|
Gran Colombia–Peru War
The Gran Colombian–Peruvian War () of 1828 and 1829 was the first international conflict fought by the Republic of Peru, which had gained its independence from Spain in 1821, and Gran Colombia, that existed between 1819 and 1830. Causes The issues that led to war were Gran Colombian claims, dating from colonial times, concerning control of the territories of Jaén and Maynas. The Royal Audience of Quito () was established in 1563 by a royal decree of the King of Spain. Its territories included, to the north, Pasto, Popayán, Cali, Buenaventura, and Buga in what is now Colombia. The Royal Audience of Quito was initially part of the Viceroyalty of Peru until 1717, when it became part of the Viceroyalty of New Granada. Borders at the time were imprecise, especially in the eastern unsettled areas, beyond the Andean cordillera, because of a lack of geographical knowledge and the low importance accorded to these unpopulated and largely inaccessible territories. The first c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombian–Peruvian Territorial Dispute
The Colombian–Peruvian territorial dispute was a territorial dispute between Colombia and Peru, which, until 1916, also included Ecuador.Ecuador and Colombia signed the Muñoz Vernaza-Suárez Treaty in 1916, ending their dispute. The dispute had its origins on each country's interpretation of what ''Real Cédula, Real Cedulas'' Spain used to precisely define its possessions in the Americas. After Spanish American wars of independence, independence, all of Spain's former territories signed and agreed to proclaim their limits in the basis of the principle of ''uti possidetis juris'', which regarded the Spanish borders of 1810 as the borders of the new republics. However, conflicting claims and disagreements between the newly formed countries eventually escalated to the point of armed conflicts on several occasions. The dispute between both states ended in the aftermath of the Colombia–Peru War, which led to the signing of the Rio Protocol (1934), Rio Protocol two years later, fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan José Flores
Juan José Flores y Aramburu (19 July 1800 – 1 October 1864) was a Venezuelan-born military general who became the first (in 1830), third (in 1839) and fourth (in 1843) President of the new Republic of Ecuador. He is often referred to as "The Founder of the Republic".Villalba, Jorge FEl General Juan José Flores, Fundador de la República del Ecuador, 1993 Character Juan José Flores' contemporaries described his physical appearance as a proud man in military uniform, slender and short but well proportioned, with a handsome countenance that radiates quick intelligence and a commanding presence. Juan José Flores appeared to be self-taught, and despite his scant rudimentary education, he became an eloquent orator and an avid reader of contemporary authors such as Rousseau, Montesquieu, Holbach, and Vattel. Juan José Flores was so fascinated with reading that in 1826 he asked for and received a shipment of books from General Santander, then vice-president of the Gran Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasto (Colombia)
Pasto, officially San Juan de Pasto (; "Saint John of Pasto"), is the capital of the department of Nariño, in southern Colombia. Pasto was founded in 1537 and named after indigenous people of the area. In the 2018 census, the municipality had a population of 392,930. Pasto is located in the Atriz Valley on the Andes cordillera, at the foot of the Galeras volcano. History The etymology of the word ''Pasto'' can be traced to the indigenous people who inhabited the region at the arrival of the Spanish conquerors, the Pastos. However, the Atriz Valley itself was inhabited by the Quillacingas. In the 2018 Colombian census, 163,873 people self-identified as Pasto, and in the 2010 Ecuadorian census, 1,409 people self-identified as Pasto. Pasto was founded in 1537 by the Spanish conquistador Sebastián de Belalcázar. In 1539 Lorenzo de Aldana, also a Spanish conquistador, moved the city to its current location, and established it under the name "San Juan de Pasto". A majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Audience Of Quito
The of Quito (sometimes referred to as or ) was an administrative unit in the Spanish Empire which had political, military, and religious jurisdiction over territories that today include Ecuador, parts of northern Peru, parts of southern Colombia and parts of northern Brazil. It was created by Royal Decree on 29 August 1563 by Philip II of Spain in the city of Guadalajara. It ended in 1822 with the incorporation of the area into the Republic of Gran Colombia. Structure The 1563 decree established its structure and district: In the City of San Francisco of El Quito, in Peru, shall reside another Royal ''Audiencia'' and Chancellery of ours, with a president; four judges of civil cases 'oidores'' who will also be judges of criminal cases 'alcaldes del crimen'' a crown attorney 'fiscal'' a bailiff 'alguacil mayor'' a lieutenant of the Gran Chancellor; and the other necessary ministers and officials; and which shall have for district the Province of Quito, and along the coast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaén, Peru
Jaén (), founded as San Leandro de Jaén and then known as Jerez de la Frontera (later Nueva Jerez de la Frontera) and finally as Jaén de Bracamoros since April 1549, is a city which is the capital of the Jaén Province in the Cajamarca Region in Peru, located in the high jungle of northern Peru. It is the seat of the Catholic Apostolic Vicariate of St. Francis Xavier, also known as Apostolic Vicariate of Jaén en Peru. Geography Climate Jaen has a warm climate all year round. It is one of the warmest cities in Peru, but does have frequent and refreshing showers. Culture Jaén is also known as Land of the Brave Bracamoros. Evidence of their culture is located at ''Hermogenes Mejía Solf Museum'', located in the same city. History Early inhabitants The origin of the city dates back to the Late Horizon period, between 1,000 and 1,500 B.C, larger settlements were located in the valleys of the present provinces of Jaén, Bagua and San Ignacio. In the valley of Jaén there li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. Peru is a Megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, with habitats ranging from the arid plains of the Pacific coastal region in the west, to the peaks of the Andes mountains extending from the north to the southeast of the country, to the tropical Amazon basin rainforest in the east with the Amazon River. Peru has Demographics of Peru, a population of over 32 million, and its capital and largest city is Lima. At , Peru is the List of countries and dependencies by area, 19th largest country in the world, and the List of South American countries by area, third largest in South America. Pre-Columbian Peru, Peruvian territory was home to Andean civilizations, several cultures during the ancient and medieval periods, and has one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peruvian Navy
The Peruvian Navy (, abbreviated MGP) is the branch of the Peruvian Military of Peru, Armed Forces tasked with surveillance, patrol and defense on lakes, rivers and the Pacific Ocean up to from the Peruvian littoral. Additional missions include assistance in safeguarding internal security, conducting emergency management, disaster relief operations and participating in international peacekeeping operations. The ''Marina de Guerra del Perú'' celebrates the anniversary of its creation in 1821 on October 8 and also commemorates the decisive Battle of Angamos, the final part of the naval campaign of the War of the Pacific between Peru and Chile at the end of 1879. History 19th century The ''Marina de Guerra del Perú'' was established on 8 October 1821 by the government of general José de San Martín. Its first actions were undertaken during the History of Peru#Wars of independence (1811–1824), War of Independence (1821–1824) using captured Spanish warships. The Peruvian Nav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
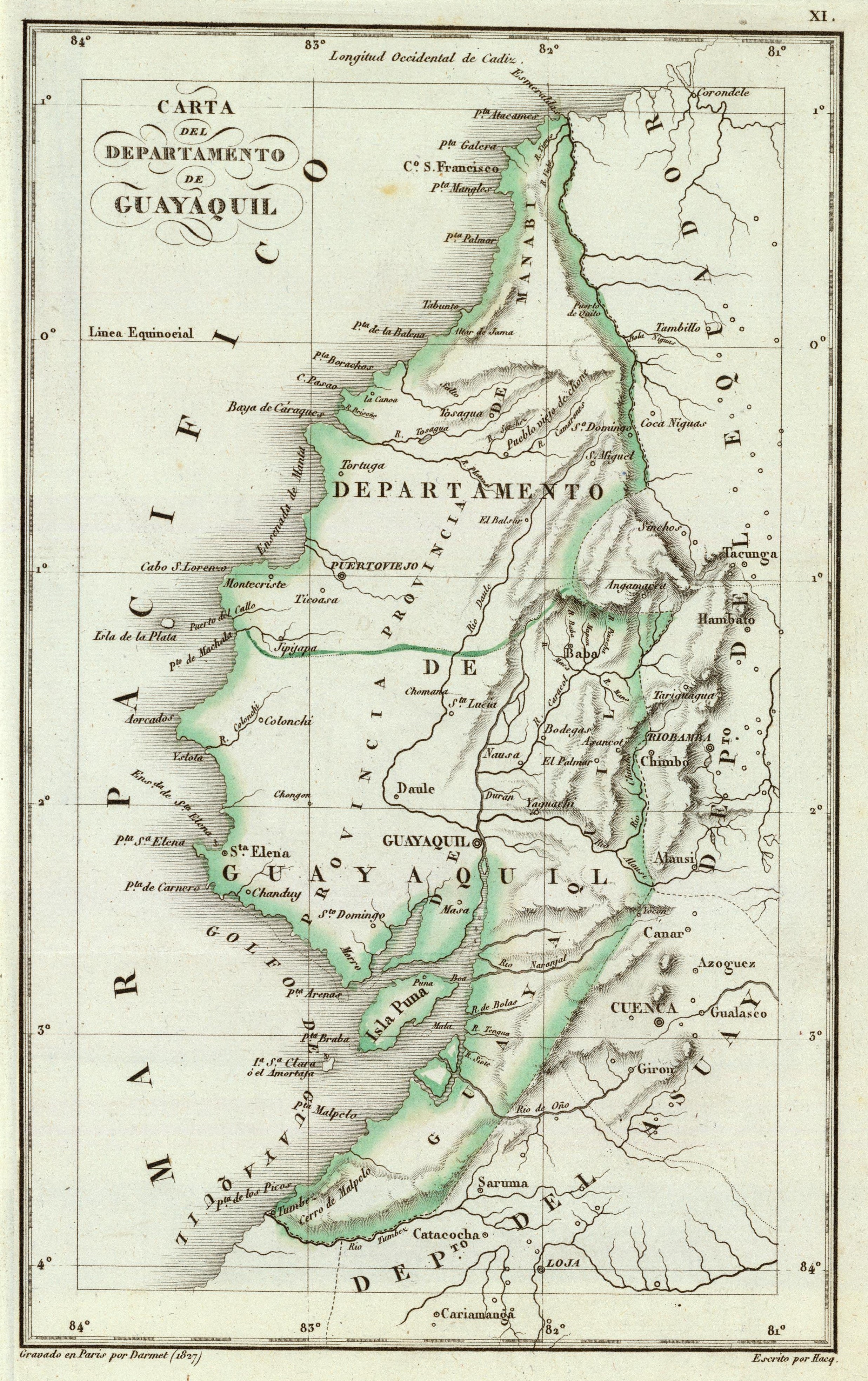
Guayaquil
Guayaquil (), officially Santiago de Guayaquil, is the largest city in Ecuador and also the nation's economic capital and main port. The city is the capital (political), capital of Guayas Province and the seat of Guayaquil Canton. The city is located on the west bank of the Guayas River, which flows into the Pacific Ocean at the Gulf of Guayaquil. With a population of 2,746,403 inhabitants, it is the most populous city in the country, and the fifth largest in the Andean Community. However, its urban fabric extends beyond its official urban parishes, encompassing nearby cities and parishes; thus, the Guayaquil metropolitan area reaches a population of 3,618,450, making it the most populous urban agglomeration in the nation, and also the fifth in the Andean Community. As the largest city, it is one of the two main development poles of the country—alongside Quito, the national capital—hosting Ecuador’s main business, financial, cultural, and sports institutions. After seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peruvian Army
The Peruvian Army (, abbreviated EP) is the branch of the Peruvian Armed Forces tasked with safeguarding the independence, sovereignty and integrity of national territory on land through military force. Additional missions include assistance in safeguarding internal security, conducting emergency management, disaster relief operations and participating in international peacekeeping operations. It celebrates the anniversary of the Battle of Ayacucho (1824) on December 9. History Military traditions in Peruvian territory go back to prehispanic times, ranging from small armed bands to the large armies assembled by the Inca Empire. After the Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire, Spanish conquest, small garrisons were kept at strategic locations but no standing army existed until the Bourbon reforms of the 18th century. The main purpose of this force was the defense of the Viceroyalty of Peru, Viceroyalty from pirates and Privateer, corsairs as well as internal rebellions. Independence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombian Navy
The Colombian Navy, officially the Colombian National Navy (), also known as the ''"Armada Nacional"'' or just the ''"Armada"'' in Spanish, is the naval branch of the Military Forces of Colombia, military forces of Colombia. The Navy is responsible for security and defence in the Colombian zones of both the Atlantic (Caribbean) and Pacific oceans, the extensive network of rivers inside the country, and a few small land areas under its direct jurisdiction. The Colombian Navy has a strength of 35,086 personnel including approximately 22,000 in the Marine Infantry corps. The acronym "ARC", () is used both as the official ship prefix for all the Colombian Navy ships, as well as a common short name for the Navy itself. Mission ::''"Protecting the blue of our flag"'' As stated in its institutional site, the mission of the Colombian Navy is: “''Contribute with the defense of the Nation through the effective use of flexible naval power in the maritime, river and land spaces und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Legion
The Royal British Legion (RBL), formerly the British Legion, is a British Charitable organization, charity providing financial, social and emotional support to members and veterans of the British Armed Forces, their families and dependants. Membership Service in the armed forces is no longer a requirement of Legion membership. The Legion has an official membership magazine, ''Legion'', which is free to all Legion members as part of their annual subscription. History The British Legion was founded on 15 May 1921 as a voice for the Ex-servicemen, ex-service community as a bringing together of four organisations: the Comrades of the Great War, the National Association of Discharged Sailors and Soldiers and the National Federation of Discharged and Demobilised Sailors and Soldiers, and incorporated the fundraising department of the Officers' Association. Field Marshal (United Kingdom), Field Marshal Douglas Haig, 1st Earl Haig, The 1st Earl Haig (1861–1928), British comman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombian Army
The National Army of Colombia () is the land warfare service branch of the Military Forces of Colombia. With over 361,420 active personnel as of 2020, it is the largest and oldest service branch in Colombia, and is the second largest army in the Americas after the US Army, United States and before Brazilian Army, Brazil. It is headed by the Commandant of the National Army (), falls under the authority of the Commandant General of the Military Forces (), and is supervised by the Ministry of National Defense (Colombia), Ministry of National Defense, which answers to the President of Colombia. The modern Colombian Army has its roots in the Army of the Commoners (), which was formed on 7 August 1819 – before the establishment of the present day Colombia – to meet the demands of the Bolívar's campaign to liberate New Granada, Revolutionary War against the Spanish Empire. After their triumph against the Spanish, the Army of the Commoners disbanded, and the Congress of Angostura c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |