|
Gnaeus Pinarius Cornelius Clemens
Gnaeus Pinarius Cornelius Clemens (fl. 1st century AD) was a Roman military officer and senator who was appointed Suffect consul during the reign of Vespasian. He is primarily known through inscriptions. Biography Possibly originating from Hispania, son of a Lucius, Clemens Pinarius' polyonymous name poses a challenge: C. Castillo has argued that he was born a Cornelius L.f. who was adopted by a Gnaeus Pinarius; Olli Salomies, however, reports that "among the numerous Pinarii I can find only one Gnaeus, whereas, on the other hand, this praenomen was much in use among the Cornelii." This led Salomies to speculate that he was originally a Gnaeus Cornelius L.f. who added the element "Pinarius" from his mother's side; but noting the existence of Gnaeus Pinarius Aemilius Cicatricula, suffect consul in 72, Salomies concluded that "it is much better to assume" the existence of a Gnaeus Pinarius, despite lack of evidence otherwise of the senator, who adopted both men. In a later article, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
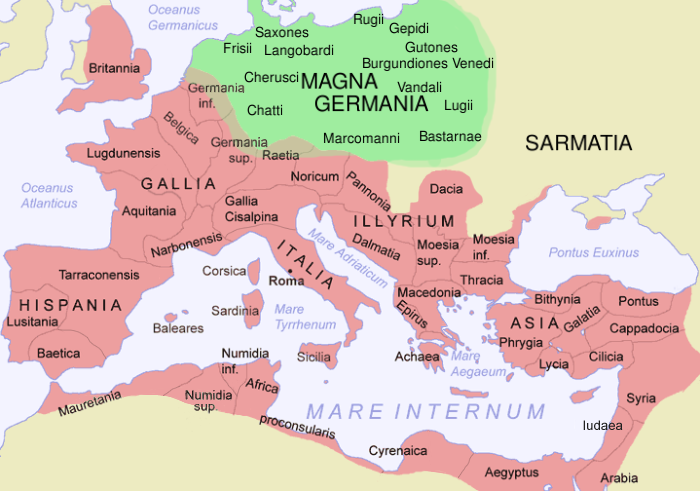
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio VIII Augusta
Legio VIII Augusta ("Augustus' Eighth Legion") was one of the oldest legions of the Imperial Roman army. In republican service They were ordered to Cisalpine Gaul around 58 BC by Julius Caesar and marched with him throughout the entirety of the Gallic Wars, especially during the battles of Gergovie and Alesia. During the war the legion won the title "Gallica." It also earned a reputation for courage. They stood with him at the Battle of Pharsalus. The legion was also present in Egypt, when Caesar captured Egypt for Cleopatra. In 46 BC, it took part in the Battle of Thapsus near what is now Bakalta, Tunisia shortly before their disbandment. In 44 BC, Octavian reconstituted the legion that had helped him attain the control of the Roman Empire. In 43 BC it took part in the siege of the Battle of Mutina (current Modena) by Marc Antony, defended by the troops of Decimus Brutus, which earned Legio VIII Gallica the nickname "Mutinensis". In imperial service In or before 9 AD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Undated Roman Consuls
This is a list of Roman consuls, individuals who were either elected or nominated to the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic, or a high office of the Empire, but for whom an exact date of when they served in office is absent. Most are reckoned to be suffect consuls, but occasionally it encompasses an ordinary consul. 3rd century BC 1st century AD 2nd century 3rd century 4th century Footnotes References {{Reflist, 30em Sources * Alföldy, Géza ''Konsulat und Senatorenstand unter der Antoninen'' Bonn: Rudolf Habelt Verlag (1977) * Jones, A. H. M.; Martindale, J. R.; Morris, J. ''The Prosopography of the later Roman Empire, Vol. I, AD 260-395'' (1971) * Leunissen, Paul M. M. ''Konsuln und Konsulare in der Zeit von Commodus bis Severus Alexander'' (1989) Roman consuls Consuls A consul is an official representative of a government who resides in a foreign country to assist and protect citizens of the consul's country, and to promote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnaeus Pinarius Cornelius Severus
Gnaeus Pinarius Cornelius Severus was a Roman politician and senator in the 2nd century AD. Biography Severus came from the gens Pinaria gens, Pinaria, an ancient Patrician (ancient Rome), patrician family that had held several consulships since the 5th century BC. He was probably the grandson of Gnaeus Pinarius Cornelius Clemens, consul in 71/72 AD.Hans George Gundel, ''The Little Pauly's Encyclopedia of Classical Antiquity'', Vol. 4, pp. 855–857 Severus belonged to the Salii, Salian priesthood, an order of patrician youths dedicated to Mars (mythology), Mars. Emperor Trajan advanced his political career, resulting in Severus achieving the quaestorship and praetorship.''Prosopographia Imperii Romani'', p. 1453 In 112 AD, he was appointed suffect consul. He also held the offices of augur and ''Rex Sacrorum, rex sacrorum''. References 2nd-century Roman consuls Suffect consuls of Imperial Rome Roman quaestors Imperial Roman praetors Augurs of the Roman Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispellum
Hispellum (modern Spello) was an ancient town of Umbria, Italy, north of Fulginiae on the road to Perusia. The Site The site of Hispellum was significant as the valley had two major rivers, the Clitumnus and Tinia mentioned by Silius Italicus, giving fertility to the land. From 220 BC the Via Flaminia gave the city a direct link to Rome. History The area of Hispellum has been occupied from the Iron Age (7th c. BC), as shown by archaeology particularly in the necropolis at Portonaccio, although most of the tombs date to the 3rd or 2nd century BC. Traces of the early settlement from 7th - 4th centuries BC have been found near the church of Sant’ Andrea. Umbria had been conquered by the Romans by approximately 260 BC. Incorporation into the Roman state occurred soon afterwards; some Umbri were given full citizenship or citizenship without the right to vote and about 40,000 Romans settled in the region. Hispellum was one of the Umbrian towns that resisted Hannibal and po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mogontiacum
''Mogontiacum'' (also ''Moguntiacum'') is the Latin name of today's city of Mainz, which it bore during its almost 500 years as part of the Roman Empire. ''Mogontiacum'' had its origins in the legionary camp built by Drusus in 13/12 BCE, which was strategically located on a above the Rhine and opposite the mouth of the Main on the . The civilian settlements ('' vici'') in the vicinity of the camp, which spread down the Rhine, quickly grew together to form a larger, urbanised settlement. However, unlike ''Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium'' (Cologne) or ''Augusta Treverorum'' (Trier), ''Mogontiacum'' was primarily a military centre until the second half of the 4th century and was apparently not a '' colonia'' either. As a result, the city never had the urban character of the other large Roman cities in Germany. Nevertheless, several monumental buildings were also erected here, as ''Mogontiacum'' was the provincial capital of the Roman province of ''Germania'' '' Superior'' with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augusta Vindelicorum
Augsburg ( , ; ; ) is a city in the Bavarian part of Swabia, Germany, around west of the Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and the regional seat of the Swabia with a well preserved Altstadt (historical city centre). Augsburg is an urban district and home to the institutions of the Landkreis Augsburg. It is the third-largest city in Bavaria (after Munich and Nuremberg), with a population of 304,000 and 885,000 in its metropolitan area. After Neuss, Trier, Worms, Cologne and Xanten, Augsburg is one of Germany's oldest cities, founded in 15 BC by the Romans as Augusta Vindelicorum and named after the Roman emperor Augustus. It was a Free Imperial City from 1276 to 1803 and the home of the patrician Fugger and Welser families that dominated European banking in the 16th century. According to Behringer, in the sixteenth century it became "the dominant centre of early capitalism", having benefited from being part of the Kaiserliche Reichspost system as "the lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest south into the Black Sea. A large and historically important river, it was once a frontier of the Roman Empire. In the 21st century, it connects ten European countries, running through their territories or marking a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , passing through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Ukraine. Among the many List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river are four national capitals: Vienna, Bratislava, Budapest, and Belgrade. Its drainage basin amounts to and extends into nine more countries. The Danube's longest headstream, the Breg (river), Breg, rises in Furtwangen im Schwarzwald, while the river carries its name from its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentoratum
Argentoratum or Argentorate was the ancient name of the city of Strasbourg. The name was first mentioned in 12 BC, when it was a Roman military outpost established by Nero Claudius Drusus. From 90 AD the Legio VIII Augusta was permanently stationed there. History The Romans under Nero Claudius Drusus established a military outpost belonging to the Germania Superior Roman province close to a Gaulish village near the banks of the Rhine, at the current location of Strasbourg, and named it Argentoratum. Its name was first mentioned in 12 BC but "Argentorate" is the toponym of the Gaulish settlement that preceded it before being latinised, though it is not known by how long. From 90 AD the Legio VIII Augusta permanently stationed in Argentoratum. The Roman camp of Argentoratum then included a cavalry section and covered an area of approximately , from approximately in Tiberian times. Other Roman legions temporarily stationed in Argentoratum were the Legio XIV Gemina and the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
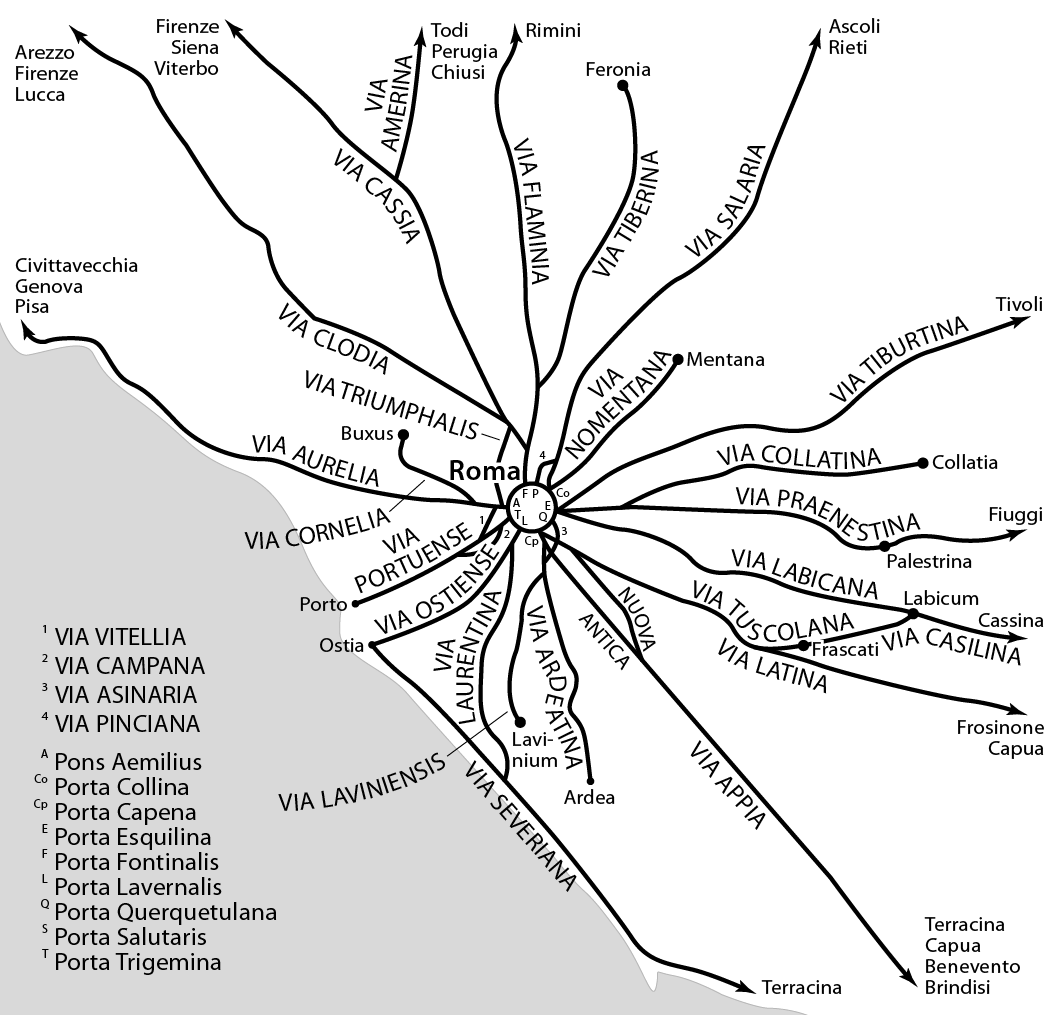
Roman Road
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, 1986. At the peak of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agri Decumates
The ''Agri Decumates'' or ''Decumates Agri'' ("Decumatian Fields") were a region of the Roman Empire's provinces of Germania Superior and Raetia, covering the Black Forest, Swabian Jura, and Franconian Jura areas between the Rhine, Main, and Danube rivers, in present southwestern Germany, including present Frankfurt, Stuttgart, Freiburg im Breisgau, and Weißenburg in Bayern. The only ancient reference to the name comes from Tacitus' book ''Germania'' (chapter 29).M. Grant, ''A Guide to the Ancient World'', p. 17Tac. Ger. 29 However, the later geographer does mention "the desert of the Helvetians" in this area. The meaning of ''Decumates'' is l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Triumph
The Roman triumph (') was a civil ceremony and religious rite of ancient Rome, held to publicly celebrate and sanctify the success of a military commander who had led Roman forces to victory in the service of the state or, in some historical traditions, one who had successfully completed a foreign war. On the day of his triumph, the general wore a crown of laurel and an all-purple, gold-embroidered triumphal '' toga picta'' ("painted" toga), regalia that identified him as near-divine or near-kingly. In some accounts, his face was painted red, perhaps in imitation of Rome's highest and most powerful god, Jupiter. The general rode in a four-horse chariot through the streets of Rome in unarmed procession with his army, captives, and the spoils of his war. At Jupiter's temple on the Capitoline Hill, he offered sacrifice and the tokens of his victory to Jupiter. In Republican tradition, only the Senate could grant a triumph. The origins and development of this honour are obscur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |