|
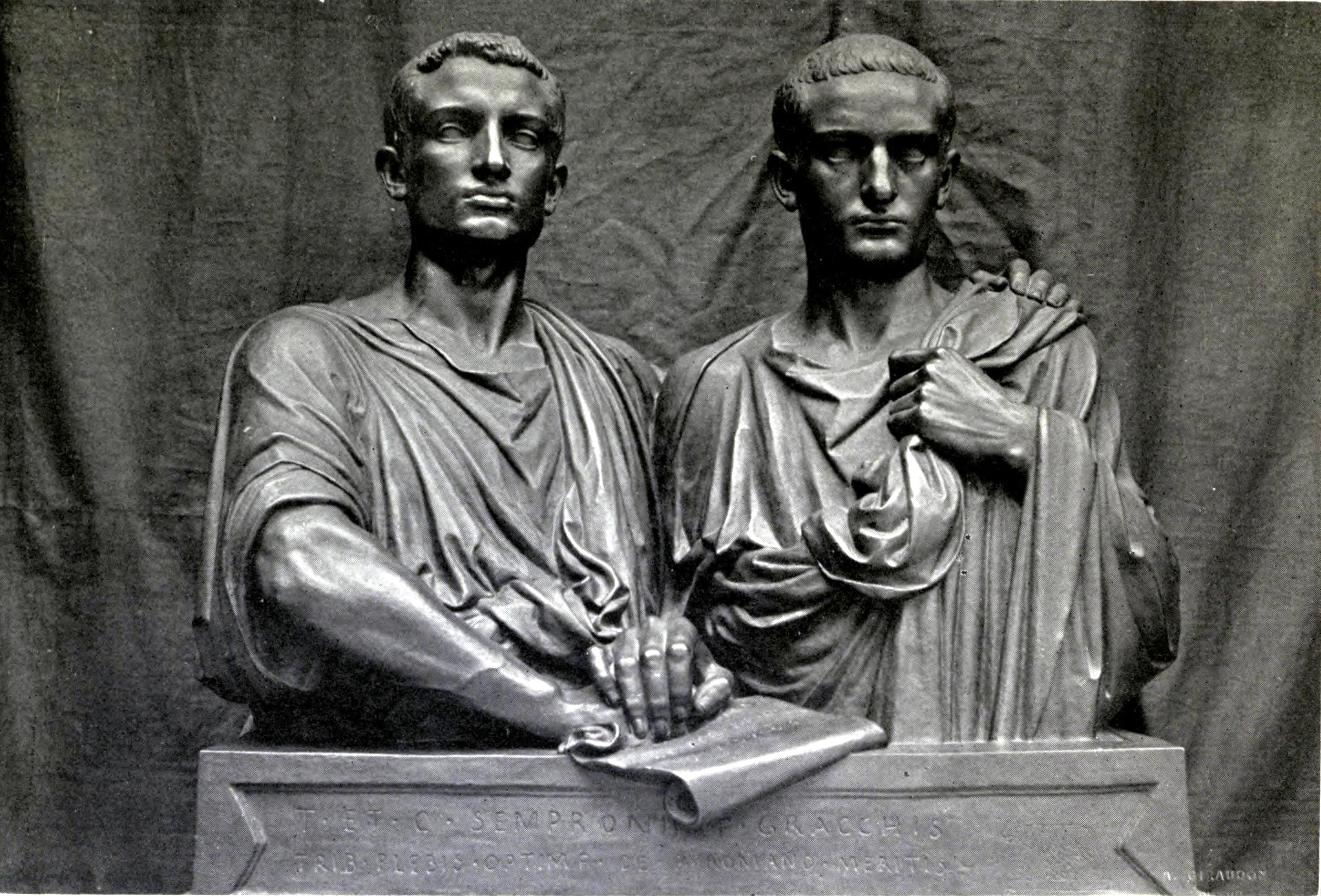
Gracchi
The Gracchi brothers were two brothers who lived during the beginning of the late Roman Republic: Tiberius Gracchus and Gaius Gracchus. They served in the Tribune of the plebs, plebeian tribunates of 133 BC and 122–121 BC, respectively. They have been received as well-born and eloquent advocates for social reform who were both killed by a reactionary political system; their terms in the tribunate precipitated a series of domestic crises which are viewed as unsettling the Roman Republic and contributing to its collapse. Tiberius Gracchus passed Lex agraria, legislation which established a commission to survey Ager publicus, Roman public land, reassert state claims to it, and redistribute it to poor rural farmers. These reforms were a reaction to a perceived decline in Italy's rural population. A decade later, Gaius Gracchus' reforms, among other things, attempted to buttress Tiberius' land commission and start Roman colonisation outside of Italy. They also were far ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornelia (mother Of The Gracchi)
Cornelia (c. 190s – c. 115 BC) was the second daughter of Scipio Africanus, Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus, a Roman general prominent in the Second Punic War, and Aemilia Paulla. Although drawing similarities to prototypical examples of virtuous Roman women, such as Lucretia, Cornelia puts herself apart from the rest because of her interest in literature, writing, and her investment in the political careers of her sons. She was the mother of the Gracchi, Gracchi brothers, and the mother-in-law of Scipio Aemilianus. Biography Cornelia married Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus (consul 177 BC), Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus, grandson of Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus (consul 238 BC), Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus, when he was already in middle age. The union proved to be a happy one, and together they had 12 children, which is very unusual by Roman standards. Six of them were boys and six were girls. Only three are known to have survived childhood: Sempronia (sister of the Gracchi), S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiberius Gracchus
Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus (; 163 – 133 BC) was a Roman politician best known for his agrarian reform law entailing the transfer of land from the Roman state and wealthy landowners to poorer citizens. He had also served in the Roman army, fighting in Africa during the Third Punic War and in Spain during the Numantine War. His political future was imperilled during his quaestorship when he was forced to negotiate a humiliating treaty with the Numantines after they had surrounded the army he was part of in Spain. Seeking to rebuild that future and reacting to a supposed decline in the Roman population which he blamed on rich families buying up Italian land, he carried a land reform bill against strong opposition by another tribune during his term as tribune of the plebs in 133 BC. To pass and protect his reforms, Tiberius unprecedentedly had the tribune who opposed his programme deposed from office, usurped the senate's prerogatives over foreign policy, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scipio Aemilianus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus Aemilianus (185 BC – 129 BC), known as Scipio Aemilianus or Scipio Africanus the Younger, was a Roman general and statesman noted for his military exploits in the Third Punic War against Carthage and during the Numantine War in Spain. He oversaw the final defeat and destruction of the city of Carthage. He was a prominent patron of writers and philosophers, the most famous of whom was the Greek historian Polybius. In politics, he opposed the populist reform program of his murdered brother-in-law, Tiberius Gracchus. Family Scipio Aemilianus was the second son of Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus, the commander of the Romans' victorious campaign in the Third Macedonian War, and his first wife, Papiria Masonis. Scipio was adopted by his first cousin, Publius Cornelius Scipio, the eldest son of his aunt Aemilia Tertia and her husband Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus, the acclaimed commander who won the decisive battle of the Second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Gracchus
Gaius Sempronius Gracchus ( – 121 BC) was a reformist Roman politician and soldier who lived during the 2nd century BC. He is most famous for his tribunate for the years 123 and 122 BC, in which he proposed a wide set of laws, including laws to establish colonies outside of Italy, engage in further land reform, reform the judicial system and system for provincial assignments, and create a subsidised grain supply for Rome. The year after his tribunate, his political enemies used political unrest – which he and his political allies had caused – as an excuse to declare martial law and march on his supporters, leading to his death. After his death, his political allies were purged in a series of trials, but most of his legislation was undisturbed. His brother was the reformer Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus. Both, known together as the Gracchi brothers, were the sons of the Gracchus who was consul in 177 and 163 BC. Background Gaius Gracchus was born i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
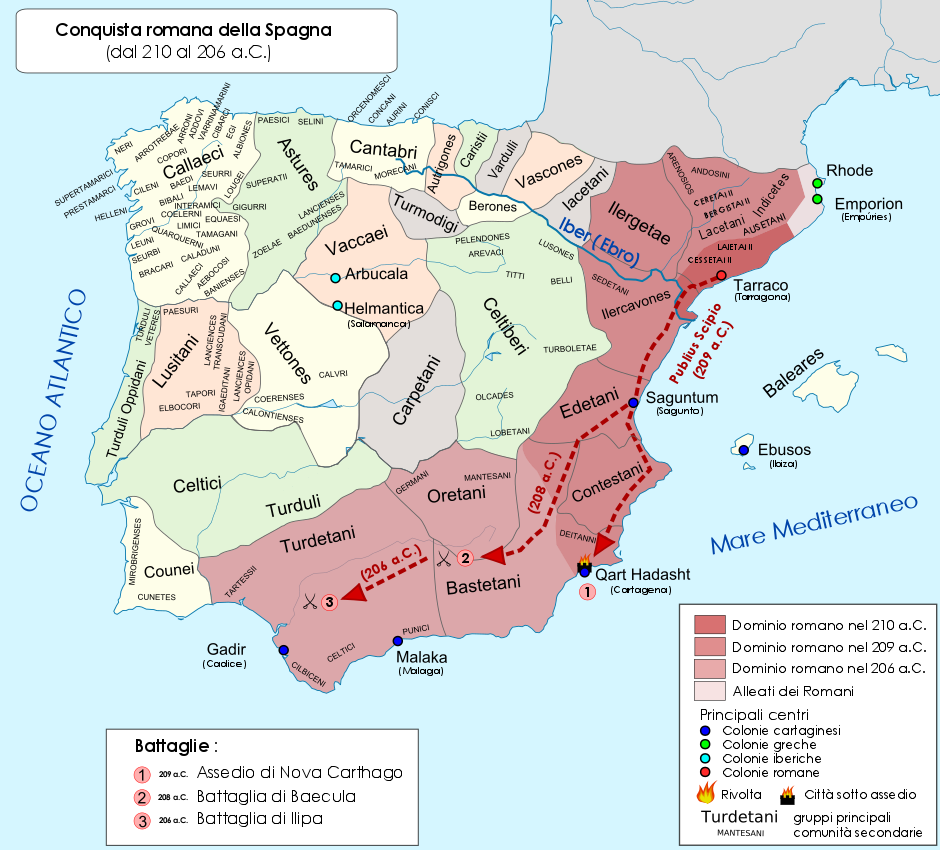
Scipio Africanus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus (, , ; 236/235–) was a Roman general and statesman who was one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Ancient Carthage, Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the greatest military commanders and strategists of all time, his greatest military achievement was the defeat of Hannibal at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC. This victory in Africa earned him the honorific epithet ''Africanus'', literally meaning 'the African', but meant to be understood as a conqueror of Africa (Roman province), Africa. Scipio's conquest of Carthaginian Iberia culminated in the Battle of Ilipa in 206 BC against Hannibal's brother Mago Barca. Although considered a hero by the Roman people, primarily for his victories against Carthage, Scipio had many opponents, especially Cato the Elder, who hated him deeply. In 187 BC, he was tried in a show trial alongside his brother for bribes they supposedly received from the Seleucid king Antiochus III ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus (consul 177 BC)
Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus ( 220 BC – 154 BC) was a Roman politician and general of the 2nd century BC. He served two consulships, one in 177 and one 163 BC, and was awarded two triumphs. He was also the father of the two famous Gracchi brothers: Tiberius and Gaius. During his tribunate in 187 or 184 BC, he interceded to save Scipio Africanus or Scipio Asiagenes from prosecution or prison, feeling that their services to the republic outweighed any alleged wrongdoing. He later married Africanus' daughter, Cornelia, after Africanus' death. A few years later, Tiberius was elected praetor and prorogued ''pro consule'' to Spain; he won victories there for which he was awarded a triumph. After his first consulship in 177 BC, he was assigned to Sardinia and on his return triumphed for the second time. In 169 BC, he was elected to the censorship and began construction of the basilica Sempronia in the forum; he later won a second consulship in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sempronia (sister Of The Gracchi)
Sempronia (170 BC – after 101 BC) was a Roman noblewoman living in the Middle and Late Roman Republic, who was most famous as the sister of the ill-fated Tiberius Gracchus (died 133 BC) and Gaius Gracchus (died 121 BC), and the wife of a Roman general Scipio Aemilianus. Background Sempronia was the oldest surviving child and only surviving daughter of Roman consul and censor Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus and his wife Cornelia. Her younger brothers were the famed Roman politicians Tiberius Gracchus and Gaius Gracchus. Her maternal grandparents were the great Roman general Scipio Africanus and his wife Aemilia Paulla; Sempronia's maternal great-uncle was another distinguished Roman general, Lucius Aemilius Paulus Macedonicus. Her father had a formidable reputation as a general (having won a triumph in Sardinia), and was known as a strict censor who was nonetheless tremendously popular. Sempronia was born in Rome around 170 BC, and was raised and educated there by her moth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François-Noël Babeuf
François-Noël Babeuf (; 23 November 1760 – 27 May 1797), also known as Gracchus Babeuf, was a French proto-communist, revolutionary, and journalist of the French Revolutionary period. His newspaper ''Le tribun du peuple'' (''The Tribune of the People'') was best known for its advocacy for the poor and calling for a popular revolt against the Directory, the government of France. He was a leading advocate for democracy and the abolition of private property. He made his own variant of Jacobinism ( Robespierrism) which is called ''Neo-Jacobinism''. Besides the influence of Robespierrism on his thought, due to his proto-communism, his political views were more aligned with the ideology of the Enragés. He angered the authorities who were clamping down hard on their radical enemies. In spite of the efforts of his Jacobin friends to save him, Babeuf was executed for his role in the Conspiracy of the Equals. The nickname "Gracchus" likened him to the Gracchi brothers, who serve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lex Agraria
A (: ) was a Roman law which dealt primarily with the viritane allotment of public lands. Such laws came largely from two sources: the disposition of lands annexed by Rome in consequence of expansion and the distribution of existing public lands to poor citizens as freeholds. Such legislation dealt almost exclusively with public lands which were held by the state and not privately owned. There were other types of Roman laws related to agriculture, including those establishing new colonies and those regulating the holding of public lands (). The most famous was that of the plebeian tribune Tiberius Gracchus, passed in 133 BC, which allotted public lands across Italy to rural plebs. Such laws were not without precedent, such as the of 232 BC which authorised viritane distributions of lands in Cisalpine Gaul and Picenum. Further such laws were also passed in the years after 133 BC, including that of Tiberius' younger brother Gaius in 122 BC, and the epigraphi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ager Publicus
The ''ager publicus'' (; ) is the Latin name for the state land of ancient Rome. It was usually acquired via the means of expropriation from enemies of Rome. History In the earliest periods of Roman expansion in central Italy, the ''ager publicus'' was used for Roman and (after 338 BC) Latin colonies. Later tradition held that as far back as the 5th century BC, the patrician and plebeian classes disputed the rights of the rich to exploit the land, and in 367 BC two Plebeian Tribunes, Gaius Licinius Solo and Lucius Sextius Sextinus Lateranus promulgated a law which limited the amount of the ''ager publicus'' to be held by any individual to 500 iugera, roughly . In the half century following the Battle of Telamon ( BC), the Romans fully absorbed Cisalpine Gaul, adding huge swathes of land to the ''ager publicus'', land which was more often than not given to new Latin colonies or to small freeholders. In the south of Italy, huge tracts of newly re-incorporated lands remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire following the War of Actium. During this period, Rome's control expanded from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean world. Roman society at the time was primarily a cultural mix of Latins (Italic tribe), Latin and Etruscan civilization, Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Ancient Roman religion and List of Roman deities, its pantheon. Its political organisation developed at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by Roman Senate, a senate. There were annual elections, but the republican system was an elective olig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ager Publicus
The ''ager publicus'' (; ) is the Latin name for the state land of ancient Rome. It was usually acquired via the means of expropriation from enemies of Rome. History In the earliest periods of Roman expansion in central Italy, the ''ager publicus'' was used for Roman and (after 338 BC) Latin colonies. Later tradition held that as far back as the 5th century BC, the patrician and plebeian classes disputed the rights of the rich to exploit the land, and in 367 BC two Plebeian Tribunes, Gaius Licinius Solo and Lucius Sextius Sextinus Lateranus promulgated a law which limited the amount of the ''ager publicus'' to be held by any individual to 500 iugera, roughly . In the half century following the Battle of Telamon ( BC), the Romans fully absorbed Cisalpine Gaul, adding huge swathes of land to the ''ager publicus'', land which was more often than not given to new Latin colonies or to small freeholders. In the south of Italy, huge tracts of newly re-incorporated lands remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |