|
Glycerol Monostearate
Glycerol monostearate, commonly known as GMS, is a monoglyceride commonly used as an emulsifier in foods. It takes the form of a white, odorless, and sweet-tasting flaky powder that is hygroscopic. Chemically it is the glycerol ester of stearic acid. It is also used as hydration powder in exercise formulas. Structure, synthesis, and occurrence Glycerol monostearate exists as three stereoisomers, 2-glycerol monostearate and the enantiomeric pair of 1-glycerol monostearate. Typically these are encountered as a mixture as many of their properties are similar. Commercial material used in foods is produced industrially by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides (from either vegetable or animal fats) and glycerol. Glycerol monostearate occurs naturally in the body as a product of the breakdown of fats by pancreatic lipase. It is present at very low levels in certain seed oils. Uses GMS is a food additive used as a thickening, emulsifying, anticaking, and preservative age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
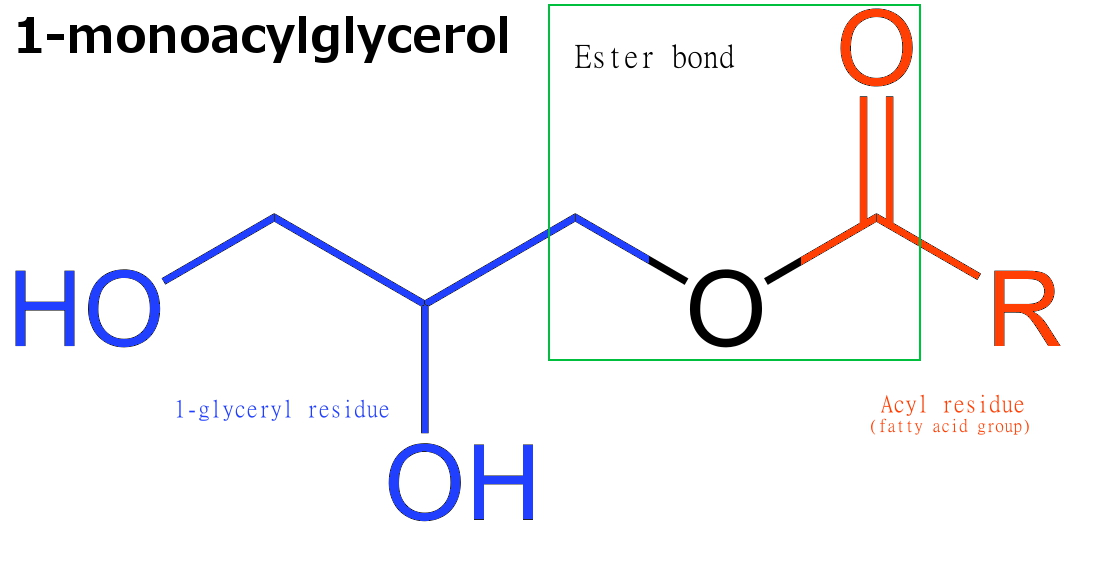
Monoglyceride
Monoglycerides (also: acylglycerols or monoacylglycerols) are a class of glycerides which are composed of a molecule of glycerol linked to a fatty acid via an ester bond. As glycerol contains both primary and secondary alcohol groups two different types of monoglycerides may be formed; 1-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to a primary alcohol, or a 2-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to the secondary alcohol. Synthesis Monoglycerides are produced both biologically and industrially. They are naturally present at very low levels (0.1-0.2%) in some seed oils such as olive oil, rapeseed oil and cottonseed oil. They are biosynthesized by the enzymatic hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoprotein lipase and the enzymatic hydrolysis of diglycerides by diacylglycerol lipase; or as an intermediate in the alkanoylation of glycerol to form fats. Several monoglycerides are pharmacologically active (e.g. 2-oleoylglycerol, 2-arachidonoylglycerol). Industrial pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticaking Agent
An anticaking agent is an additive placed in powdered or granulated materials, such as table salt or confectioneries, to prevent the formation of lumps ( caking) and for easing packaging, transport, flowability, and consumption. Caking mechanisms depend on the nature of the material. Crystalline solids often cake by formation of liquid bridge and subsequent fusion of microcrystals. Amorphous materials can cake by glass transitions and changes in viscosity. Polymorphic phase transitions can also induce caking. Some anticaking agents function by absorbing excess moisture or by coating particles and making them water-repellent. Calcium silicate (CaSiO3), a commonly used anti-caking agent, added to e.g. table salt, absorbs both water and oil. Anticaking agents are also used in non-food items such as road salt, fertilisers, cosmetics, and detergents. Some studies suggest that anticaking agents may have a negative effect on the nutritional content of food; one such study indicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-ionic Surfactants
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons (e.g. K+ (potassium ion)) while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons (e.g. Cl− (chloride ion) and OH− (hydroxide ion)). Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed ''monatomic ions'', ''atomic ions'' or ''simple ions'', while ions consisting of two or more atoms are termed polyatomic ions or ''molecular ions''. If only a + or − is present, it indicate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid Esters
Fatty is a derogatory term for someone who is obese. It may refer also to: People Nickname * Roscoe Arbuckle (1887–1933), American actor and comedian * Fatty Briody (1858–1903), American Major League Baseball player * Bob Fothergill (1897–1938), American Major League Baseball outfielder * William Foulke (footballer) (1874–1916), English cricketer and footballer * Richard Lamb (1907–1974), Australian racing cyclist * Fatty Lawrence (1903–1976), American college gridiron football player * W. T. McLain (1885–1938), American college gridiron football player, lawyer and politician * Charles H. Smith (American football), University of Michigan football player in 1893–1894 * Fatty Taylor (1946–2017), retired American Basketball Association and National Basketball Association player * Paul Vautin (born 1959), Australian former rugby league footballer and coach, television presenter and commentator * Thomas Walsh (mobster) (died 1929), New York City mobster * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicinal Diols of changed physical/molecular structure at the boundary of many liquids and a barrier has been described as the interfacial layer or the vicinal layer.
{{disambig ...
Vicinal ''("In the neighbourhood of")'' is a general adjective used as a standard, specific, technical descriptor in a range of contexts, including: * Vicinal (chemistry), stands for any two functional groups bonded to two adjacent atoms. * Vicinal tramway or ''Buurtspoor'', a system of narrow gauge tramways or local railways in Belgium. * In materials science, a "vicinal substrate" is a thin-film substrate whose surface normal deviates slightly from a major crystallographic axis. * In physics, the exclusion zone An exclusion zone is a geographic area in which specific activities are prohibited by an authority. The United States Department of Defense defines an exclusion zone is a territory where an authority prohibits specific activities in a specific g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Additives
Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. Some additives, such as vinegar ( pickling), salt ( salting), smoke (smoking) and sugar (crystallization), have been used for centuries to preserve food. This allows for longer-lasting foods, such as bacon, sweets, and wines. With the advent of ultra-processed foods in the late 20th century, many additives having both natural and artificial origin were introduced. Food additives also include substances that may be introduced to food indirectly (called "indirect additives") in the manufacturing process through packaging, storage or transport. In Europe and internationally, many additives are designated with E numbers, while in the United States, additives in amounts deemed safe for human consumption are designated as GRAS. Identification To regulate these additives and inform consumers each additive is assigned a unique number called an "E number", which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Pharmacopoeia
The ''British Pharmacopoeia'' (''BP'') is the national pharmacopoeia of the United Kingdom. It is an annually published collection of quality standards for medicinal substances in the UK, which is used by individuals and organisations involved in pharmaceutical research, development, manufacture and testing. Pharmacopoeial standards are publicly available and legally enforceable standards of quality for medicinal products and their constituents. The ''British Pharmacopoeia'' is an important statutory component in the control of medicines, which complements and assists the licensing and inspection processes of the UK's Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). Together with the ''British National Formulary'' (BNF), the ''British Pharmacopoeia'' defines the UK's pharmaceutical standards. Pharmacopoeial standards are compliance requirements; that is, they provide the means for an independent judgement as to the overall quality of an article, and apply throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monolaurin
Monolaurin (abbreviated GML; also called glycerol monolaurate, glyceryl laurate, and 1-lauroyl-glycerol) is a monoglyceride. It is the mono-ester formed from glycerol and lauric acid. Its chemical formula is C15H30O4. Occurrence Monolaurin is found in coconut oil and may be similar to other monoglycerides found in human breast milk. Lauric acid can be ingested in coconut oil and the human body converts it into monolaurin. Furthermore, coconut oil, coconut cream, grated coconut and others products are sources of lauric acid and, consequently, monolaurin. Uses Monolaurin is most commonly used as a surfactant in cosmetics, such as deodorants. As a food additive it is also used as an emulsifier or preservative. Monolaurin is also marketed as a dietary supplement. Monolaurin is sold as a dietary supplement and as an ingredient in certain foods. The United States Food and Drug Administration categorizes it as generally recognized as safe Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyceryl Hydroxystearate
Glyceryl hydroxystearate, also known as glyceryl monohydroxystearate (GMHS), is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C21 H42 O5. It is a whitish- or pale yellow-colored powder found in a variety of cosmetics and skin-care products. Uses Glyceryl hydroxystearate is an ingredient found in some personal-care products. It is commonly used as an emollient, emulsifying agent, or bodying agent. It is often found in facial-care, foot-care, and lip-care products, sunblock, self-tanners, moisturizers, shampoos, creams, lotions, soap Soap is a salt (chemistry), salt of a fatty acid (sometimes other carboxylic acids) used for cleaning and lubricating products as well as other applications. In a domestic setting, soaps, specifically "toilet soaps", are surfactants usually u ...s, concealers, and roll-ons and sun-exposure treatments. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Glyceryl hydroxystearate Fatty acid esters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whipped Cream
Whipped cream, also known as Chantilly cream or (), is high-fat dairy cream that has been aerated by whisking until it becomes light, fluffy, and capable of holding its shape. This process incorporates air into the cream, creating a semi-solid colloid. It is commonly sweetened with white sugar and sometimes flavored with vanilla. Whipped cream is often served on desserts and hot beverages, and used as an ingredient in desserts. Fat content Cream with high butterfat content—typically 30%–36%—is used for whipping, as fat globules contribute to forming stable air bubbles. During whipping, partially coalesced fat molecules create a stabilized network that traps air bubbles. The resulting colloid has about twice the volume of the original cream. If whipping is prolonged further, the fat droplets stick together, destroying the colloid and forming butter. Low-fat cream, or milk, does not have enough fat to whip effectively. Production Cream is usually whipped with a whisk, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Cream
Ice cream is a frozen dessert typically made from milk or cream that has been flavoured with a sweetener, either sugar or an alternative, and a spice, such as Chocolate, cocoa or vanilla, or with fruit, such as strawberries or peaches. Food colouring is sometimes added in addition to Food stabilizer, stabilizers. The mixture is cooled below the freezing point of water and stirred to incorporate air spaces and prevent detectable ice crystals from forming. It can also be made by Whisk, whisking a flavoured cream base and liquid nitrogen together. The result is a smooth, semi-solid foam that is solid at very low temperatures (below ). It becomes more Ductility, malleable as its temperature increases. Ice cream may be served in dishes, eaten with a spoon, or licked from edible wafer Ice cream cone, ice cream cones held by the hands as finger food. Ice cream may be served with other desserts—such as cake or pie—or used as an ingredient in cold dishes—like ice cream floats, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seed Oils
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of edible plants. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed oils, or fats from seeds. Olive oil, palm oil, and rice bran oil are examples of fats from other parts of plants. In common usage, vegetable ''oil'' may refer exclusively to vegetable fats which are liquid at room temperature. Vegetable oils are usually edible. History In antiquity Olive oil has been a part of human culture for millennia.Ruth Schuster (December 17, 2014). "8,000-year old olive oil found in Galilee, earliest known in world", ''Haaretz''. Retrieved December 17, 2014. Archaeological evidence shows that olives were turned into olive oil by 6000 BC and 4500 BC in present-day Israel. Pagnol, p. 19, says the 6th millennium in Jericho, but cites no source. In ancient Egypt, plant oils including cedar oil, cypress oil, and olive oil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |