|
Graft-versus-host Disease
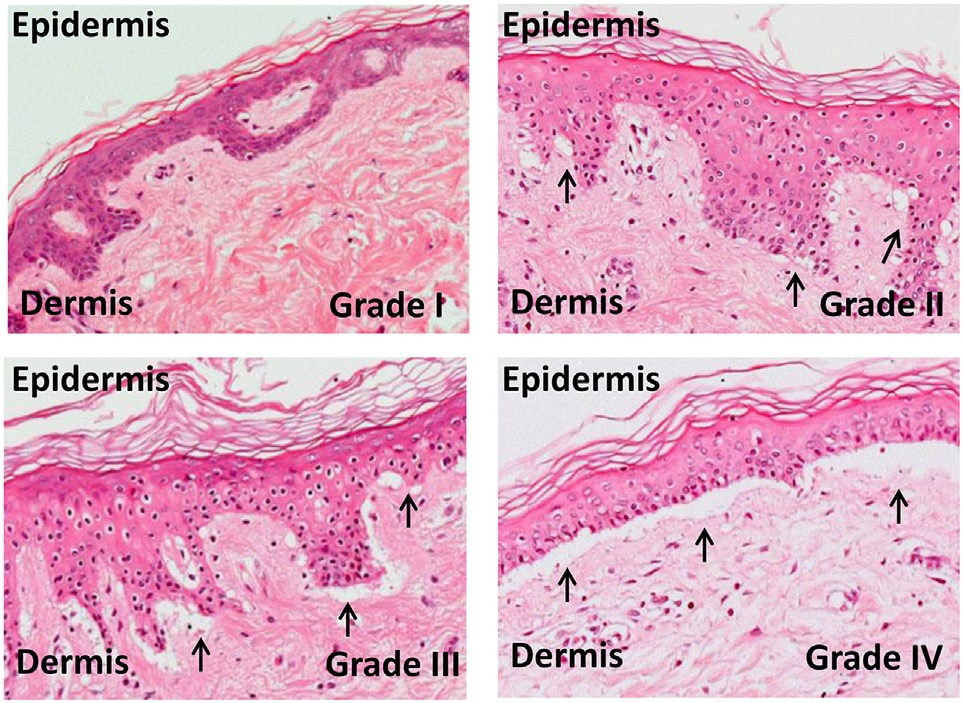
Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is a syndrome, characterized by inflammation in different organs. GvHD is commonly associated with bone marrow transplants and stem cell transplants. White blood cells of the donor's immune system which remain within the donated tissue (the graft) recognize the recipient (the host) as foreign (non-self). The white blood cells present within the transplanted tissue then attack the recipient's body's cells, which leads to GvHD. This should not be confused with a transplant rejection, which occurs when the immune system of the transplant recipient rejects the transplanted tissue; GvHD occurs when the donor's immune system's white blood cells reject the recipient. The underlying principle ( alloimmunity) is the same, but the details and course may differ. GvHD can also occur after a blood transfusion, known as ''Transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease'' or TA-GvHD if the blood products used have not been gamma irradiated or treated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndrome
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek language, Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a syndrome is paired with a definite cause this becomes a disease. In some instances, a syndrome is so closely linked with a pathogenesis or cause that disease#Terminology, the words ''syndrome'', ''disease'', and ''disorder'' end up being used interchangeably for them. This substitution of terminology often confuses the reality and meaning of medical diagnoses. This is especially true of heredity, inherited syndromes. About one third of all phenotypes that are listed in Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM are described as dysmorphic, which usually refers to the facial gestalt. For example, Down syndrome, Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome, and Andersen–Tawil syndrome are disorders with known pathogeneses, so each is more than just a set of sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (; ; also hematopoiesis in American English, sometimes h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult human, roughly ten billion () to a hundred billion () new blood cells are produced per day, in order to maintain steady state levels in the peripheral circulation.Semester 4 medical lectures at Uppsala University 2008 by Leif Jansson Process Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) reside in the medulla of the bone ( bone marrow) and have the unique ability to give rise to all of the different mature blood cell types and tissues. HSCs are self-renewing cells: when they differentiate, at least some of their daughter cells remain as HSCs so the pool of stem cells is not depleted. This phenomenon is called asymmetric division. The other daughters of HSCs ( myeloid and lymphoid progenitor cells) can follow any of the other diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Leukocyte Antigens
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans that encode cell-surface proteins responsible for regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) found in many animals. Mutations in HLA genes may be linked to autoimmune diseases such as type I diabetes, and celiac disease. The HLA gene complex resides on a 3 Mbp stretch within chromosome 6, p-arm at 21.3. HLA genes are highly polymorphic, which means that they have many different alleles, allowing them to fine-tune the adaptive immune system. The proteins encoded by certain genes are also known as ''antigens'', as a result of their historic discovery as factors in organ transplants. HLAs corresponding to MHC class I ( A, B, and C), all of which are the HLA Class1 group, present peptides from inside the cell. For example, if the cell is infected by a virus, the HLA system brings fragments of the viru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce additional normal blood cells. HSCT may be autologous (the patient's own stem cells are used), syngeneic (stem cells from an identical twin), or allogeneic (stem cells from a donor). It is most often performed for patients with certain cancers of the blood or bone marrow, such as multiple myeloma, leukemia, some types of lymphoma and immune deficiencies. In these cases, the recipient's immune system is usually suppressed with radiation or chemotherapy before the transplantation. Infection and graft-versus-host disease are major complications of allogeneic HSCT. HSCT remains a dangerous procedure with many possible complications; it is reserved for patients with life-threatening diseases. As survival following the procedure ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Intercourse
Sexual intercourse (also coitus or copulation) is a sexual activity typically involving the insertion of the Erection, erect male Human penis, penis inside the female vagina and followed by Pelvic thrust, thrusting motions for sexual pleasure, sexual reproduction, reproduction, or both.Sexual intercourse most commonly means penile–vaginal penetration for sexual pleasure or sexual reproduction; dictionary sources state that it especially means this, and scholarly sources over the years agree. See, for example; * * * * * * * * This is also known as vaginal intercourse or vaginal sex. Sexual penetration is an instinctive form of sexual behaviour and psychology among humans. Other forms of sexual penetration, penetrative sexual intercourse include anal sex (penetration of the Human anus, anus by the penis), oral sex (penetration of the mouth by the penis or oral penetration of the female genitalia), Fingering (sexual act), fingering (sexual penetration by the fingers) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scarring
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a natural part of the healing process. With the exception of very minor lesions, every wound (e.g., after accident, disease, or surgery) results in some degree of scarring. An exception to this are animals with complete regeneration, which regrow tissue without scar formation. Scar tissue is composed of the same protein (collagen) as the tissue that it replaces, but the fiber composition of the protein is different; instead of a random basketweave formation of the collagen fibers found in normal tissue, in fibrosis the collagen cross-links and forms a pronounced alignment in a single direction. This collagen scar tissue alignment is usually of inferior functional quality to the normal collagen randomised alignment. For example, scars in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage." Pain motivates organisms to withdraw from damaging situations, to protect a damaged body part while it heals, and to avoid similar experiences in the future. Congenital insensitivity to pain may result in reduced life expectancy. Most pain resolves once the noxious stimulus is removed and the body has healed, but it may persist despite removal of the stimulus and apparent healing of the body. Sometimes pain arises in the absence of any detectable stimulus, damage or disease. Pain is the most common reason for physician consultation in most developed countries. It is a major symptom in many medical conditions, and can interfere with a person's quality of life and general fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vaginal opening and hymen, vaginal introitus is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucous membrane, mucosal tissue called the hymen. The vagina allows for Copulation (zoology), copulation and birth. It also channels Menstruation (mammal), menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. To accommodate smoother penetration of the vagina during sexual intercourse or other sexual activity, vaginal moisture increases during sexual arousal in human females and other female mammals. This increase in moisture provides vaginal lubrication, which reduces friction. The texture of the vaginal walls creates friction for the penis during sexual intercourse and stimulates it toward ejaculation, en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exocrine Glands
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of two types of glands in the human body, the other being endocrine glands, which secrete their products directly into the bloodstream. The liver and pancreas are both exocrine and endocrine glands; they are exocrine glands because they secrete products—bile and pancreatic juice—into the gastrointestinal tract through a series of ducts, and endocrine because they secrete other substances directly into the bloodstream. Exocrine sweat glands are part of the integumentary system; they have eccrine and apocrine types. Classification Structure Exocrine glands contain a glandular portion and a duct portion, the structures of which can be used to classify the gland. * The duct portion may be branched (called compound) or unbranched (called sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesoderm, the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord, are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leukocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ) was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elafin
Elafin, also known as peptidase inhibitor 3 or skin-derived antileukoprotease (SKALP), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PI3'' gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei .... Function This gene encodes an elastase-specific protease inhibitor, which contains a WAP-type four-disulfide core (WFDC) domain, and is thus a member of the WFDC domain family. Most WFDC gene members are localized to chromosome 20q12-q13 in two clusters: centromeric and telomeric. This gene belongs to the centromeric cluster. Clinical significance Elafin has been found to have utility in serving as a biomarker for graft versus host disease of the skin. Elafin plays some role in gut inflammation. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and Shortness of breath, difficulty breathing. The severity of the condition is variable. Pneumonia is usually caused by infection with viruses or bacteria, and less commonly by other microorganisms. Identifying the responsible pathogen can be difficult. Diagnosis is often based on symptoms and physical examination. Chest X-rays, blood tests, and Microbiological culture, culture of the sputum may help confirm the diagnosis. The disease may be classified by where it was acquired, such as community- or hospital-acquired or healthcare-associated pneumonia. Risk factors for pneumonia include cystic fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), sickle cell disease, asthma, diabetes, heart failure, a history of smoking, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |