|
Gods, Demons And Others
''Gods, Demons and Others'' is a collection of short stories by R. K. Narayan adapted from Indian history and mythology, including epics like '' The Ramayana'' and ''Mahābhārata''. In this book, Narayan provides both vitality and an original viewpoint to ancient legends. Introduction "Gods, Demons and Others'' is a collection of ancient tales from India's complex history and mythology presented in their traditional setting, albeit with Narayan's urbane and affectionate, satirical style, bereft of any didactic interludes. The selection of stories includes only those that center on outstanding personalities who transcend the boundaries of time and age. The book consists of 15 stories. Book outline ;Lavana The story of Lavana, a king on a spiritual journey (not the asura mentioned in the Ramayana that is different). ;Chudala The story of a king trying to attain self-realisation. ;Yayati The story of Yayati, an asura king. ;Devi The story of the Goddess Devi, responsible for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinemann (publisher)
William Heinemann Ltd., with the imprint Heinemann, was a London publisher founded in 1890 by William Heinemann. Their first published book, 1890's ''The Bondman'', was a huge success in the United Kingdom and launched the company. He was joined in 1893 by Sydney Pawling. Heinemann died in 1920 and Pawling sold the company to Doubleday, having worked with them in the past to publish their works in the United States. Pawling died in 1922 and new management took over. Doubleday sold his interest in 1933. Through the 1920s, the company was well known for publishing works by famous authors that had previously been published as serials. Among these were works by H. G. Wells, Rudyard Kipling, W. Somerset Maugham, George Moore, Max Beerbohm, and Henry James, among others. This attracted new authors to publish their first editions with the company, including Graham Greene, Edward Upward, J.B. Priestley and Vita Sackville-West. Throughout, the company was also known for its class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
śloka
Shloka or śloka ( sa, श्लोक , from the root , Macdonell, Arthur A., ''A Sanskrit Grammar for Students'', Appendix II, p. 232 (Oxford University Press, 3rd edition, 1927). in a broader sense, according to Monier-Williams's dictionary, is "any verse or stanza; a proverb, saying"; but in particular it refers to the 32-line verse, derived from the Vedic ''anuṣṭubh'' metre, used in the '' Bhagavad Gita'' and many other works of classical Sanskrit literature. In its usual form it consists of four ''pādas'' or quarter-verses, of 8 syllables each, or (according to an alternative analysis) of two half-verses of 16 syllables each. The metre is similar to the Vedic ''anuṣṭubh'' metre, but with stricter rules. The ''śloka'' is the basis for Indian epic poetry, and may be considered the Indian verse form ''par excellence'', occurring as it does far more frequently than any other metre in classical Sanskrit poetry. The ''śloka'' is the verse-form generally used in the ''Mah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dushyanta
Dushyanta ( sa, दुष्यन्त, translit=Duṣyanta) is a king of the Chandravamsha (Lunar) dynasty featured in Hindu literature. He is the husband of Shakuntala and the father of Bharata. He appears in the Mahabharata and in Kalidasa's play, Abhijnanashakuntalam ( 300 CE). Legend According to the ''Mahabharata'', Dushyanta is the son of Ilin and Rathantī, also rendered Ilina and Rathantara, respectively. According to primogeniture, Dushyanta succeeds his father, for he is the eldest among his siblings Sura, Bhima, Pravashu, and Vasu. He rules as the king of Hastinapura. Mahabharata The Mahabharata narrates that King Dushyanta was once hunting in the forests, when he struck a fawn with his arrow. The fawn fled to the ashrama of Sage Kanva, and the king followed it. Upon reaching the ashrama, the king saw Shakuntala watering the plants, accompanied by her friends, named Anasuya and Priyamvada. Dushyanta and Shakuntala fell in love with each other. Since the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viswamitra
Vishvamitra ( sa, विश्वामित्र, ) is one of the most venerated rishis or sages of ancient India. According to Hindu tradition, he is stated to have written most of the Mandala 3 of the Rigveda, including the Gayatri Mantra. The Puranas mention that only 24 rishis since antiquity have understood the whole meaning of —and thus wielded the whole power of — the Gayatri Mantra. Vishvamitra is supposed to have been the first, and Yajnavalkya the last. Before renouncing his kingdom and royal status, Brahmarishi Vishvamitra was a king, and thus he retained the title of Rajarshi, or 'royal sage'. Textual background Historically, Viśvāmitra Gāthina was a Rigvedic rishi who was the chief author of Mandala 3 of the Rigveda. Viśvāmitra was taught by Jamadagni Bhārgava. He was the purohita of the Bharata tribal king Sudās, until he was replaced by Vasiṣṭha. He aided the Bharatas in crossing the Vipāś and Śutudrī rivers (modern Beas and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shakuntala
Shakuntala (Sanskrit: ''Śakuntalā'') is the wife of Dushyanta and the mother of Emperor Bharata. Her story is told in the '' Adi Parva'' of the ancient Indian epic ''Mahabharata'' and dramatized by many writers, the most famous adaption being Kalidasa's play '' Abhijñānaśākuntala'' (''The Sign of Shakuntala''). Legends Birth Once, Vishvamitra started to meditate to earn the status of a Brahmarshi. The intensity of his penance frightened Indra. He feared that Vishvamitra might want his throne. To end his penance, Indra sent Menaka, an apsara, to lure him and bring him out of his penance. Menaka reached Vishwamitra's meditating spot and started to seduce him. Vishvamitra could not control his lust and desire and his penance was broken. Vishvamitra and Menaka lived together for a few years and a daughter was born to them. Later, Vishvamitra realized that all those things were Indra's tricks. He realized that he needed to control his emotions. Vishvamitra left Menaka an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
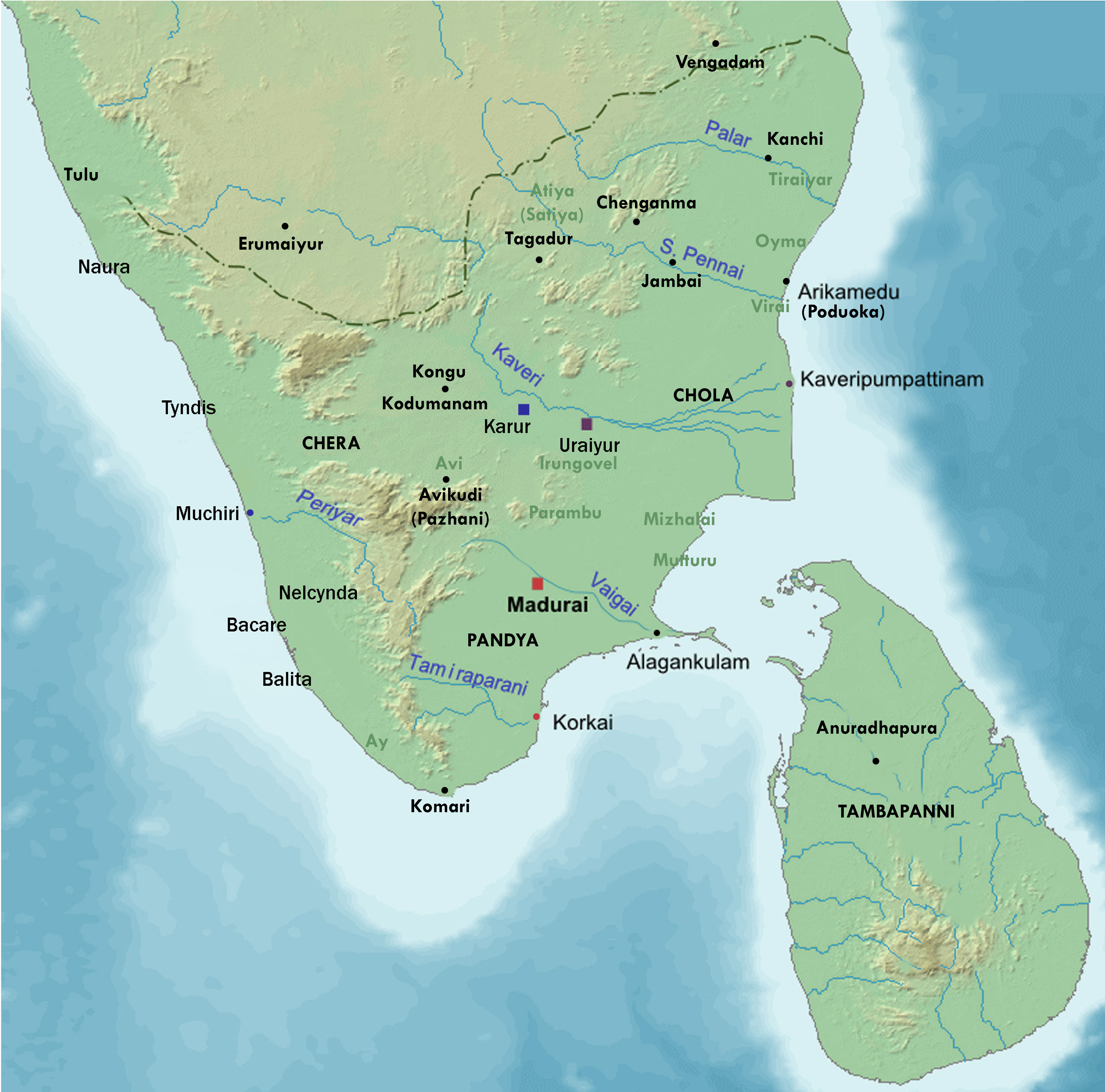
Silappathigaram
''Cilappatikāram'' ( ta, சிலப்பதிகாரம் ml, ചിലപ്പതികാരം,IPA: ʧiləppət̪ikɑːrəm, ''lit.'' "the Tale of an Anklet"), also referred to as ''Silappathikaram'' or ''Silappatikaram'', is the earliest Tamil epic. It is a poem of 5,730 lines in almost entirely ''akaval'' (''aciriyam'') meter. The epic is a tragic love story of an ordinary couple, Kannaki and her husband Kovalan. The ''Silappathikaram'' has more ancient roots in the Tamil bardic tradition, as Kannaki and other characters of the story are mentioned or alluded to in the Sangam literature such as in the ''Naṟṟiṇai'' and later texts such as the ''Kovalam Katai''. It is attributed to a prince-turned-monk Iḷaṅkõ Aṭikaḷ, and was probably composed in the 5th or 6th century CE. The ''Silappatikaram'' is set in a flourishing seaport city of the early Chola kingdom. Kannaki and Kovalan are a newly married couple, in love, and living in bliss. Over time, Koval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Language
Tamil (; ' , ) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is an official language of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, the sovereign nations of Sri Lanka and Singapore, and the Indian territory of Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry. Tamil is also spoken by significant minorities in the four other South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is also spoken by the Tamil diaspora found in many countries, including Malaysian Tamil, Malaysia, Myanmar Tamils, Myanmar, Tamil South Africans, South Africa, British Tamils, United Kingdom, Tamil Americans, United States, Tamil Canadians, Canada, Tamil Australians, Australia and Tamil Mauritians, Mauritius. Tamil is also natively spoken by Sri Lankan Moors. One of 22 scheduled languages in the Constitution of India, Tamil was the first to be classified as a Languages of India, classical language of India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannagi (Tamil Mythology)
Kannagi ( ta, கண்ணகி) sometimes spelled Kannaki, is a legendary Tamil people, Tamil woman who forms the central character of the Tamil Epic poetry, epic ''Silapadhigaaram, Cilappatikaram''. Kannagi is described as the chaste woman who stays with her husband despite his unfaithfulness, their attempt to rebuild their marriage after her husband had lost everything but repented, how her husband is falsely framed then punished without the due checks and processes of justice. Kannagi proves and protests the injustice, then curses the king and city of Madurai leading to the death of the unjust Early Pandyan Kingdom, Pandyan Nedunj Cheliyan I, King of Madurai, who had wrongfully put her husband Kovalan to death. The society that had made her suffer, suffers in retribution as the city Madurai is burnt to the ground because of her curse. In the Chera/Perumals of Makotai, Chera (Kerala) and Tamil tradition, Kannagi has been deified as the symbol – sometimes as goddess – of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markandeya
Bhargava Markandeya ( sa, मार्कण्डेय ) is an ancient rishi (sage) born in the clan of Bhrigu Rishi (Bhargava Brahmins Community). The Markandeya Purana especially, comprises a dialogue between Markandeya and a sage called Jaimini, and a number of chapters in the Bhagavata Purana are dedicated to his conversations and prayers. He is also mentioned in the Mahabharata. Markandeya is venerated within all mainstream Hindu traditions. Today, Markandeya Tirtha, where the sage Markandeya wrote the Markandeya Purana is situated on a trekking route to the Yamunotri Shrine in the Uttarkashi district, Uttarakhand.Yamunotri Temple website. Rescued by K ...
|
Savitri And Satyavan
In Hinduism, Savitri and Satyavan ( sa, सावित्री ''Sāvitrī'' and ''Satyavān'') are a legendary couple, known for Savitri's love and devotion to her husband Satyavan. According to the legend, princess Savitri marries an exiled prince named Satyavan, who was prophesied to die early. The later part of legend focuses on Savitri's wit and love, which saved her husband from the death god Yama. The oldest known version of the story of Savitri and Satyavan is found in '' Vana Parva'' ("The Book of the Forest") of the ''Mahabharata''. The story occurs as a multiply- embedded narrative in the ''Mahabharata'' as told by sage Markandeya. When Yudhishthira asks Markandeya whether there has ever been a woman whose devotion matched Draupadi's, Markandeya replies by relating this story. Story The childless king of the Madra Kingdom, Ashwapati, lives ascetically for many years and offers oblations to Sun God Savitr. His consort is Malavika. Finally, pleased by the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damayanti
''Damayanti'' (Sanskrit: दमयंती) is a character in a love story found in the Vana Parva book of the Mahabharata. She was the daughter of Bhima (not the Pandava one) and a princess of the Vidarbha Kingdom, who married King Nala of the Nishadha Kingdom. The character is also found in other Hindu texts by many authors in numerous Indian languages. She, along with Nala, are the central characters in the 12th century text Nishadha Charita, one of the five ''mahakavyas'' (great epic poems) in the canon of Sanskrit literature, written by Sriharsha. Story Damayanti was the Yadava princess of Vidarbha Kingdom. One day, a beautiful swan came to her and told her about Nala, king of Nishadha. The swan was sent by Nala after hearing about her from it. After hearing about Nala, she was impressed with him and wanted to marry him. A swayamvara was organized by Damayanti's father and Nala was also invited. Damayanti chose Nala out of the kings and princes and married. After a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nala
Nala (Sanskrit: नल) is a character in the '' Vana Parva'' book of the ''Mahabharata''. He was the king of Nishadha Kingdom and the son of Veerasena. Nala was known for his skill with horses and for his culinary expertise. He married princess Damayanti, of the Vidarbha Kingdom. He was blessed by goddess Kali. He was also a great cook and wrote the first-ever book on cookery, Pakadarpanam (Sanskrit: पाकदर्पण). Even today, a consistently good chef/cook is credited as someone with Nala-Bhagam to mean that their dish tastes as if Nala has prepared it. He is said to have been able to cook a full meal without lighting fire. Story Nala's story is told in the Vana Parva of the Mahabharata and was adapted into various versions. According to the 12th century text Nishadha Charita, one of the five '' mahakavyas'' (great epic poems) in the canon of Sanskrit literature, written by Sriharsha, Nala, King of Nishadha, found a beautiful swan in a forest. The swan tol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |