|
Granatenwerfer 16
The kleine Granatenwerfer 16 or Gr.W.16 ''(Small Grenade Launcher Model 1916)'' in English, was an infantry mortar used by the Central Powers during the First World War. It was designed by a Hungarian priest named Father Vécer and was first used by the Austro-Hungarian Army in 1915. In Austro-Hungarian service, they received the nickname "Priesterwerfers". In 1916 Germany began producing a modified version under license for the Imperial German Army. Background The majority of military planners before the First World War were wedded to the concept of fighting an offensive war of rapid maneuver which before mechanization meant a focus on cavalry and light horse artillery firing shrapnel shells at formations of troops in the open. The problem facing the combatants was that their light field guns were designed for direct fire and only had limited angles of elevation and were not capable of providing the high-angle indirect fire needed to deal with enemy troops in dug-in positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich or simply Germany, was the period of the German Reich; . from the unification of Germany in 1871 until the German revolution of 1918–1919, November Revolution in 1918, when the German Reich changed its form of government from a monarchy to a Weimar Republic, republic. The German Empire consisted of States of the German Empire, 25 states, each with its own nobility: four constituent Monarchy, kingdoms, six Grand duchy, grand duchies, five Duchy, duchies (six before 1876), seven Principality, principalities, three Free imperial city, free Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City-state, cities, and Alsace–Lorraine, one imperial territory. While Prussia was one of four kingdoms in the realm, it contained about two-thirds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
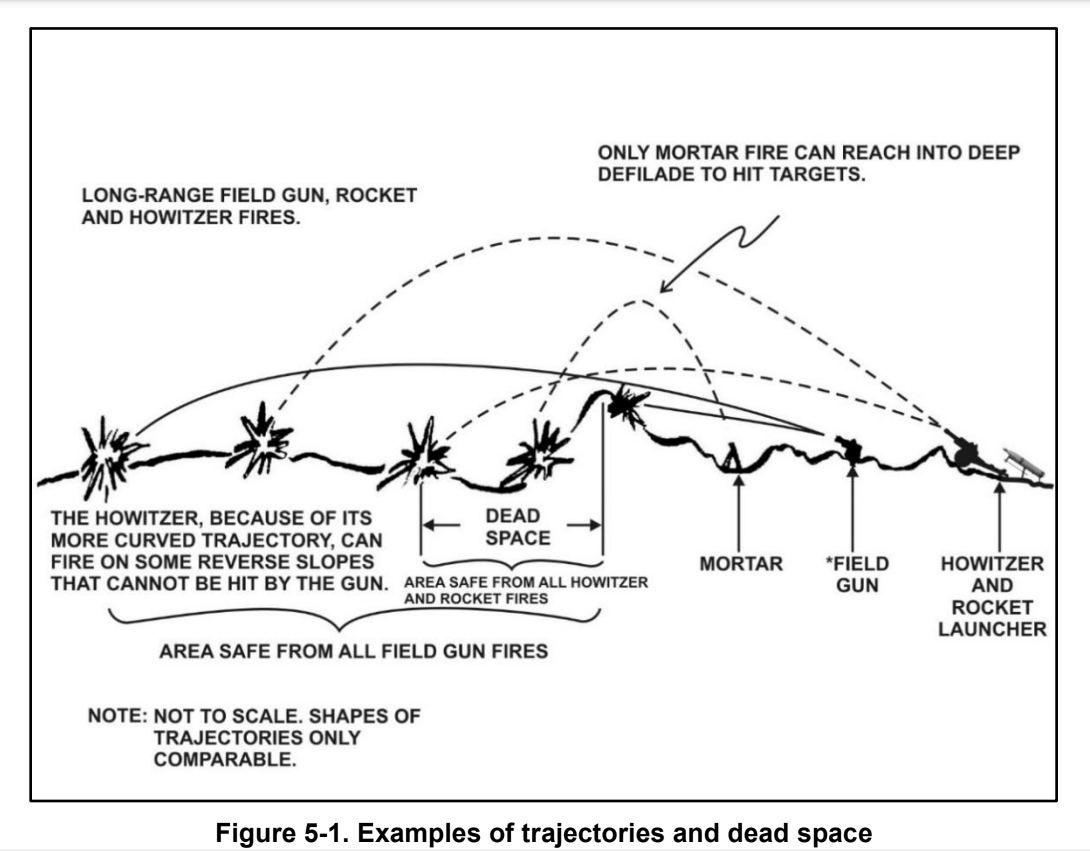
Indirect Fire
Indirect fire is aiming and firing a projectile without relying on a direct line of sight between the gun and its target, as in the case of direct fire. Aiming is performed by calculating azimuth and inclination, and may include correcting aim by observing the fall of shot and calculating new angles. Description Indirect fire is most commonly used by field artillery and mortars (although field artillery was originally and until after World War I a direct fire weapon, hence the bullet-shields fitted to the carriages of guns such as the famous M1897 75 mm). It is also used with missiles, howitzers, rocket artillery, multiple rocket launchers, cruise missiles, ballistic missiles, naval guns against shore targets, sometimes with machine guns, and has been used with tank and anti-tank guns and by anti-aircraft guns against surface targets. There are two dimensions in aiming a weapon: * In the horizontal plane (azimuth); and * In the vertical plane (elevation), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slingshot
A slingshot or catapult is a small hand-powered projectile weapon. The classic form consists of a Y-shaped frame, with two tubes or strips made from either a natural rubber or synthetic elastic material. These are attached to the upper two ends. The other ends of the strips lead back to a pouch that holds the projectile. One hand holds the frame, while the other hand grasps the pocket and draws it back to the desired extent to provide power for the projectile—up to a full span of the arms with sufficiently long bands. Other names include catapult (United Kingdom), peashooter (United States), gulel (India), (South Africa), or ging, shanghai, pachoonga (Australia and New Zealand) Use and history Slingshots depend on strong Elasticity (physics), elastic materials for their projectile firepower, typically vulcanization, vulcanized natural rubber or the equivalent such as silicone rubber tubing, and thus date no earlier than the invention of vulcanized rubber by Charles Goodyear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
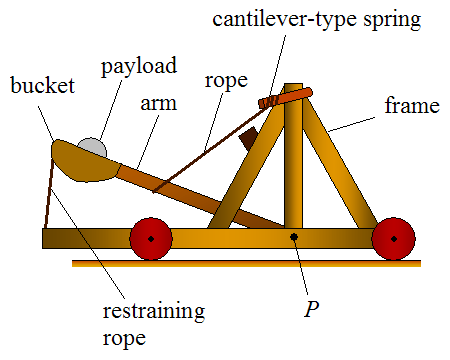
Catapult
A catapult is a ballistics, ballistic device used to launch a projectile at a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden release of stored potential energy to propel its payload. Most convert Tension (mechanics), tension or Torsion (mechanics), torsion energy that was more slowly and manually built up within the device before release, via springs, bows, twisted rope, elastic, or any of numerous other materials and mechanisms which allow the catapult to launch a projectile such as rocks, cannon balls, or debris. During wars in the ancient times, the catapult was usually known to be the strongest heavy weaponry. In modern times the term can apply to devices ranging from a simple hand-held implement (also called a "slingshot") to a mechanism for Aircraft catapult, launching aircraft from a ship. The earliest catapults date to at least the 7th century BC, with Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossbow
A crossbow is a ranged weapon using an Elasticity (physics), elastic launching device consisting of a Bow and arrow, bow-like assembly called a ''prod'', mounted horizontally on a main frame called a ''tiller'', which is hand-held in a similar fashion to the stock (firearms), stock of a long gun. Crossbows shoot arrow-like projectiles called ''crossbow bolt, bolts'' or ''quarrels''. A person who shoots crossbow is called a ''crossbowman'', an ''arbalister'' or an ''arbalist (crossbowman), arbalist'' (after the arbalest, a European crossbow variant used during the 12th century). Crossbows and bows use the same elastic launch principles, but differ in that an archer using a Bow and arrow, bow must draw-and-shoot in a quick and smooth motion with limited or no time for aiming, while a crossbow's design allows it to be spanned and cocked ready for use at a later time and thus affording them unlimited time to aim. When shooting bows, the archer must fully perform the bow draw, draw, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flamethrower
A flamethrower is a ranged incendiary device designed to project a controllable jet of fire. First deployed by the Byzantine Empire in the 7th century AD, flamethrowers saw use in modern times during World War I, and more widely in World War II as a tactical weapon against fortifications. Most military flamethrowers use liquid fuel, typically either heated oil or diesel, but commercial flamethrowers are generally blowtorches using gaseous fuels such as propane. Gases are safer in peacetime applications because their flames have less mass flow rate and dissipate faster and often are easier to extinguish. Apart from the military applications, flamethrowers have peacetime applications where there is a need for controlled burning, such as in sugarcane harvesting and other land-management tasks. Various forms are designed for an operator to carry, while others are mounted on vehicles. Military use Modern flamethrowers were first used during the trench warfare condition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grenade
A grenade is a small explosive weapon typically thrown by hand (also called hand grenade), but can also refer to a Shell (projectile), shell (explosive projectile) shot from the muzzle of a rifle (as a rifle grenade) or a grenade launcher. A modern hand grenade generally consists of an explosive charge ("filler"), a detonator mechanism, an internal Firing pin, striker to trigger the detonator, an arming safety secured by a transport safety. The user removes the transport safety before throwing, and once the grenade leaves the hand the arming safety gets released, allowing the striker to trigger a Percussion cap, primer that ignites a fuze (sometimes called the delay element), which burns down to the detonator and explodes the main charge. Grenades work by dispersing fragments (fragmentation grenades), shockwaves (High explosive, high-explosive, Anti-tank grenade, anti-tank and stun grenades), chemical aerosols (Smoke grenade, smoke, Grenade#Chemical and gas, gas and Grenade#Chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Shield
A U.S. Marine manning an M240 machine gun equipped with a gun shield A gun shield is a flat (or sometimes curved) piece of armor designed to be mounted on a crew-served weapon such as a machine gun, automatic grenade launcher, or artillery piece. Military Some mounted machine guns and artillery pieces are equipped with metal armor plates to protect the gunners from small arms fire and shrapnel from explosions. They were fitted to some armored fighting vehicles and patrol boats during the Vietnam War. Gun shields fell out of widespread use after the Vietnam War, but they have seen a resurgence in popularity during the 1980s and 1990s. Israeli military analysts began urging the use of gun shields, pointing to the grave risk to soldiers exposed to fire from automatic weapons. In particular, it was noted that many casualties were hit in areas not protected by body armor or a helmet, such as the neck or face. The United States Armed Forces began using gun shields in the earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corrugated Galvanised Iron
Corrugated galvanised iron (CGI) or steel, colloquially corrugated iron (near universal), wriggly tin (taken from UK military slang), pailing (in Caribbean English), corrugated sheet metal (in North America), zinc (in Cyprus and Nigeria) or custom orb / corro sheet (Australia), is a building material composed of sheets of hot-dip galvanizing, hot-dip galvanised mild steel, cold forming, cold-rolled to produce a linear ridged pattern in them. Although it is still popularly called "iron" in the UK, the material used is actually steel (which is iron alloyed with carbon for strength, commonly 0.3% carbon), and only the surviving vintage sheets may actually be made up of 100% iron. The corrugations increase the bending strength of the sheet in the direction perpendicular to the corrugations, but not parallel to them, because the steel must be stretched to bend perpendicular to the corrugations. Normally each sheet is manufactured longer in its strong direction. CGI is lightweight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trench Warfare
Trench warfare is a type of land warfare using occupied lines largely comprising Trench#Military engineering, military trenches, in which combatants are well-protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from artillery. It became archetypically associated with World War I (1914–1918), when the Race to the Sea rapidly expanded trench use on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front starting in September 1914.. Trench warfare proliferated when a Weapons of World War I, revolution in firepower was not matched by similar advances in mobility (military), mobility, resulting in a grueling form of warfare in which the defender held the advantage. On the Western Front in 1914–1918, both sides constructed elaborate trench, underground, and dugout (shelter), dugout systems opposing each other along a front (military), front, protected from assault by barbed wire. The area between opposing trench lines (known as "no man's land") was fully exposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (World War I)
The Western Front was one of the main Theatre (warfare), theatres of war during World War I. Following the outbreak of war in August 1914, the Imperial German Army, German Army opened the Western Front by German invasion of Belgium (1914), invading Luxembourg and Belgium, then gaining military control of important industrial regions in Third Republic of France, France. The German advance was halted with the First Battle of the Marne, Battle of the Marne. Following the Race to the Sea, both sides dug in along a meandering line of fortified trench warfare, trenches, stretching from the North Sea to the Swiss frontier with France, the position of which changed little except during early 1917 and again in 1918. Between 1915 and 1917 there were several offensives along this Front (military), front. The attacks employed massive artillery bombardments and massed infantry advances. Entrenchments, machine gun emplacements, barbed wire, and artillery repeatedly inflicted severe casualties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |