|
Gotha
Gotha () is the fifth-largest city in Thuringia, Germany, west of Erfurt and east of Eisenach with a population of 44,000. The city is the capital of the district of Gotha and was also a residence of the Ernestine Wettins from 1640 until the end of monarchy in Germany in 1918. The House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha originating here spawned many European rulers, including the royal houses of the United Kingdom, Belgium, Portugal (until 1910) and Bulgaria (until 1946). In the Middle Ages, Gotha was a rich trading town on the trade route ''Via Regia'' and between 1650 and 1850, Gotha saw a cultural heyday as a centre of sciences and arts, fostered by the dukes of Saxe-Gotha. The first duke, Ernest the Pious, was famous for his wise rule. In the 18th century, the '' Almanach de Gotha'' was first published in the city. The publisher Justus Perthes and the encyclopedist Joseph Meyer made Gotha a leading centre of German publishing around 1800. In the early 19th century, Gotha was a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almanach De Gotha
The ''Almanach de Gotha'' () is a directory of Europe's royalty and higher nobility, also including the major governmental, military and diplomatic corps, as well as statistical data by country. First published in 1763 by C. W. Ettinger in Gotha in Thuringia, Germany at the ducal court of Frederick III, Duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg, it came to be regarded as an authority in the classification of monarchies and their courts, reigning and former dynasties, princely and ducal families, and the genealogical, biographical and titulary details of Europe's highest level of aristocracy. It was published from 1785 annually by Justus Perthes Publishing House in Gotha, until 1944. In 1992, the family of Justus Perthes re-established its right to use the name ''Almanach de Gotha''. In 1998, a London-based publisher, John Kennedy, acquired the rights for use of the title of ''Almanach de Gotha'' from Justus Perthes Verlag Gotha GmbH, then a fully-owned subsidiary of Ernst Klett Schu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Saxe-Coburg And Gotha
The House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha ( ; ) is a European royal house of German origin. It takes its name from its oldest domain, the Ernestine duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, and its members later sat on the thrones of Belgium, Bulgaria, Portugal, the United Kingdom and its dominions. Founded in 1826 by Ernest Anton, the sixth duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld, it is a cadet branch of the Saxon House of Wettin. One agnatic branch currently reigns in Belgiumthe descendants of Leopold Iand another reigned in the United Kingdom until the death of Elizabeth IIthe descendants of Albert, Prince Consort. In 1917, the First World War caused the British king George V to officially change the name from "''Saxe-Coburg and Gotha''" to "'' Windsor''" in the United Kingdom. In Belgium, due to similar resentment against Germany after the Great War, the use of the name was also changed in 1920 by King Albert I to "''de Belgique''" ( French), "''van België''" ( Dutch) or "''von Belgien''" ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothaer Waggonfabrik
''Gothaer Waggonfabrik'' (''Gotha'', GWF) was a German manufacturer of rolling stock established in the late nineteenth century at Gotha. During the two world wars, the company expanded into aircraft building. World War I In World War I, Gotha was the manufacturer of a highly successful series of bombers based on a 1914 design by Oskar Ursinus and developed by Hans Burkhard. From 1917, the Burkhard-designed twin pusher biplane bomber aircraft were capable of carrying out strategic bombing missions over England, the first heavier-than-air aircraft used in this role. Several dozen of these bombers were built in a number of subtypes - the Ursinus-based Gotha G.I, and the succeeding Burkhard-designed G.II, G.III, G.IV, and G.V. This last variant was the most prolific, with thirty-six in squadron service at one point. Inter war years Whilst Germany was prohibited from military aircraft manufacture by the Treaty of Versailles, Gotha returned to its railway endeavours, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justus Perthes (publishing Company)
Justus Perthes Publishers () was established in 1785 in Gotha, Germany. Justus Perthes was primarily a publisher of geographical and historical atlases and educational wall maps. They published the Almanach de Gotha (German ''Gothaischer Genealogischer Hofkalender'') from 1785 to 1944, and ''Petermanns Geographische Mitteilungen'' from 1855 to 2004. In 2016 the publisher was dissolved. Almanacs In 1778, Johann Georg Justus Perthes worked as a bookseller in Gotha. He founded the publishing firm ''Justus Perthes'' in September 1785, when he got a fifteen-year lease to publish the ''Almanach de Gotha'', an annual French-language compilation of statistics on nations of the world. This almanac was published from 1763 to 1777 by Carl Wilhelm Ettinger in Gotha. It was only after the second 15-year lease in 1816 that the almanac was published with the Perthes publishing house imprint. The publication of the almanac as a Justus Perthes publication ceased in 1944. In later years, Perthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest I, Duke Of Saxe-Gotha
Ernest I, called "Ernest the Pious" (25 December 1601 – 26 March 1675), was a duke of Saxe-Gotha and Saxe-Altenburg. The duchies were later merged into Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg. He was the ninth but sixth surviving son of Johann II, Duke of Saxe-Weimar, and Dorothea Maria of Anhalt. His mother was a granddaughter of Christoph, Duke of Württemberg, and great-granddaughter of Ulrich, Duke of Württemberg. Life Left an orphan early in life (his father died in 1605 and his mother in 1617), he was brought up in a strict manner, and was gifted and precocious but not physically strong. He soon showed traits of the piety of the time. As ruler, by his character and governmental ability as well as by personal attention to matters of state, he introduced a golden age for his subjects after the ravages of the Thirty Years' War. By wise economy, which did not exclude fitting generosity or display on proper occasions, he freed his land from debt, left at his death a considerable sum in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Wettin
The House of Wettin () was a dynasty which included Saxon monarch, kings, Prince Elector, prince-electors, dukes, and counts, who once ruled territories in the present-day German federated states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its origins can be traced back to the town of Wettin, Saxony-Anhalt. The Wettins gradually rose to power within the Holy Roman Empire. Members of the family became the rulers of several Middle Ages, medieval states, starting with the Saxon Eastern March in 1030. Other states they gained were Meissen in 1089, Thuringia in 1263, and Saxony in 1423. These areas cover large parts of Central Germany (cultural area), Central Germany as a cultural area of Germany. The family divided into two ruling branches in 1485 by the Treaty of Leipzig: the Ernestine and Albertine branches. The older Ernestine branch played a key role during the Protestant Reformation. Many ruling monarchs outside Germany were later tied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Gotha
Saxe-Gotha () was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine duchies, Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin, Wettin dynasty in the former Landgraviate of Thuringia. The ducal residence was erected at Gotha (town), Gotha. History The duchy was established in 1640, when Duke Wilhelm, Duke of Saxe-Weimar, Wilhelm von Saxe-Weimar created a subdivision for his younger brother Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha, Ernest I the Pious. Duke Ernest took his residence at Gotha (town), Gotha, where he had ''Schloss Friedenstein'' built between 1643 and 1654. At the same time, the Duchy of Saxe-Eisenach was created for the third brother Albert IV, Duke of Saxe-Eisenach, Albert IV. Nevertheless, Albert died in 1644, and Ernest inherited large parts of his duchy, though not the core territory around the residence at Eisenach and the Wartburg, which fell to his elder brother Wilhelm of Saxe-Weimar. Ernest could also incorporate several remaining estates of the extinct House of Henneberg in 166 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotha (district)
Gotha (German language, German: ''Landkreis Gotha'') is a Kreis (district) in western central Thuringia, Germany. Neighboring districts are Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis, Sömmerda (district), Sömmerda, the Kreis-free city Erfurt, Ilm-Kreis, Schmalkalden-Meiningen and the Wartburgkreis. Geography Gotha borders the Thuringian Basin in the north and east, with a low point of about 200 meters (656 feet) in the northern part of the district. Fahner Heights, a muschelkalk ridge with a height of 413 meters (1,355 feet), is located in the extreme north, between the municipalities of Tonna, Germany, Tonna and Bienstädt. The land rises to about 900 meters (2,953 feet) in the Thuringian Forest, which covers the south-western area of the district. The Rennsteig hiking trail follows a ridge line through the forest. The highest point in the district is Großer Inselsberg at 916.5 m (3,007 ft), on the border with Schmalkalden-Meiningen. The southern area of the district also has 3 dams: the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area. Erfurt is the capital and largest city. Other cities include Jena, Gera and Weimar. Thuringia is bordered by Bavaria, Hesse, Lower Saxony, Saxony, and Saxony-Anhalt. It has been known as "the green heart of Germany" () from the late 19th century due to its broad, dense forest. Most of Thuringia is in the Saale drainage basin, a bank (geography), left-bank tributary of the Elbe. Thuringia is home to the Rennsteig, Germany's best-known hiking, hiking trail. Its winter resort of Oberhof, Germany, Oberhof makes it a well-equipped winter sports destination – half of Germany's 136 Winter Olympics, Winter Olympic gold medals had been won by Thuringian athletes as of 2014. Thuringia was favoured by or was the birthplace of three key intellectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
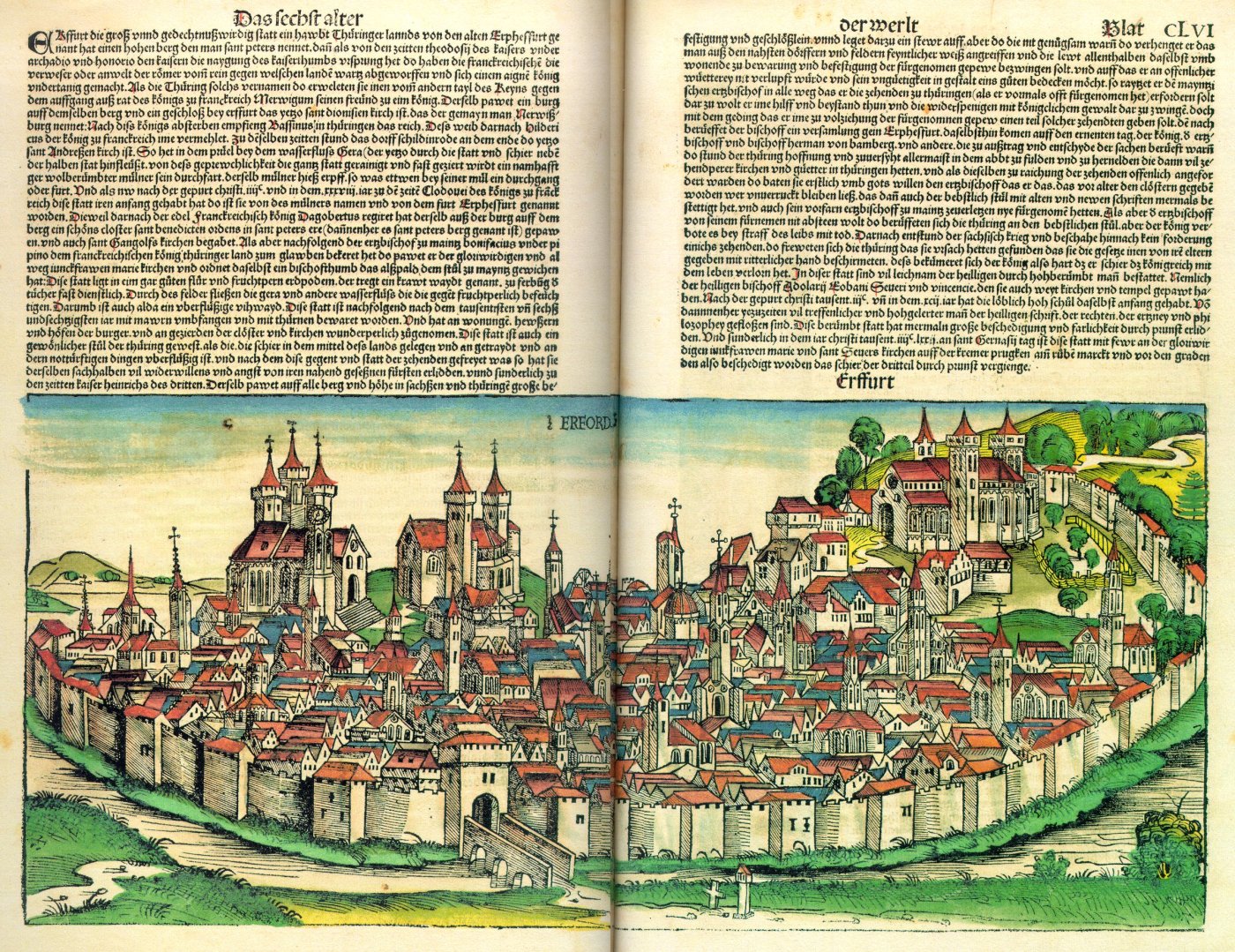
Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital (political), capital and largest city of the Central Germany (cultural area), Central German state of Thuringia, with a population of around 216,000. It lies in the wide valley of the Gera (river), River Gera, in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest, and in the middle of a line of the six largest Thuringian cities ('':de:Thüringer Städtekette, Thüringer Städtekette''), stretching from Eisenach in the west, via Gotha, Erfurt, Weimar and Jena, to Gera in the east. Together with Kassel and Göttingen, it is one of the cities with more than 100,000 inhabitants lying closest to the geographic centre of Germany. Erfurt is south-west of Leipzig, north-east of Frankfurt, south-west of Berlin and north of Munich. Erfurt's old town is one of the best preserved medieval city centres in Germany. The Gera (river), Gera is spanned by the Krämerbrücke, Merchants' Bridge (''Krämerbrücke''), one of the rare bridges with ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Meyer (publisher)
Joseph Meyer (9 May 1796 - 27 June 1856) was a German industrialist and publisher, most noted for his encyclopaedia, Meyers Konversations-Lexikon. Biography Meyer was born at Gotha, Germany, and was educated as a merchant in Frankfurt am Main. He went to London in 1816, but returned to Germany in 1820 after business adventures and stock speculations fell through. Here he invested in enterprises such as the textile trade (1820–24). Soon after the first steam-hauled railway had started in December 1835, Meyer started to make business plans to start the first railways. He also bought some concessions for iron mining. In 1845 he founded the ''Deutsche Eisenbahnschienen-Compagnie auf Actien'' (German Railway Rail joint stock company). Meyer operated very successfully as a publisher, employing a system of serial subscription to publications, which was new at that time. To this end he founded a company, Bibliographisches Institut, in Gotha in 1826. It published several editions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
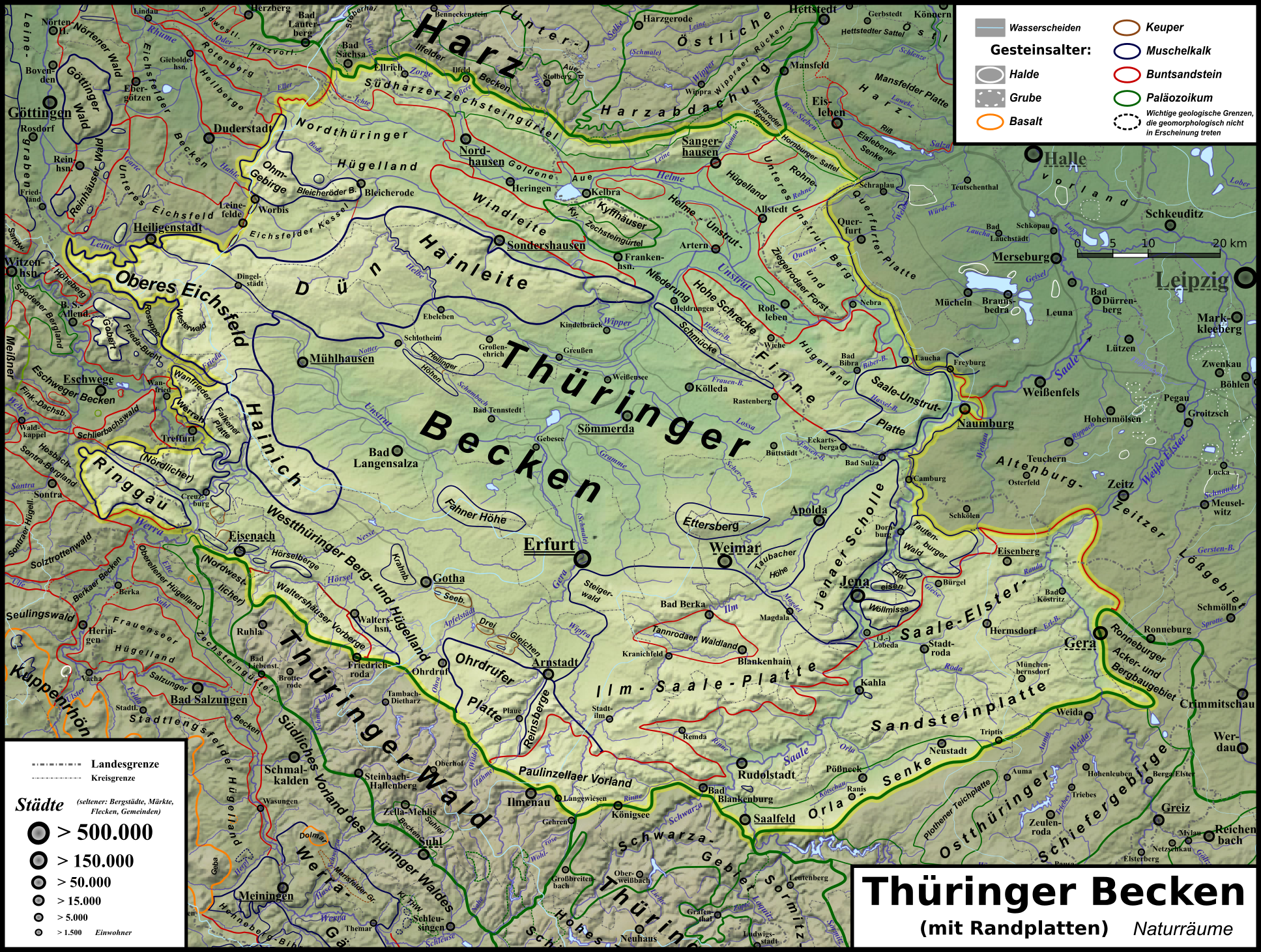
Thuringian Basin
The Thuringian Basin () is a depression (geology), depression in the central and northwest part of Thuringia in Germany which is crossed by several rivers, the longest of which is the Unstrut. It stretches about from north to south and around from east to west. Its height varies from about 150 to . The Basin is surrounded by a wide outer girdle of limestone (Muschelkalk) ridges (including Hainich, Dün, Hainleite, Hohe Schrecke, Schmücke, Finne (hills), Finne), and to the southwest by the Thuringian Forest and to the southeast by sharply divided terraces (the Ilm-Saale and Ohrdruf Muschelkalk plateaus, and the Saale-Elster Bunter sandstone plateau). The Thuringian Basin belongs to the triassic period, during which horizontal beds of Bunter sandstone, Muschelkalk and Keuper were laid down. Below those lie the salt and gypsum layers of Magnesian Limestone (Zechstein). In the Cenozoic era the surrounding ridges were uplifted, whilst the Thuringian Basin sank to form a saucer-shaped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |