|
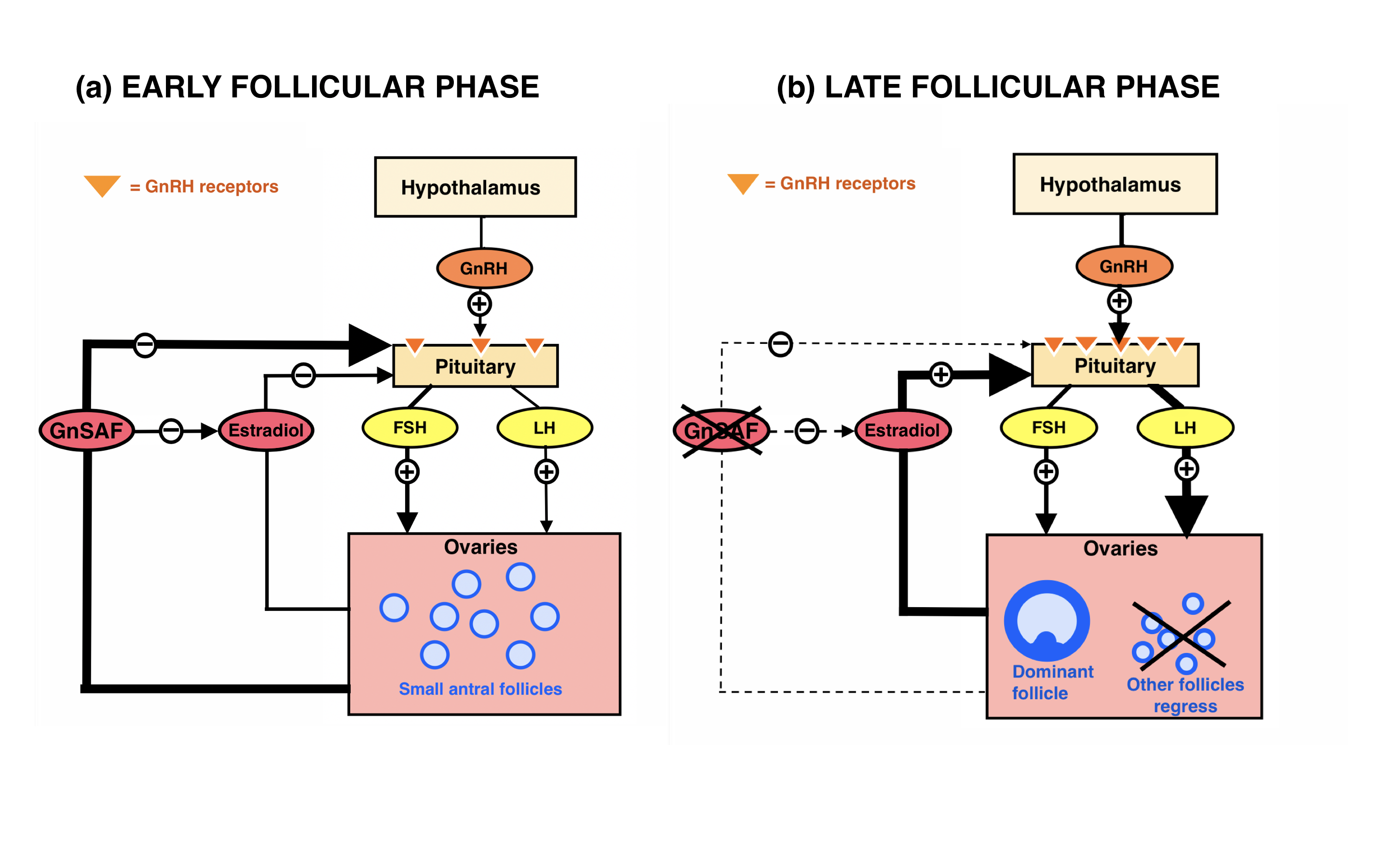
Gonadotropin Surge-attenuating Factor
Gonadotropin surge-attenuating factor (GnSAF) is a nonsteroidal ovarian hormone produced by the granulosa cells of small antral ovarian follicles in females. GnSAF is involved in regulating the secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary and the ovarian cycle. During the early to mid-follicular phase of the ovarian cycle, GnSAF acts on the anterior pituitary to attenuate LH release, limiting the secretion of LH to only basal levels. At the transition between follicular and luteal phase, GnSAF bioactivity declines sufficiently to permit LH secretion above basal levels, resulting in the mid-cycle LH surge that initiates ovulation. In normally ovulating women, the LH surge only occurs when the oocyte is mature and ready for extrusion. GnSAF bioactivity is responsible for the synchronised, biphasic nature of LH secretion. Molecular structure and characteristics GnSAF is a large molecule consisting of subunits that has the same structure as the carboxyl terminal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonsteroidal
A nonsteroidal compound is a drug that is not a steroid nor a steroid derivative. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are distinguished from corticosteroids as a class of anti-inflammatory agents. List of nonsteroidal steroid receptor modulators Examples include the following: * Estrogens: benzestrol, bifluranol, estrobin (DBE), diethylstilbestrol (stilbestrol), dienestrol, erteberel, fosfestrol, hexestrol (dihydroxystilbestrol), methallenestril, methestrol, methestrol dipropionate, paroxypropione, prinaberel, and triphenylethylene, as well as many xenoestrogens * : acolbifene, afimoxifene, arzoxifene, bazedoxifene, broparestrol, chlorotrianisene, clomifene, clomifenoxide, cyclofenil, droloxifene, enclomifene, endoxifen, ethamoxytriphetol, fispemifene, idoxifene, lasofoxifene, levormeloxifene, miproxifene, nafoxidine, nitromifene, ormeloxifene, ospemifene, panomifene, pipendoxifene, raloxifene, tamoxifen, toremifene, trioxifene, zin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. Peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides have an N-terminal (amine group) and C-terminal (carboxyl g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atresia
Atresia is a condition in which an orifice or passage in the body is (usually abnormally) closed or absent. Types Anotia Anotia is characterized by the complete absence of the ear and is extremely rare. This condition may affect one or both ears, though one missing ear is more common. Anotia is also linked to conductive hearing loss, a condition in which sound waves do not travel well through the ear and sound is not efficiently conducted from the outer ear canal to the eardrum. Anotia has no known cause. An associated syndrome, such as Treacher Collins or Goldenhar syndrome, may affect up to 40% of patients. Anotia is typically diagnosed through a physical examination at birth. Prenatal ultrasounds may help with early detection. Total ear reconstruction is the standard treatment for Anotia. Biliary atresia Biliary atresia (BA) is a rare disease marked by an unknown-origin biliary obstruction that manifests in the neonatal period. The classic clinical triad of Biliar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. In RNA splicing, introns are removed and exons are covalently joined to one another as part of generating the mature RNA. Just as the entire set of genes for a species constitutes the genome, the entire set of exons constitutes the exome. History The term ''exon'' is a shortening of the phrase ''expressed region'' and was coined by American biochemist Walter Gilbert in 1978: "The notion of the cistron... must be replaced by that of a transcription unit containing regions which will be lost from the mature messengerwhich I suggest we call introns (for intragenic regions)alternating with regions which will be expressedexons." This definition was originally made for protein-coding transcripts that are spliced before b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (biology)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA for the purpose of gene expression. Some segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins, called messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, Antiparallel (biochemistry), antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. In virology, the term transcription is used when referring to mRNA synthesis from a viral RNA molecule. The genome of many Orthornavirae, RNA viruses is composed of Sense (molecular biology), negative-sense RNA which acts as a template for positive sense viral messenger RNA - a necessary step in the synthesis of viral proteins needed for viral replication. This process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process (including its Regulation of gene expression, regulation) by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, proteins or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as Transfer RNA, transfer RNA (tRNA) and Small nuclear RNA, small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional List of RNAs, non-coding RNA. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and viruses—to generate the macromolecule, macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, ''i.e.'' observable trait. The genetic information stored in DNA represents the genotype, whereas the phenotype results from the "interpretation" of that informati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocrine glands, secreting various hormones that play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal period through menopause. Structure Each ovary is whitish in color and located alongside the lateral wall of the uterus in a region called the ovarian fossa. The ovarian fossa is the region that is bounded by the external iliac artery and in front of the ureter and the internal iliac artery. This area is about 4 cm x 3 cm x 2 cm in size.Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . The ovaries are surrounded by a capsule, and have an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The capsule is of dense connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-Catalysis, catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthesis) serve as enzyme substrate (chemistry), substrates, with conversion by the living organism either into simpler or more complex Product (chemistry), products. Examples of biosynthetic pathways include those for the production of amino acids, lipid membrane components, and nucleotides, but also for the production of all classes of biological macromolecules, and of acetyl-coenzyme A, adenosine triphosphate, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and other key intermediate and transactional molecules needed for metabolism. Thus, in biosynthesis, any of an array of Chemical compound, compounds, from simple to complex, are converted into other compounds, and so it includes both the catabolism and anabolism (building up and breaking down) of comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Follicle-stimulating Hormone
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a gonadotropin, a glycoprotein polypeptide hormone. FSH is synthesized and secreted by the gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary gland and regulates the development, growth, puberty, pubertal maturation, and reproductive processes of the body. FSH and luteinizing hormone (LH) work together in the reproductive system. Structure FSH is a 35.5 kDa glycoprotein protein dimer, heterodimer, consisting of two polypeptide units, alpha and beta. Its structure is similar to those of luteinizing hormone (LH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). The chorionic gonadotropin alpha, alpha subunits of the glycoproteins LH, FSH, TSH, and hCG are identical and consist of 96 amino acids, while the beta subunits vary. Both subunits are required for biological activity. FSH has a beta subunit of 111 amino acids (FSH β), which confers its specific biologic action, and is responsible for interaction with the follicl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulatory System
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek meaning ''heart'', and Latin meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Many invertebrates such as arthropods have an open circulatory system with a he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |