|
Grammatischer Wechsel
In historical linguistics, the German term ' ("grammatical alternation") refers to the effects of Verner's law when they are viewed synchronically within the paradigm of a Germanic verb. Overview According to Grimm's law, the Proto-Indo-European (PIE) voiceless stops ''*p'', ''*t'', ''*k'' and ''*kʷ'' usually became Proto-Germanic ''*f'', ''*θ'' (dental fricative), ''*x'' and ''*xʷ'' (velar fricative). Karl Verner identified the principle that they instead become the voiced consonants ''*b'', ''*d'', ''*g'', ''*gʷ'' if they were word-internal and immediately preceded by an unaccented vowel in PIE. Furthermore, PIE ''*s'', which usually came into Germanic unchanged, became ''*z'' in this position; this ''*z'' later became North and West Germanic ''*r''. Consequently, five pairs of consonants emerged, each pair representing a single PIE phoneme. The following table shows the precise developments from Proto-Indo-European through Proto-Germanic to Old Norse, West Germanic, Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Linguistics
Historical linguistics, also known as diachronic linguistics, is the scientific study of how languages change over time. It seeks to understand the nature and causes of linguistic change and to trace the evolution of languages. Historical linguistics involves several key areas of study, including the reconstruction of ancestral languages, the classification of languages into families, ( comparative linguistics) and the analysis of the cultural and social influences on language development. This field is grounded in the uniformitarian principle, which posits that the processes of language change observed today were also at work in the past, unless there is clear evidence to suggest otherwise. Historical linguists aim to describe and explain changes in individual languages, explore the history of speech communities, and study the origins and meanings of words ( etymology). Development Modern historical linguistics dates to the late 18th century, having originally grown o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature dates from the mid-7th century. After the Norman Conquest of 1066, English was replaced for several centuries by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oïl, type of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during the subsequent period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into what is now known as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles (tribe), Angles, Saxons and Jutes. As the Germanic settlers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
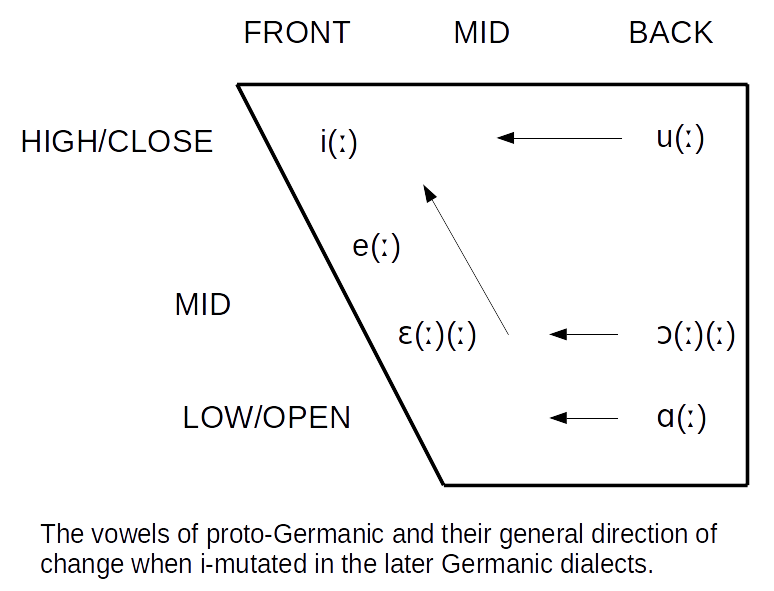
Germanic Umlaut
The Germanic umlaut (sometimes called i-umlaut or i-mutation) is a type of linguistic umlaut (linguistics), umlaut in which a back vowel changes to the associated front vowel (fronting (phonology), fronting) or a front vowel becomes closer to (raising (phonetics), raising) when the following syllable contains , , or . It took place separately in various Germanic languages starting around 450 or 500 Common Era, CE and affected all of the early languages except Gothic language, Gothic. An example of the resulting vowel alternation is the English plural ''foot ~ feet'' (from Proto-Germanic , pl. ). Germanic umlaut, as covered in this article, does not include other historical vowel phenomena that operated in the history of the Germanic languages such as Germanic a-mutation and the various language-specific processes of u-mutation (other), u-mutation, nor the earlier Indo-European ablaut (''vowel gradation''), which is observable in the conjugation of Germanic strong ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternation (linguistics)
In linguistics, an alternation is the phenomenon of a morpheme exhibiting variation in its phonological realization. Each of the various realizations is called an alternant. The variation may be conditioned by the phonological, morphological, and/or syntactic environment in which the morpheme finds itself. Alternations provide linguists with data that allow them to determine the allophones and allomorphs of a language's phonemes and morphemes and to develop analyses determining the distribution of those allophones and allomorphs. The term "sound change" refers to diachronic changes, which occur in a language's sound system. On the other hand, "alternation" refers to changes that happen synchronically (within the language of an individual speaker, depending on the neighbouring sounds) and do not change the language's underlying system. Phonologically conditioned alternation An example of a phonologically conditioned alternation is the English plural marker commonly spel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhotacism (sound Change)
Rhotacism ( ) or rhotacization is a sound change that converts one consonant (usually a voiced alveolar consonant: , , , or ) to a rhotic consonant in a certain environment. The most common may be of to . When a dialect or member of a language family resists the change and keeps a sound, this is sometimes known as ''zetacism''. The term comes from the Greek letter ''rho'', denoting . Albanian The southern ( Tosk) dialects, the base of Standard Albanian, changed to , but the northern ( Gheg) dialects did not: * vs. 'the voice' * vs. 'the knee' * vs. 'Albania' * vs. 'Albania' (older name of the country) * vs. 'burnt' * vs. 'wood' * vs. 'did' * vs. 'caught' * vs. 'dust' * vs. 'love' Aramaic In Aramaic, Proto-Semitic ''n'' changed to ''r'' in a few words: * ''bar'' "son" as compared to Hebrew בֵן ''ben'' (from Proto-Semitic *''bnu'') * ''trên'' and ''tartên'' "two" (masculine and feminine form respectively) as compared to Demotic Arabic ''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preterite
The preterite or preterit ( ; abbreviated or ) is a grammatical tense or verb form serving to denote events that took place or were completed in the past; in some languages, such as Spanish, French, and English, it is equivalent to the simple past tense. In general, it combines the perfective aspect (event viewed as a single whole; it is not to be confused with the similarly named perfect) with the past tense and may thus also be termed the ''perfective past''. In grammars of particular languages the preterite is sometimes called the ''past historic'', or (particularly in the Greek grammatical tradition) the '' aorist''. When the term "preterite" is used in relation to specific languages, it may not correspond precisely to this definition. In English it can be used to refer to the simple past verb form, which sometimes (but not always) expresses perfective aspect. The case of German is similar: the ''Präteritum'' is the simple (non-compound) past tense, which does not always ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Language
Gothic is an extinct language, extinct East Germanic languages, East Germanic language that was spoken by the Goths. It is known primarily from the ''Codex Argenteus'', a 6th-century copy of a 4th-century Bible translation, and is the only East Germanic language with a sizeable text corpus. All others, including Burgundian language (Germanic), Burgundian and Vandalic language, Vandalic, are known, if at all, only from proper names that survived in historical accounts, and from loanwords in other, mainly Romance languages, Romance, languages. As a Germanic language, Gothic is a part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is the earliest Germanic language that is attested in any sizable texts, but it lacks any modern descendants. The oldest documents in Gothic date back to the fourth century. The language was in decline by the mid-sixth century, partly because of the military defeat of the Goths at the hands of the Franks, the elimination of the Goths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradigm Levelling
In linguistics, morphological leveling or paradigm leveling is the generalization of an inflection across a linguistic paradigm, a group of forms with the same stem in which each form corresponds in usage to different syntactic environments, or between words. The result of such leveling is a paradigm that is less varied, having fewer forms. When a language becomes less synthetic, it is often a matter of morphological leveling. An example is the conjugation of English verbs, which has become almost unchanging today (see also null morpheme), thus contrasting sharply, for example, with Latin, in which one verb has dozens of forms, each one expressing a different tense, aspect, mood, voice, person, and number. For instance, English ''sing'' has only two forms in the present tense (I/you/we/they ''sing'' and he/she ''sings''), but its Latin equivalent has six: one for each combination of person and number. Types There are two types of paradigm leveling. Paradigm internal levelin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Strong Verb
In the Germanic languages, a strong verb is a verb that marks its past tense by means of Indo-European ablaut, changes to the stem vowel. A minority of verbs in any Germanic language are strong; the majority are ''Germanic weak verb, weak verbs'', which form the past tense by means of a dental consonant, dental suffix. In modern English, strong verbs include ''sing'' (present ''I sing'', simple past, past ''I sang'', past participle ''I have sung'') and ''drive'' (present ''I drive'', past ''I drove'', past participle ''I have driven''), as opposed to weak verbs such as ''open'' (present ''I open'', past ''I opened'', past participle ''I have opened''). Not all verbs with a change in the stem vowel are strong verbs, however: they may also be irregular weak verbs such as ''bring, brought, brought'' or ''keep, kept, kept''. The key distinction is that the system of strong verbs has its origin in the earliest sound system of Proto-Indo-European, whereas weak verbs use a dental ending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Weak Verb
In the Germanic languages, weak verbs are by far the largest group of verbs, and are therefore often regarded as the norm (the regular verbs). They are distinguished from the Germanic strong verbs by the fact that their past tense form is marked by an inflection containing a , , or sound (as in English ''I walk~I walked'') rather than by changing the verb's root vowel (as in English ''I rise~I rose''). Whereas the strong verbs are the oldest group of verbs in Germanic, originating in Indo-European, the weak verbs arose as an innovation in proto-Germanic. Originally the weak verbs consisted of new verbs coined from pre-existing nouns (for example the noun ''name'' was turned into the verb ''to name''), or coined from strong verbs to express the sense of causing the action denoted by that strong verb (for example the strong verb ''to rise'' was turned into the weak verb ''to raise''). However, over time, the weak verbs have become the normal form of verbs in all Germanic languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athematic
In Indo-European studies, a thematic vowel or theme vowel is the vowel or from Indo-European ablaut, ablaut placed before the Suffix#Inflectional suffixes, ending of a Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European (PIE) word. Nouns, adjectives, and verbs in the Indo-European languages with this vowel are thematic, and those without it are athematic. Used more generally, a thematic vowel is any vowel found at the end of the word stem, stem of a word. Outside Indo-European, the term "thematic vowel" is also used in the grammar of Kartvelian languages (see Georgian verb paradigm for more information on thematic vowels). Proto-Indo-European Proto-Indo-European verbs, PIE verbs and Proto-Indo-European nominals, nominals (nouns and adjectives) consist of three parts: :\underbrace_ The thematic vowel, if present, occurs at the end of the suffix (which may include other vowels or consonants) and before the ending: * 'heat' > Ancient Greek (''thérmos'') * '(he) bears' > Sanskri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High German Consonant Shift
In historical linguistics, the High German consonant shift or second Germanic consonant shift is a phonological development (sound change) that took place in the southern parts of the West Germanic languages, West Germanic dialect continuum. The shift is used to distinguish High German from other continental West Germanic languages, namely Low Franconian (including standard Dutch language, Dutch) and Low German, which experienced no shift. The shift resulted in the affrication or spirantization of the West Germanic voiceless stop consonants /t/, /p/, and /k/, depending on position in a word. A related change, the devoicing of the voiced stopped consonants /d/, /b/ and /g/, was less widespread, with only the devoicing of /d/ being found in most dialects. There is no consensus on when the High German consonant shift occurred; it probably began between the 3rd and 5th centuries and was complete before the first written examples in Old High German, the earliest recorded stage of High ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |