|
Gothism
Gothicism or Gothism ( sv, Göticism ; la, Gothicismus) was a cultural movement in Sweden, centered on the belief in the glory of the Swedish Geats, who were identified with the Goths. The founders of the movement were Nicolaus Ragvaldi and the brothers Johannes and Olaus Magnus. The belief continued to hold power in the 17th century, when Sweden was a great power following the Thirty Years' War, but lost most of its sway in the 18th. It was renewed by the Viking revival and Romantic nationalism in the early 19th century, this time with the Vikings as heroic figures. Origins The name is derived from the Gothicists' belief that the Goths had originated from Sweden, based on Jordanes' account of a Gothic ''urheimat'' in Scandinavia (Scandza). The Gothicists took pride in the Gothic tradition that the Ostrogoths and their king Theodoric the Great, who assumed power in the Roman Empire, had Scandinavian ancestry. This pride was expressed as early as the medieval chronicles, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
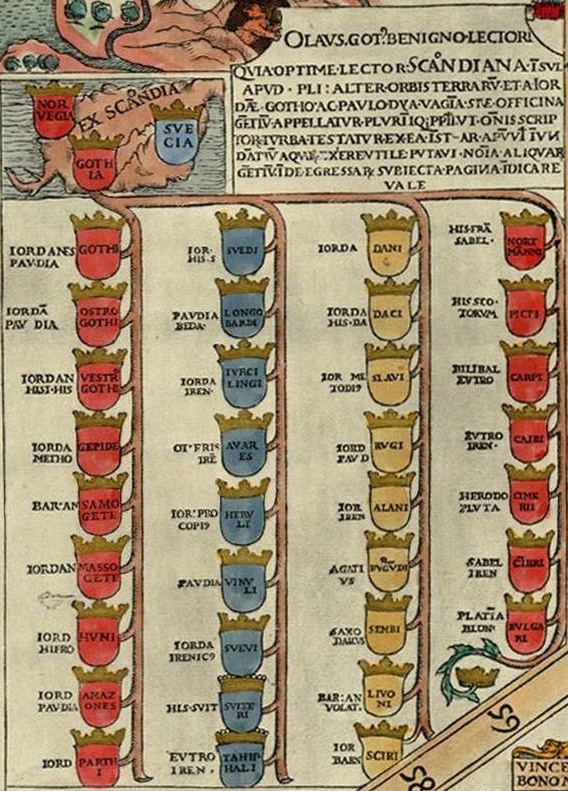
Carta Marina Ex Scandia
Carta is Latin and Italian for "paper" and is Spanish and Portuguese "letter". In English it takes the form "card" or " chart". Most of its uses pertain to its meaning as "paper", "chart", or "map", for example in ''Magna Carta''. Carta may refer to: *Carta (publisher), an Israeli publishing and mapping company *Carta (software company), a software company from Palo Alto, California *Carta (material), a trade name for FR-2, a composite material used in the manufacture of printed circuit boards People with the surname *Angelico Carta (1886-?), Italian military officer *Antonella Carta (born 1967), Italian footballer *Fabio Carta (born 1977), Italian short track speed skater *John Carta (1946–1990), American parachutist *Marco Carta (born 1985), Italian singer *Maria Carta (1934–1994), Italian singer-songwriter See also * CARTA (other) * Cârța (other) Cârța may refer to: * Cârța, Harghita, a commune in Harghita County, Romania * Cârța, Sibiu, a com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also refer more narrowly to the Scandinavian Peninsula (which excludes Denmark but includes part of Finland), or more broadly to include all of Finland, Iceland, and the Faroe Islands. The geography of the region is varied, from the Norwegian fjords in the west and Scandinavian mountains covering parts of Norway and Sweden, to the low and flat areas of Denmark in the south, as well as archipelagos and lakes in the east. Most of the population in the region live in the more temperate southern regions, with the northern parts having long, cold, winters. The region became notable during the Viking Age, when Scandinavian peoples participated in large scale raiding, conquest, colonization and trading mostly throughout Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norse Saga
is a series of science fantasy role-playing video games by Square Enix. The series originated on the Game Boy in 1989 as the creation of Akitoshi Kawazu at Square. It has since continued across multiple platforms, from the Super NES to the PlayStation 2. The series is notable for its emphasis on open world exploration, non-linear branching plots, and occasionally unconventional gameplay. This distinguishes the games from most of Square's other franchises. Development The ''SaGa'' series was created by game designer Akitoshi Kawazu, whose contributions prior to the franchise's introduction include '' Final Fantasy'' and '' Final Fantasy II''. At a time when Nintendo's Game Boy was becoming popular worldwide due to the puzzle game '' Tetris'', then-Square president Masashi Miyamoto requested that a development team create a game for the handheld console. Kawazu and fellow designer Koichi Ishii suggested that the company develop a role-playing video game, thus making '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuscript
A manuscript (abbreviated MS for singular and MSS for plural) was, traditionally, any document written by hand – or, once practical typewriters became available, typewritten – as opposed to mechanically printed or reproduced in some indirect or automated way. More recently, the term has come to be understood to further include ''any'' written, typed, or word-processed copy of an author's work, as distinguished from the rendition as a printed version of the same. Before the arrival of printing, all documents and books were manuscripts. Manuscripts are not defined by their contents, which may combine writing with mathematical calculations, maps, music notation, explanatory figures, or illustrations. Terminology The study of the writing in surviving manuscripts, the "hand", is termed palaeography (or paleography). The traditional abbreviations are MS for manuscript and MSS for manuscripts, while the forms MS., ms or ms. for singular, and MSS., mss or mss. f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its surrounding areas) is home to over 65% of the population. Iceland is the biggest part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge that rises above sea level, and its central volcanic plateau is erupting almost constantly. The interior consists of a plateau characterised by sand and lava fields, mountains, and glaciers, and many glacial rivers flow to the sea through the lowlands. Iceland is warmed by the Gulf Stream and has a temperate climate, despite a high latitude just outside the Arctic Circle. Its high latitude and marine influence keep summers chilly, and most of its islands have a polar climate. According to the ancient manuscript , the settlement of Iceland began in 874 AD when the Norwegian chieftain Ingólfr Arnarson became the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jutes
The Jutes (), Iuti, or Iutæ ( da, Jyder, non, Jótar, ang, Ēotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nations, along with the Angles and the Saxons: There is no consensus amongst historians of the origins on the Jutes. However, there is some archaeological evidence to support a theory that they originated from the eponymous Jutland Peninsula (then called ''Iutum'' in Latin) and to have populated parts of the North Frisian coast. Based on contemporary sources, it appears that they were a tribe of admixed Gutones, Cimbri, Teutons and Charudes, also called ''Eudoses'', ''Eotenas'', ''Iutae'' and ''Euthiones''. The Jutes invaded and settled in southern Britain in the later fifth century during the Migration Period, as part of a larger wave of Germanic settlement into Britain. Settlement in southern Britain During the period after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historia De Gentibus Septentrionalibus
''Historia de Gentibus Septentrionalibus'' was a monumental work by Olaus Magnus on the Nordic countries, printed in Rome 1555. It was a work which long remained for the rest of Europe the authority on Swedish matters. Its popularity increased by the numerous woodcuts of people and their customs, amazing the rest of Europe. It is still today a valuable repertory of much curious information in regard to Scandinavian customs and folklore. It was translated into Italian (1565), German (1567), English (1658) and Dutch (1665). Abridgments of the work appeared also at Antwerp (1558 and 1562), Paris (1561), Basel (1567), Amsterdam (1586), Frankfurt (1618) and Leiden (1652). An exemplar was given to William Cecil during the Swedish king's wooing of queen Elizabeth I of England, and in 1822 it would be referred to by Sir Walter Scott.Wawn, Andrew (2000). The Vikings and the Victorians: Inventing the Old North in Nineteenth-Century Britain. Cambridge: Brewer. . pp. 17f. Notes Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historia De Omnibus Gothorum Sueonumque Regibus
The ''Historia de omnibus Gothorum Sueonumque regibus'' (''The history of all Geatish and Swedish kings'') is a posthumously published, partly pseudo-historical work by Johannes Magnus, Sweden's last Catholic archbishop. In 1554 (ten years after his death) it was published in Latin by his brother Olaus Magnus. The ''Historia'' was implicitly critical of King Gustav Vasa, who had introduced the Protestant Reformation in 1527 and caused the exile of Johannes Magnus. It was nevertheless used widely by Gustav Vasa's sons and successors, to whom it had been dedicated, since it extolled the glorious past of the Swedish kingdom. In particular, the sons used the (fictitious) king-list which began with Magog, grandson of Noah. As a consequence, Eric XIV and Charles IX adopted much higher regnal numbers than warranted by the historical sources. A Swedish translation was published by Ericus Benedicti Schroderus in 1620. A modern Swedish version, translated by Kurt Johannesson and with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Basel
The Council of Florence is the seventeenth ecumenical council recognized by the Catholic Church, held between 1431 and 1449. It was convoked as the Council of Basel by Pope Martin V shortly before his death in February 1431 and took place in the context of the Hussite Wars in Bohemia and the rise of the Ottoman Empire. At stake was the greater conflict between the conciliar movement and the principle of papal supremacy. The Council entered a second phase after Emperor Sigismund's death in 1437. Pope Eugene IV convoked a rival Council of Ferrara on 8 January 1438 and succeeded in drawing some of the Byzantine ambassadors who were in attendance at Basel to Italy. The remaining members of the Council of Basel first suspended him, declared him a heretic, and then in November 1439 elected an antipope, Felix V. After becoming the Council of Florence (having moved to avoid the plague in Ferrara), the Council concluded in 1445 after negotiating unions with the various eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicle
A chronicle ( la, chronica, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and local events, the purpose being the recording of events that occurred, seen from the perspective of the chronicler. A chronicle which traces world history is a universal chronicle. This is in contrast to a narrative or history, in which an author chooses events to interpret and analyze and excludes those the author does not consider important or relevant. The information sources for chronicles vary. Some are written from the chronicler's direct knowledge, others from witnesses or participants in events, still others are accounts passed down from generation to generation by oral tradition.Elisabeth M. C. Van Houts, ''Memory and Gender in Medieval Europe: 900–1200'' (Toronto; Buffalo : University of Toronto Press, 1999), pp. 19–20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
.jpg)

