White Men's Land, to have been "dressed in white garments, uttered loud cries, bore long poles, and wore fringes." Another report identifies it with the ''Albani'' people, with "hair and skin as white as snow." Scholars and writers disagree on the nature of the land, from either being treated as a myth based on faded knowledge of lands in the western ocean, to theories on actually locating it somewhere in North America. History Mythical origins Celtic folklore tells of a mythical land across the western ocean often referred to as the Celtic Otherworld, also known as Annwn or Aval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their Viking expansion, overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 7th to the 15th centuries. The Proto-Norse language developed into Old Norse by the 8th century, and Old Norse began to develop into the modern North Germanic languages in the mid-to-late 14th century, ending the language phase known as Old Norse. These dates, however, are not absolute, since written Old Norse is found well into the 15th century. Old Norse was divided into three dialects: Old West Norse, ''Old West Norse'' or ''Old West Nordic'' (often referred to as ''Old Norse''), Old East Norse, ''Old East Norse'' or ''Old East Nordic'', and ''Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immrama
An immram (; plural immrama; ga, iomramh , 'voyage') is a class of Old Irish tales concerning a hero's sea journey to the Otherworld (see Tír na nÓg and Mag Mell). Written in the Christian era and essentially Christian in aspect, they preserve elements of Irish mythology. The immrama are identifiable by their focus on the exploits of the heroes during their search for the Otherworld, located in these cases in the islands far to the west of Ireland. The hero sets out on his voyage for the sake of adventure or to fulfill his destiny, and generally stops on other fantastic islands before reaching his destination. He may or may not be able to return home again. Definition The immrama are generally confused with a similar Irish genre, the '' echtrae'' or "adventure". Both types of story involve a hero's journey to an "otherworld", whether a Christian paradise, a fairyland, the land of the gods or a utopia. They are distinguished by date; echtrai are older, dating from the 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorfinn Karlsefni
Thorfinn Karlsefni Thórdarson was an Icelandic explorer. Around the year 1010, he followed Leif Eriksson's route to Vinland in a short-lived attempt to establish a permanent settlement there with his wife Gudrid Thorbjarnardóttir and their followers. Nickname The byname ''Karlsefni'' means "makings of a man" according to the preface of Magnus Magnusson and Hermann Pálsson, although the Cleasby-Vigfusson dictionary glosses it as "a thorough man", elaborated elsewhere as a "real man", a "sterling man". History Thorfinn's expeditions are documented in the '' Grœnlendinga saga'' ("Saga of the Greenlanders" henceforth Grl.) and '' Eiríks saga rauða'' ("Saga of Eirik the Red" Henceforth Eir.),Manuscripts of ''Eiríks saga rauða'' are indicated by the sigla: A=Hauksbok, B=AM 557=Skálholtsbók in which together are referred to as "The Vinland Sagas." The two sources differ significantly in their details (see #Saga sources below). Greenland In Greenland, Thorfinn met and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skyhorse Pub
Skyhorse Publishing, Inc. is an American independent book publishing company founded in 2006 and headquartered in New York City, with a satellite office in Brattleboro, Vermont. History The current president and publisher is founder Tony Lyons, former president and publisher of Lyons Press until 2004. As noted by '' Publishers Weekly'', "Skyhorse's list will have some similarities to the old Lyons Press, with books on sports, flyfishing, nature and history a central part of Skyhorse's publishing program. The list includes narrative nonfiction, military history, gambling and business titles. In addition, onyLyons intends to bring back 'forgotten classics'." Growth and expansion In 2010, Skyhorse acquired Arcade Publishing with its portfolio of 500 titles, as well as another 300 titles through the acquisition of Allworth Press. Skyhorse also announced the 2011 acquisition of Sports Publishing with its 800 titles, and the launch of a children's and young adult imprint ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north of the coast of Caithness and has about 70 islands, of which 20 are inhabited. The largest island, the Mainland, has an area of , making it the sixth-largest Scottish island and the tenth-largest island in the British Isles. Orkney’s largest settlement, and also its administrative centre, is Kirkwall. Orkney is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, as well as a constituency of the Scottish Parliament, a lieutenancy area, and an historic county. The local council is Orkney Islands Council, one of only three councils in Scotland with a majority of elected members who are independents. The islands have been inhabited for at least years, originally occupied by Mesolithic and Neolithic tribes and then by the Picts. Orkney wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorfinn Turf-Einarsson, Earl Of Orkney
Thorfinn Torf-EinarssonCrawford (1987) p. 63 also known as Thorfinn Skull-splitterThomson (2008) p. 57 (from the Old Norse ''Þorfinnr hausakljúfr'') was a 10th-century Earl of Orkney. He appears in the '' Orkneyinga saga'' and briefly in '' St Olaf's Saga'', as incorporated into the ''Heimskringla''. These stories were first written down in Iceland in the early 13th century and much of the information they contain is "hard to corroborate". Family Thorfinn was the youngest son of Torf-Einarr, himself the son of Rognvald Eysteinsson, the first Earl of Orkney. Torf-Einarr had two other sons, Arnkel and Erlend who "fell in a war expedition"Sturlason, Snorri Chapter 99. "History of the Earls of Orkney". at an unspecified location in England along with Erik Bloodaxe.''Orkneyinga Saga'' (1981) Chapter 8. p. 33 Erik's widow, Gunnhildr then fled north to Orkney with her sons who used the islands as a base for summer raiding expeditions. Thorfinn had five sons: Arnfinn, Havard, Hlodvir, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. The title originates in the Old English word ''eorl'', meaning "a man of noble birth or rank". The word is cognate with the Scandinavian form '' jarl'', and meant " chieftain", particularly a chieftain set to rule a territory in a king's stead. After the Norman Conquest, it became the equivalent of the continental count (in England in the earlier period, it was more akin to a duke; in Scotland, it assimilated the concept of mormaer). Alternative names for the rank equivalent to "earl" or "count" in the nobility structure are used in other countries, such as the ''hakushaku'' (伯爵) of the post-restoration Japanese Imperial era. In modern Britain, an earl is a member of the peerage, ranking below a marquess and above a viscount. A feminine form of ''earl'' never developed; instead, ''countess'' is used. Etymology The term ''earl'' has been compared to the name of the Heruli, and to runic ''erilaz''. Proto-Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
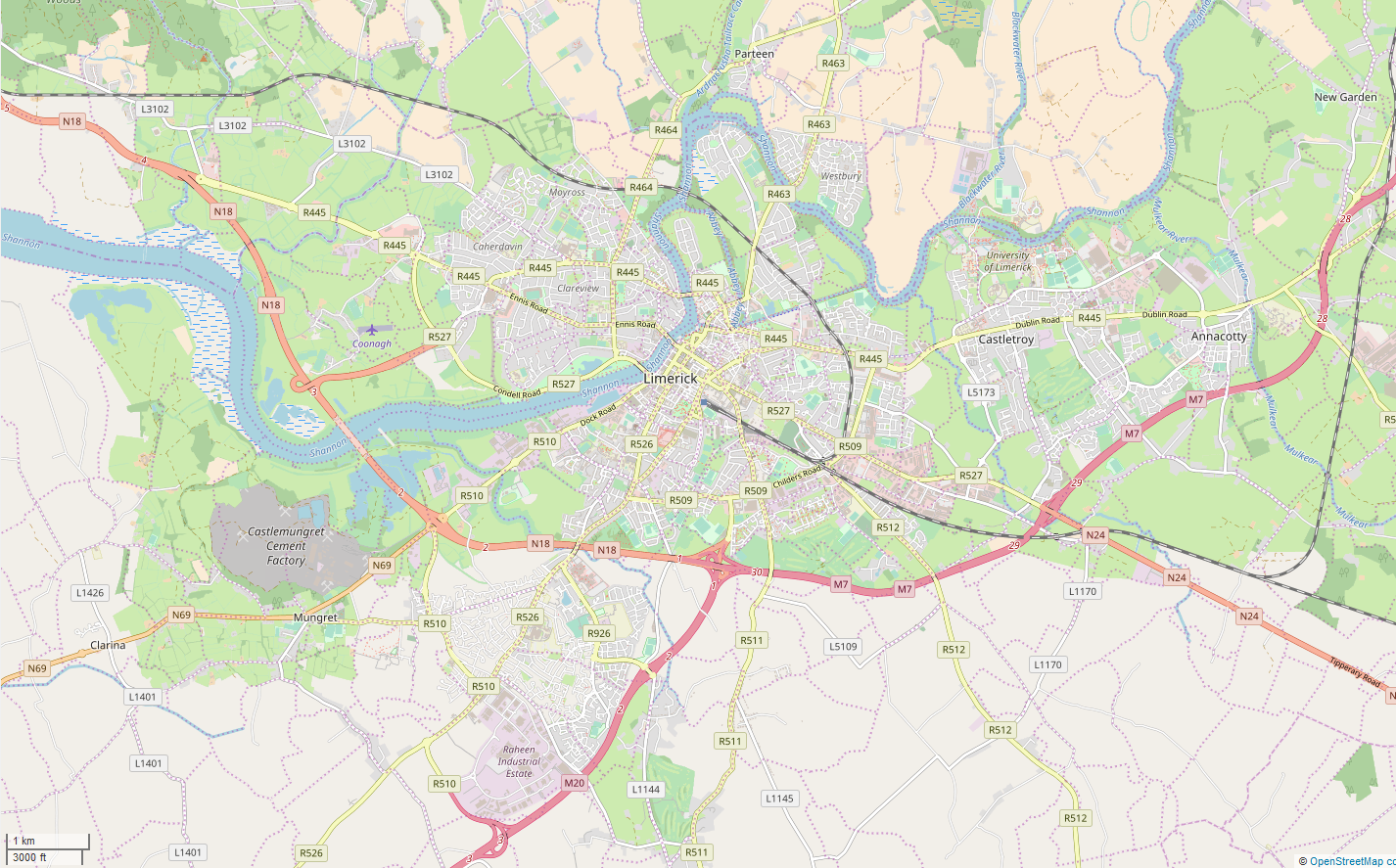
Limerick
Limerick ( ; ga, Luimneach ) is a western city in Ireland situated within County Limerick. It is in the province of Munster and is located in the Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region. With a population of 94,192 at the 2016 census, Limerick is the third-most populous urban area in the state, and the fourth-most populous city on the island of Ireland at the 2011 census. The city lies on the River Shannon, with the historic core of the city located on King's Island, which is bounded by the Shannon and Abbey Rivers. Limerick is also located at the head of the Shannon Estuary, where the river widens before it flows into the Atlantic Ocean. Limerick City and County Council is the local authority for the city. Geography and political subdivisions At the 2016 census, the Metropolitan District of Limerick had a population of 104,952. On 1 June 2014 following the merger of Limerick City and County Council, a new Metropolitan District of Limerick was formed wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest on Earth. Geopolitically, Ireland is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Ireland), which covers five-sixths of the island, and Northern Ireland, which is part of the United Kingdom. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million living in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landnámabók
(, "Book of Settlements"), often shortened to , is a medieval Icelandic written work which describes in considerable detail the settlement () of Iceland by the Norse in the 9th and 10th centuries CE. is divided into five parts and over 100 chapters. The first part tells of how the island was found. The latter parts count settlers quarter by quarter, beginning with west and ending with south. It traces important events and family history into the 12th century. More than 3,000 people and 1,400 settlements are described. It tells where each settler settled and provides a brief genealogy. Sometimes short anecdote-like stories are also included. lists 435 men (' or ) as the initial settlers, the majority of them settling in the northern and southwestern parts of the island. It remains an invaluable source on both the history and genealogy of the Icelandic people. Some have suggested a single author, while others have believed it to have been put together when people met at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JHU Press
The Johns Hopkins University Press (also referred to as JHU Press or JHUP) is the publishing division of Johns Hopkins University. It was founded in 1878 and is the oldest continuously running university press in the United States. The press publishes books and journals, and operates other divisions including fulfillment and electronic databases. Its headquarters are in Charles Village, Baltimore. In 2017, after the retirement of Kathleen Keane who is credited with modernizing JHU Press for the digital age, the university appointed new director Barbara Pope. Overview Daniel Coit Gilman, the first president of the Johns Hopkins University, inaugurated the press in 1878. The press began as the university's Publication Agency, publishing the '' American Journal of Mathematics'' in its first year and the '' American Chemical Journal'' in its second. It published its first book, ''Sidney Lanier: A Memorial Tribute'', in 1881 to honor the poet who was one of the university's first wri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Dee
John Dee (13 July 1527 – 1608 or 1609) was an English mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, teacher, occultist, and alchemist. He was the court astronomer for, and advisor to, Elizabeth I, and spent much of his time on alchemy, divination, and Hermetic philosophy. As an antiquarian, he had one of the largest libraries in England at the time. As a political advisor, he advocated the foundation of English colonies in the New World to form a " British Empire", a term he is credited with coining. Dee eventually left Elizabeth's service and went on a quest for additional knowledge in the deeper realms of the occult and supernatural. He aligned himself with several individuals who may have been charlatans, travelled through Europe and was accused of spying for the English crown. Upon his return to England, he found his home and library vandalised. He eventually returned to the Queen's service, but was turned away when she was succeeded by James I. He died in poverty in Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |