|
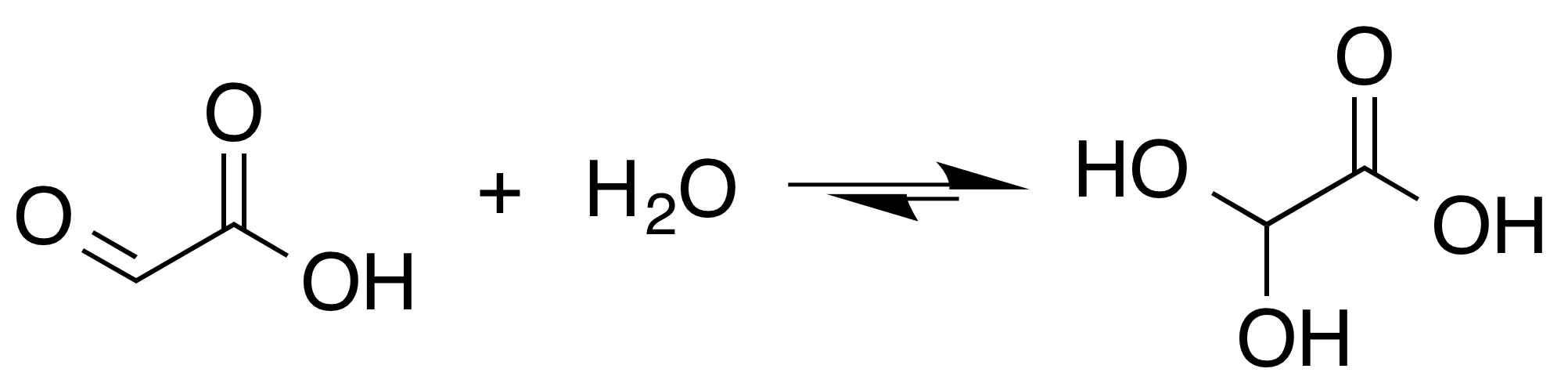
Glyoxylate
Glyoxylic acid or oxoacetic acid is an organic compound. Together with acetic acid, glycolic acid, and oxalic acid, glyoxylic acid is one of the C2 carboxylic acids. It is a colourless solid that occurs naturally and is useful industrially. Structure and nomenclature The structure of glyoxylic acid is shown as having an aldehyde functional group. The aldehyde is only a minor component of the form most prevalent in some situations. Instead, glyoxylic acid often exists as a hydrate or a cyclic dimer. For example, in the presence of water, the carbonyl rapidly converts to a geminal diol (described as the "monohydrate"). The equilibrium constant (''K'') is 300 for the formation of dihydroxyacetic acid at room temperature: Dihydroxyacetic acid has been characterized by X-ray crystallography. : In aqueous solution, this monohydrate exists in equilibrium with a hemi acylal dimer form:Georges Mattioda and Yani Christidis “Glyoxylic Acid” Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycolic Acid
Glycolic acid (or hydroxyacetic acid; chemical formula ) is a colorless, odorless and hygroscopic crystal, crystalline solid, highly solubility, soluble in water. It is used in various skin care, skin-care products. Glycolic acid is widespread in nature. A glycolate (sometimes spelled "glycollate") is a Salt (chemistry), salt or ester of glycolic acid. History The name "glycolic acid" was coined in 1848 by French chemist Auguste Laurent (1807–1853). He proposed that the amino acid glycine—which was then called ''glycocolle''—might be the amine of a hypothetical acid, which he called "glycolic acid" (''acide glycolique''). Glycolic acid was first prepared in 1851 by German chemist Adolph Strecker (1822–1871) and Russian chemist Nikolai Nikolaevich Sokolov (1826–1877). They produced it by treating hippuric acid with nitric acid and nitrogen dioxide to form an ester of benzoic acid and glycolic acid (), which they called "benzoglycolic acid" (''Benzoglykolsäure''; also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society and professional association in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 49,000 in the world. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge (named after Thomas Graham (chemist), Thomas Graham, the first president of the Chemical Society) where ''RSC Publishing'' is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing and Shanghai, People' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geminal Diol
A geminal diol (or gem-diol for short) is any organic compound having two hydroxyl functional groups () bound to the same carbon atom. Geminal diols are a subclass of the diols, which in turn are a special class of alcohols. Most of the geminal diols are considered unstable. The simplest geminal diol is methanediol or . Other examples are: * dihydroxymalinic acid * decahydroxycyclopentane *chloral hydrate Reactions Hydration equilibrium Geminal diols can be viewed as ketone (or aldehyde) hydrates. The two hydroxyl groups in a geminal diol are easily converted to a carbonyl or keto group C=O by loss of one water molecule. Conversely, a keto group can combine with water to form the geminal hydroxyl groups. The equilibrium in water solution may be shifted towards either compound. For example, the equilibrium constant for the conversion of acetone to propane-2,2-diol is about 10−3, while that of formaldehyde to methanediol is 103.Eric V. Anslyn, Dennis A. Dougherty ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amidation
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, as in asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a derivative of a carboxylic acid () with the hydroxyl group () replaced by an amino group (); or, equivalently, an acyl (alkanoyl) group () joined to an amino group. Common amides are formamide (), acetamide (), benzamide (), and dimethylformamide (). Some uncommon examples of amides are ''N''-chloroacetamide () and chloroformamide (). Amides are qualified as primary, secondary, and tertiary according to the number of acyl groups bounded to the nitrogen atom. Nomenclature The core of amides is called the amide group (specifically, carboxamide group). In the usual n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjugate Base
A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid gives a proton () to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as it loses a hydrogen ion in the reverse reaction. On the other hand, a conjugate base is what remains after an acid has donated a proton during a chemical reaction. Hence, a conjugate base is a substance formed by the removal of a proton from an acid, as it can gain a hydrogen ion in the reverse reaction. Because some acids can give multiple protons, the conjugate base of an acid may itself be acidic. In summary, this can be represented as the following chemical reaction: \text + \text \; \ce \; \text + \text Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and Martin Lowry introduced the Brønsted–Lowry theory, which said that any compound that can give a proton to another compound is an acid, and the compound that receives the proton is a base. A proton is a subatomic particle in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry's Law
In physical chemistry, Henry's law is a gas law that states that the amount of dissolved gas in a liquid is directly proportional at equilibrium to its partial pressure above the liquid. The proportionality factor is called Henry's law constant. It was formulated by the English chemist William Henry, who studied the topic in the early 19th century. In simple words, it states that the partial pressure of a gas in the vapour phase is directly proportional to the mole fraction of a gas in solution. An example where Henry's law is at play is the depth-dependent dissolution of oxygen and nitrogen in the blood of underwater divers that changes during decompression, going to decompression sickness. An everyday example is carbonated soft drinks, which contain dissolved carbon dioxide. Before opening, the gas above the drink in its container is almost pure carbon dioxide, at a pressure higher than atmospheric pressure. After the bottle is opened, this gas escapes, moving the partial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxyl
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e.g., alkyl, alkenyl, aryl), or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They often have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid () is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named as a " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen-bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, covalently bonded to a more electronegative donor atom or group (Dn), interacts with another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor (Ac). Unlike simple dipole–dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding arises from charge transfer (nB → σ*AH), orbital interactions, and quantum mechanical delocalization, making it a resonance-assisted interaction rather than a mere electrostatic attraction. The general notation for hydrogen bonding is Dn−H···Ac, where the solid line represents a polar covalent bond, and the dotted or dashed line indicates the hydrogen bond. The most frequent donor and acceptor atoms are nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), and fluorine (F), due to their high electronegativity and ability to engage in stronger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conformational Isomerism
In chemistry, rotamers are chemical species that differ from one another primarily due to rotations about one or more single bonds. Various arrangements of atoms in a molecule that differ by rotation about single bonds can also be referred to as conformations. Conformers/rotamers differ little in their energies, so they are almost never separable in a practical sense. Rotations about single bonds are subject to small energy barriers. When the time scale for interconversion is long enough for isolation of individual rotamers (usually arbitrarily defined as a half-life of interconversion of 1000 seconds or longer), the species are termed atropisomers (''see:'' atropisomerism). The Ring flip, ring-flip of substituted cyclohexanes constitutes a common form of conformers. The study of the energetics of bond rotation is referred to as conformational analysis. In some cases, conformational analysis can be used to predict and explain product selectivity, mechanisms, and rates of reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |