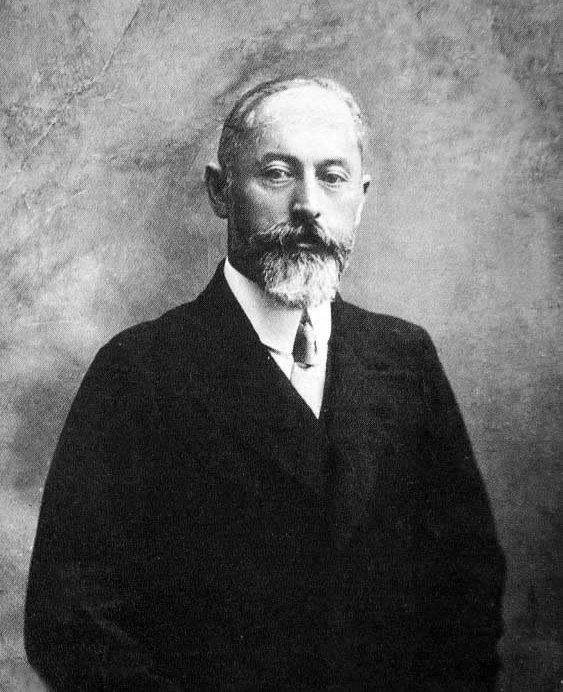|
Golos Truda
''Golos Truda'' (russian: Голос Труда ''The Voice of Labour'') was a Russian-language anarchist newspaper. Founded by working-class Russian expatriates in New York City in 1911, ''Golos Truda'' shifted to Petrograd during the Russian Revolution The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ... in 1917, when its editors took advantage of the general amnesty and right of return for political dissidents. There, the paper integrated itself into the anarchist labour movement, pronounced the necessity of a social revolution of and by the workers, and situated itself in opposition to the myriad of other left-wing movements. The rise to power of the Bolsheviks marked the turning point for the newspaper however, as the new government enacted increasingly repressive measures agai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menshevik
The Mensheviks (russian: меньшевики́, from меньшинство 'minority') were one of the three dominant factions in the Russian socialist movement, the others being the Bolsheviks and Socialist Revolutionaries. The factions emerged in 1903 following a dispute within the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) between Julius Martov and Vladimir Lenin. The dispute originated at the 2nd Congress of the RSDLP, ostensibly over minor issues of party organization. Martov's supporters, who were in the minority in a crucial vote on the question of party membership, came to be called ''Mensheviks'', derived from the Russian ('minority'), while Lenin's adherents were known as ''Bolsheviks'', from ('majority'). Despite the naming, neither side held a consistent majority over the course of the entire 2nd Congress, and indeed the numerical advantage fluctuated between both sides throughout the rest of the RSDLP's existence until the Russian Revolution. The split pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirement of William P. Sisler in 2017, the university appointed as Director George Andreou. The press maintains offices in Cambridge, Massachusetts near Harvard Square, and in London, England. The press co-founded the distributor TriLiteral LLC with MIT Press and Yale University Press. TriLiteral was sold to LSC Communications in 2018. Notable authors published by HUP include Eudora Welty, Walter Benjamin, E. O. Wilson, John Rawls, Emily Dickinson, Stephen Jay Gould, Helen Vendler, Carol Gilligan, Amartya Sen, David Blight, Martha Nussbaum, and Thomas Piketty. The Display Room in Harvard Square, dedicated to selling HUP publications, closed on June 17, 2009. Related publishers, imprints, and series HUP owns the Belknap Press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of Russia since the latter half of the 16th century, after the Russians conquered lands east of the Ural Mountains. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to merely one-fifth of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk and Omsk are the largest cities in the region. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic region and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia extends eastwards from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. The river Yenisey divides Siberia into two parts, Western and Eastern. Siberia stretches southwards from the Arctic Ocean to the hills of nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans an archipelago of 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa. Tokyo is the nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the most densely populated and urbanized. About three-fourths of the country's terrain is mountainous, concentrating its population of 123.2 million on narrow coastal plains. Japan is divided into 47 administrative prefectures and eight traditional regions. The Greater Tokyo Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuel Komroff
Manuel Komroff (September 7, 1890 – 10 December 1974) was an American playwright, screenwriter, novelist, editor and translator. He was born in New York where he began his working life as a journalist. He also spent some time in Russia during the Russian revolution. Marco Polo One of his most successful publications was his edited version of '' The Travels of Marco Polo'', first published in 1926. He not only added a chapter which was missing in the William Marsden translation, but also revised parts of the Henry Yule editions. Works Novels *''The Grace of Lambs'' (1925, Boni & Liveright) *''Juggler's Kiss'' (1927, Boni & Liveright) *''Coronet'' (1930, Coward-McCann) *''Two Thieves'' (1931, Coward-McCann) *''I, the Tiger'' (1933, Coward-McCann) *''The March of the Hundred'' (1939, Coward-McCann) * ''The Christmas Letter'' (1941 American Artists Group, N.Y.) *''In the Years of Our Lord'' (1942, Harper & Bros.) *''Echo of Evil'' (1948, Farrar, Straus and Giroux) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferrer Center
The Ferrer Center and Stelton Colony were an anarchist social center and colony, respectively, organized to honor the memory of anarchist pedagogue Francisco Ferrer and to build a school based on his model in the United States. In the widespread outcry following Ferrer's execution in 1909 and the international movement that sprung in its wake, a group of New York anarchists convened as the Ferrer Association in 1910. Their headquarters, the Ferrer Center, hosted a variety of cultural events in the avant-garde arts and radical politics, including lectures, discussions, and performances. It was also home to the Ferrer Modern School, a libertarian, day school that emphasized unplanned, undogmatic curriculum. The Center moved several times throughout Manhattan to establish a space conducive to children's play. Following a bomb plot and police infiltration, several anarchists from the association decided to take the school out to the country. The school moved to what would become t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the city, up from 631,486 in 2016. The Greater Vancouver area had a population of 2.6million in 2021, making it the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Greater Vancouver, along with the Fraser Valley, comprises the Lower Mainland with a regional population of over 3 million. Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada, with over 5,700 people per square kilometre, and fourth highest in North America (after New York City, San Francisco, and Mexico City). Vancouver is one of the most ethnically and linguistically diverse cities in Canada: 49.3 percent of its residents are not native English speakers, 47.8 percent are native speakers of neither English nor French, and 54.5 percent of residents belong to visible minority groups. It has been consistently rank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Rocker
Johann Rudolf Rocker (March 25, 1873 – September 19, 1958) was a German anarchist writer and activist. He was born in Mainz to a Roman Catholic artisan family. His father died when he was a child, and his mother when he was in his teens, so he spent some time in an orphanage. As a youth he worked as a cabin boy on river boats and was then apprenticed as a typographer. He became involved in trade unionism and joined the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) before coming under the influence of anarchists such as Mikhail Bakunin and Peter Kropotkin. With other libertarian youth, he was expelled from the SPD, and his anarchist activism led to him fleeing Germany for Paris, where he came into contact with syndicalist and Jewish anarchist ideas and practices. In 1895, he moved to London. Apart from brief spells in Liverpool and elsewhere, he remained in East London for most of the next two decades, acting a key figure in the Yiddish-language anarchist scene there, including ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Provisional Government
The Russian Provisional Government ( rus, Временное правительство России, Vremennoye pravitel'stvo Rossii) was a provisional government of the Russian Republic, announced two days before and established immediately after the abdication of Nicholas II. The intention of the provisional government was the organization of elections to the Russian Constituent Assembly and its convention. The provisional government, led first by Prince Georgy Lvov and then by Alexander Kerensky, lasted approximately eight months, and ceased to exist when the Bolsheviks gained power in the October Revolution in October Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="ovember, Old Style and New Style dates">N.S.1917. According to Harold Whitmore Williams, the history of the eight months during which Russia was ruled by the Provisional Government was the history of the steady and systematic disorganization of the army. For most of the life of the Provisional Government, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worker Collective
A worker cooperative is a cooperative owned and self-managed by its workers. This control may mean a firm where every worker-owner participates in decision-making in a democratic fashion, or it may refer to one in which management is elected by every worker-owner who each have one vote. History Worker cooperatives rose to prominence during the Industrial Revolution as part of the labour movement. As employment moved to industrial areas and job sectors declined, workers began organizing and controlling businesses for themselves. Worker cooperatives were originally sparked by "critical reaction to industrial capitalism and the excesses of the industrial revolution." Some worker cooperatives were designed to "cope with the evils of unbridled capitalism and the insecurities of wage labor". The philosophy that underpinned the cooperative movement stemmed from the socialist writings of thinkers including Robert Owen and Charles Fourier. Robert Owen, considered by many as the fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chichester
Chichester () is a cathedral city and civil parish in West Sussex, England.OS Explorer map 120: Chichester, South Harting and Selsey Scale: 1:25 000. Publisher:Ordnance Survey – Southampton B2 edition. Publishing Date:2009. It is the only city in West Sussex and is its county town. It was a Roman and Anglo-Saxon settlement and a major market town from those times through Norman and medieval times to the present day. It is the seat of the Church of England Diocese of Chichester, with a 12th-century cathedral. The city has two main watercourses: the Chichester Canal and the River Lavant. The Lavant, a winterbourne, runs to the south of the city walls; it is hidden mostly in culverts when close to the city centre. History Roman period There is no recorded evidence that the city that became Chichester was a settlement of any size before the coming of the Romans. The area around Chichester is believed to have played a significant part during the Roman invasion of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Workers Of The World
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), members of which are commonly termed "Wobblies", is an international labor union that was founded in Chicago in 1905. The origin of the nickname "Wobblies" is uncertain. IWW ideology combines general unionism with industrial unionism, as it is a general union, subdivided between the various industries which employ its members. The philosophy and tactics of the IWW are described as "revolutionary industrial unionism", with ties to socialist, syndicalist, and anarchist labor movements. In the 1910s and early 1920s, the IWW achieved many of their short-term goals, particularly in the American West, and cut across traditional guild and union lines to organize workers in a variety of trades and industries. At their peak in August 1917, IWW membership was estimated at more than 150,000, with active wings in the United States, the UK, Canada, and Australia. The extremely high rate of IWW membership turnover during this era (estimated at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |