|
Gour Express
Gour Express is an express train of the Indian Railways connecting Kolkata with the district of Malda via Barddhaman , Rampurhat. The train covers a distance of up to Malda with the numbers 13153/54. Timeline The Gour Express commenced operations as a triweekly express service between Sealdah and Malda from 20 April 1980. The train proved successful and the then railway minister A. B. A. Ghani Khan Choudhury played a key role in increasing the frequency of the service. On 2 October 1982, he flagged off the first run of the train as a daily service Important stoppages * * * * * * * * * * * * (only for 13154 service) * * * Timings # 13153 leaves Sealdah around 22:05 everyday and reaches Malda Town at 5:55 next day. # 13154 departs Malda Town around 21:25 everyday and reaches Sealdah at 5:00 next day. Coach composition The train consists of 21 passenger coaches. The train runs with the following coach composition - * 1 Composite 1st A/C * 3 A/C 2-tier coaches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Express Trains In India
India has a system of express trains, operated by Indian Railways which comes under the purview of the Ministry of Railways (India), Ministry of Railways of Government of India. , it maintains over of tracks, spanning across in route length, and operates nearly 3,000 express trains daily. According to the Ministry of Railways, express trains travel faster and have limited stops than Slow and fast passenger trains in India, ordinary passenger trains. Any passenger train with an average speed higher than is considered super-fast. , India does not have any operational High-speed railway, high-speed trains. The maximum operational speed of is achieved by Gatimaan Express and Rani Kamalapati (Habibganj)–Hazrat Nizamuddin Vande Bharat Express on the Tughlakabad railway station, TughlakabadAgra Cantonment railway station, Agra section. Earlier steam locomotive operated trains largely operated below . With the introduction of electric locomotives in later 1920s and newer steam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malda, West Bengal
Malda, also known as English Bazar, is a city in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the sixth largest city (urban agglomeration) in West Bengal. It is the headquarters of the Malda district as well as of the Malda division of West Bengal. It consists of two municipalities, viz. English Bazar Municipality and Old Malda Municipality, under Malda Metropolitan Area. The city is located on the banks of the Mahananda River. Malda was an undeveloped city which was enlarging from 1925 to 1930. The city is growing rapidly nowadays with its population inching towards half a million. Etymology The name ''English Bazar'' is a calque of ''Angrezābād'' ("English-town"), applied in the 17th century to the surroundings of the English factory. wikisource:Hobson-Jobson/E, English-Bazar It was named in accordance with the factories built on the banks of River Mahananda by the British. The English traders set their factories here for the high profitable trade. Geography Location Malda is lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Named Passenger Trains Of India
Named may refer to something that has been given a name. Named may also refer to: * named (computing), a widely used DNS server * Naming (parliamentary procedure) * The Named (band), an American industrial metal group In literature: * ''The Named'', a fantasy novel by Marianne Curley * The Named, a fictional race of prehistoric big cats, depicted in ''The Books of the Named'' series by Clare Bell See also * Name (other) * Names (other) Names are words or terms used for identification. Names may also refer to: * ''Names'' (EP), by Johnny Foreigner * ''Names'' (journal), an academic journal of onomastics * The Names (band), a Belgian post-punk band * ''The Names'' (novel), b ... * Naming (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport In Maldah
Transport (in British English) or transportation (in American English) is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipelines, and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles, and operations. Transport enables human trade, which is essential for the development of civilizations. Transport infrastructure consists of both fixed installations, including roads, railways, airways, waterways, canals, and pipelines, and terminals such as airports, railway stations, bus stations, warehouses, trucking terminals, refueling depots (including fuel docks and fuel stations), and seaports. Terminals may be used both for the interchange of passengers and cargo and for maintenance. Means of transport are any of the different kinds of transport facilities used to carry people or cargo. They may include vehicles, riding animals, and pack animals. Vehicles may inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport In Kolkata
Kolkata the Capital of the Indian state of West Bengal has a good transportation system. Kolkata's transport system is diverse, with a mix of modern and traditional modes of transport catering to the city's large population. The primary modes include: * Buses:- Both government and privately operated buses are there * Kolkata Suburban Railway:- The suburban train network connects Kolkata with surrounding areas like Howrah, Sealdah, and other suburbs, handling large volumes of daily commuters. * Kolkata Metro:- The Kolkata Metro, Urban rail transit in India, India's first underground metro system, plays a vital role in reducing traffic congestion. * Trams:- Kolkata is the only Indian city with a functioning tram network, operated by Calcutta Tramways Company. Though slow, trams are iconic and still run in certain parts of the city. * Taxis and Auto-rickshaws:- Yellow taxis are icon of Kolkata, along with app-based taxi services like Uber and Ola. Auto-rickshaws also operate on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gangarampur Railway Station
Gangarampur railway station is located in Dakshin Dinajpur district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It serves Gangarampur city and the surrounding areas. The station was built in 2004, and the first train ran on 30 December 2004. The station is located at the south side of the town, near Gangarampur College. A few express trains, like the Gour Express, Tebhaga Express and Balurghat–Siliguri Intercity Express, Howrah Express, Malda Town passenger, Old Malda passenger, stop at Gangarampur railway station. Gangarampur Railway Bridge Trains cross the Gangarampur Railway Bridge over Punarbhaba River The Punarbhaba (also ''Poonorvoba''; ) is a river of Bangladesh and India's West Bengal, with a total length of , a width of and a mean depth of . It originates from the lowlands of Thakurgaon District of Bangladesh. The river's upper part is a ... near Gangarampur railway station. Image:Gangarampur Railway Bridge.jpeg References Railway stations in India opened in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Malda Junction Railway Station
Old Malda Junction railway station is a junction railway station in Malda district, West Bengal West Bengal (; Bengali language, Bengali: , , abbr. WB) is a States and union territories of India, state in the East India, eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabi .... Its code is OMLF. It serves Malda. The station consists of three platforms. The platforms are not well sheltered. It lacks many facilities including water and sanitation. Major trains Some of the important trains that runs from Malda are : * New Jalpaiguri -Malda Town Express * Balurghat–Malda Town Passenger (unreserved) * Balurghat Malda Town Passenger (unreserved) * Katihar–Malda Town Passenger (unreserved) * Malda Court–Siliguri Jn DMU * Malda Town New Jalpaiguri Passenger (unreserved) * Singhabad Old Malda Passenger (unreserved) References Railway stations in Malda district Katihar railway division Railway junct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WAP-7
The Indian locomotive class WAP-7 is a class of 25 kV AC electric locomotives that was developed in 1999 by Chittaranjan Locomotive Works (CLW) for Indian Railways. The model name stands for broad gauge (W), AC Current (A), Passenger traffic (P) locomotive, 7th generation (7). They entered service in 2000. A total of 1909 WAP-7 have been built, with more units being built at CLW, Banaras Locomotive Works (BLW) and Patiala Locomotive Works (PLW). The WAP-7 has been serving passengers for Indian Railways since their introduction in 1999. It is a passenger variant of the WAG-9 freight locomotive with a modified gear ratio to pull lighter loads at higher speeds. With an output of 6,125 hp, it is the most powerful passenger locomotive in the Indian Railways fleet, and the most numerous passenger locomotive in India. The WAP-7 is capable of hauling 24 coach trains at speeds . It also capable of hauling 26 coaches trains at speeds of 130 km/h. History The WAP-7 is largely used b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WAP-4
The Indian locomotive class WAP-4 is a class of 25 kV AC electric locomotives that was developed in 1993 by Chittaranjan Locomotive Works for Indian Railways. The model name stands for broad gauge (W), AC Current (A), Passenger traffic (P) locomotive, 4th generation (4). They entered service in late 1994. A total of 778 WAP-4 were built at CLW between 1993 and 2015, which made them the most numerous class of mainline electric passenger locomotive until the WAP-7. The WAP-4 is one of the most successful locomotives of Indian Railways serving passenger trains for over 29 years. This class provided the basic design for other locomotives like the WAP-6. Despite the introduction of more modern types of locomotives like WAP-7, a significant number are still in use, both in mainline duties. Production of this class was halted in December 2015 with locomotive number 25051 being the last unit to be rolled out. As of March 2025, all locomotives except those lost in accidents still re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
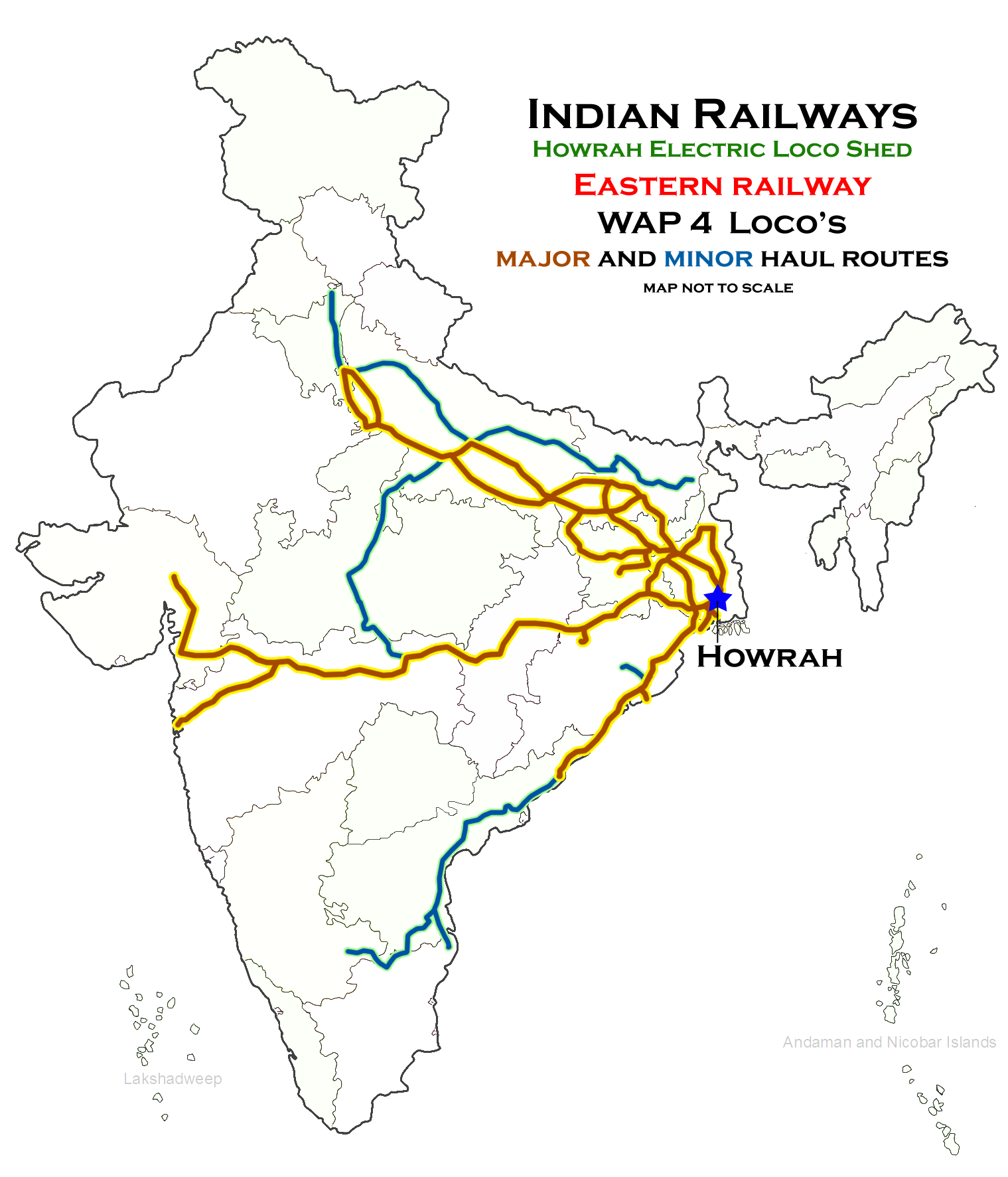
Electric Loco Shed, Howrah
Electric Loco Shed, Howrah is a motive power depot performing locomotive maintenance and repair facility for electric locomotives of the Indian Railways, located at Howrah of the Eastern Railway zone in West Bengal, India. It is one of the two electric locomotive sheds of the Eastern Railway, the others being at Asansol Junction railway station, Asansol (ASN). History Steam locomotive sheds used to exist at Howrah until the late 1970s. After Eastern Railway set a deadline to eliminate all steam locomotive operations by 1990, a push was given towards establishing electric locomotion as the primary motive power, and the steam locomotive sheds was decommissioned. To meet the needs of exponentially increasing rail traffic on the new continuous broad-gauge lines from Kolkata to rest of India with the completion of gauge conversion, the Howrah was selected by Indian Railways for a new electric locomotive shed. New electric locomotive shed was inaugurated in the late 2001s with In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sealdah
Sealdah is a neighbourhood of Central Kolkata in Kolkata district in the Indian state of West Bengal. Etymology Jackals (''sheal'' in Bengali) howled around Sealdah. Antiquarians identify it as Shrigaldwipa (Jackal Island). Nearby Beliaghata was a port in the Salt Lakes.Nair, P. Thankappan, ''The Growth and Development of Old Calcutta'', in ''Calcutta, the Living City'', Vol. I, edited by Sukanta Chaudhuri, pp. 12-19j, Oxford University Press, . History The East India Company obtained from the Mughal emperor Farrukhsiyar, in 1717, the right to rent from 38 villages surrounding their settlement. Of these 5 lay across the Hooghly in what is now Howrah district. The remaining 33 villages were on the Calcutta side. After the fall of Siraj-ud-daulah, the last independent Nawab of Bengal, it purchased these villages in 1758 from Mir Jafar and reorganised them. These villages were known en-bloc as ''Dihi Panchannagram'' and Shealdah was one of them. Sealdah was described in 1757 as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |