|
Glycans
The terms glycans and polysaccharides are defined by IUPAC as synonyms meaning "compounds consisting of a large number of monosaccharides linked glycosidically". However, in practice the term glycan may also be used to refer to the carbohydrate portion of a glycoconjugate, such as a glycoprotein, glycolipid, or a proteoglycan, even if the carbohydrate is only an oligosaccharide. Glycans usually consist solely of O-glycosidic linkages of monosaccharides. For example, cellulose is a glycan (or, to be more specific, a glucan) composed of β-1,4-linked D-glucose, and chitin is a glycan composed of β-1,4-linked ''N''-acetyl-D-glucosamine. Glycans can be homo- or heteropolymers of monosaccharide residues, and can be linear or branched. Glycans and proteins Glycans can be found attached to proteins as in glycoproteins and proteoglycans. In general, they are found on the exterior surface of cells. O- and N-linked glycans are very common in eukaryotes but may also be found, alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-linked-Glycan
The terms glycans and polysaccharides are defined by IUPAC as synonyms meaning "compounds consisting of a large number of monosaccharides linked glycosidically". However, in practice the term glycan may also be used to refer to the carbohydrate portion of a glycoconjugate, such as a glycoprotein, glycolipid, or a proteoglycan, even if the carbohydrate is only an oligosaccharide. Glycans usually consist solely of O-glycosidic linkages of monosaccharides. For example, cellulose is a glycan (or, to be more specific, a glucan) composed of β-1,4-linked D-glucose, and chitin is a glycan composed of β-1,4-linked ''N''-acetyl-D-glucosamine. Glycans can be homo- or heteropolymers of monosaccharide residues, and can be linear or branched. Glycans and proteins Glycans can be found attached to proteins as in glycoproteins and proteoglycans. In general, they are found on the exterior surface of cells. O- and N-linked glycans are very common in eukaryotes but may also be found, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteoglycan
Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a "core protein" with one or more covalently attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The point of attachment is a serine (Ser) residue to which the glycosaminoglycan is joined through a tetrasaccharide bridge (e.g. chondroitin sulfate-GlcA- Gal-Gal- Xyl-PROTEIN). The Ser residue is generally in the sequence -Ser- Gly-X-Gly- (where X can be any amino acid residue but proline), although not every protein with this sequence has an attached glycosaminoglycan. The chains are long, linear carbohydrate polymers that are negatively charged under physiological conditions due to the occurrence of sulfate and uronic acid groups. Proteoglycans occur in connective tissue. Types Proteoglycans are categorized by their relative size (large and small) and the nature of their glycosaminoglycan chains. Types include: Certain members are considered members of the "small leucine-rich prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
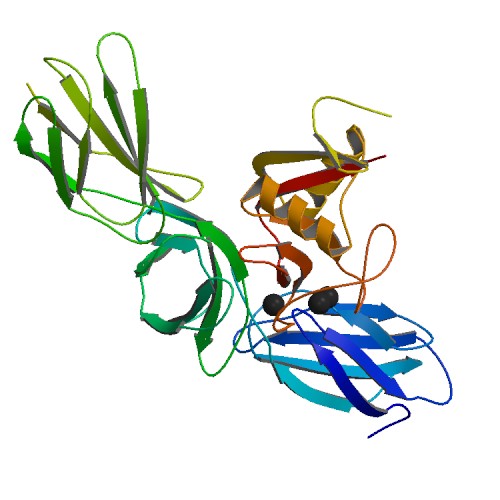
Glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. Secreted extracellular proteins are often glycosylated. In proteins that have segments extending extracellularly, the extracellular segments are also often glycosylated. Glycoproteins are also often important integral membrane proteins, where they play a role in cell–cell interactions. It is important to distinguish endoplasmic reticulum-based glycosylation of the secretory system from reversible cytosolic-nuclear glycosylation. Glycoproteins of the cytosol and nucleus can be modified through the reversible addition of a single GlcNAc residue that is considered reciprocal to phosphorylation and the functions of these are likely to be an additional regulatory mechanism that controls phosphorylation-based signalling. In co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycoconjugate
Glycoconjugates are the classification family for carbohydrates – referred to as glycans – which are covalently linked with chemical species such as proteins, peptides, lipids, and other compounds. Glycoconjugates are formed in processes termed glycosylation. Glycoconjugates are very important compounds in biology and consist of many different categories such as glycoproteins, glycopeptides, peptidoglycans, glycolipids, glycosides, and lipopolysaccharides. They are involved in cell–cell interactions, including cell–cell recognition; in cell–matrix interactions; in detoxification processes. Generally, the carbohydrate part(s) play an integral role in the function of a glycoconjugate; prominent examples of this are neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) and blood proteins where fine details in the carbohydrate structure determine cell binding (or not) or lifetime in circulation. Although the important molecular species DNA, RNA, ATP, cAMP, cGMP, NADH, NADPH, and coenz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannose
Mannose is a sugar monomer of the aldohexose series of carbohydrates. It is a C-2 epimer of glucose. Mannose is important in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylation of certain proteins. Several congenital disorders of glycosylation are associated with mutations in enzymes involved in mannose metabolism. Mannose is not an essential nutrient; it can be produced in the human body from glucose, or converted into glucose. Mannose provides 2–5 kcal/g. It is partially excreted in the urine. Etymology The root of both "mannose" and "mannitol" is manna, which the Bible describes as the food supplied to the Israelites during their journey in the region of Sinai. Several trees and shrubs can produce a substance called manna, such as the "manna tree" ('' Fraxinus ornus'') from whose secretions mannitol was originally isolated. Structure Mannose commonly exists as two different-sized rings, the pyranose (six-membered) form and the furanose (five-membered) form. Eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fucose
Fucose is a hexose deoxy sugar with the chemical formula C6H12O5. It is found on ''N''-linked glycans on the mammalian, insect and plant cell surface. Fucose is the fundamental sub-unit of the seaweed polysaccharide fucoidan. The α(1→3) linked core of fucose is a suspected carbohydrate antigen for IgE-mediated allergy. Two structural features distinguish fucose from other six-carbon sugars present in mammals: the lack of a hydroxyl group on the carbon at the 6-position (C-6) (thereby making it a deoxy sugar) and the L -configuration. It is equivalent to 6-deoxy--galactose. In the fucose-containing glycan structures, fucosylated glycans, fucose can exist as a terminal modification or serve as an attachment point for adding other sugars. In human ''N''-linked glycans, fucose is most commonly linked α-1,6 to the reducing terminal β-''N''-acetylglucosamine. However, fucose at the non-reducing termini linked α-1,2 to galactose forms the H antigen, the substructure of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with water (hydrolysis) using amylase enzymes as catalyst, which produces constituent sugars ( monosaccharides, or oligosaccharides). They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Examples include storage polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen and galactogen and structural polysaccharides such as cellulose and chitin. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure, these macromolecules can have distinct properties from their monosaccharide building blocks. They may be amorphous or even insoluble in water. When all the monosaccharides in a polysaccharide are the same type, the polysaccharide is called a homopolysaccharide or homoglycan, but whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycolipid
Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond. Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the connections that allow cells to connect to one another to form tissues. Glycolipids are found on the surface of all eukaryotic cell membranes, where they extend from the phospholipid bilayer into the extracellular environment. Structure The essential feature of a glycolipid is the presence of a monosaccharide or oligosaccharide bound to a lipid moiety. The most common lipids in cellular membranes are glycerolipids and sphingolipids, which have glycerol or a sphingosine backbones, respectively. Fatty acids are connected to this backbone, so that the lipid as a whole has a polar head and a non-polar tail. The lipid bilayer of the cell membrane consists of two layers of lipids, with the inner and outer surfaces of the membrane made up of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequon
A sequon is a sequence of consecutive amino acids in a protein that can serve as the attachment site to a polysaccharide, frequently an N-linked-Glycan. The polysaccharide is linked to the protein via the nitrogen atom in the side chain of asparagine (Asn). The sequon for N-glycosylation is either Asn-X-Ser or Asn-X-Thr, where X is any amino acid except proline, Ser denoting serine and Thr threonine. Occasionally, other amino acids can take the place of Ser and Thr, such as in the leukocyte White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mul ... surface protein (CD69), where the amino acid sequence Asn-X-Cys is an acceptable sequon for the addition of N-linked glycans. References {{Wiktionary, sequon Peptide sequences Glycoproteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuraminic Acid
Neuraminic acid (5-amino-3,5-dideoxy-D-''glycero''-D-''galacto''-non-2-ulosonic acid) is an acidic (in particular ulosonic) amino sugar with a backbone formed by nine carbon atoms. Although 9-carbon sugars do not occur naturally, neuraminic acid may be regarded as a theoretical 9-carbon ketose in which the first link of the chain (the –CH2OH at position 1) is oxidised into a carboxyl group (–C(=O)OH), the hydroxyl group at position 3 is deoxidised (oxygen is removed from it), and the hydroxyl group at position 5 is substituted with an amino group (–NH2). Neuraminic acid may also be visualized as the product of an aldol-condensation of pyruvic acid and D-mannosamine (2-amino-2-deoxy-mannose). Neuraminic acid does not occur naturally, but many of its derivatives are found widely distributed in animal tissues and in bacteria, especially in glycoproteins and gangliosides. The ''N''- or ''O''-substituted derivatives of neuraminic acid are collectively known as sialic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactose
Galactose (, '' galacto-'' + '' -ose'', "milk sugar"), sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a monosaccharide sugar that is about as sweet as glucose, and about 65% as sweet as sucrose. It is an aldohexose and a C-4 epimer of glucose. A galactose molecule linked with a glucose molecule forms a lactose molecule. Galactan is a polymeric form of galactose found in hemicellulose, and forming the core of the galactans, a class of natural polymeric carbohydrates. D-Galactose is also known as brain sugar since it is a component of glycoproteins (oligosaccharide-protein compounds) found in nerve tissue. Etymology The word ''galactose'' was coined by Charles Weissman in the mid-19th century and is derived from Greek ''galaktos'' (of milk) and the generic chemical suffix for sugars ''-ose''. The etymology is comparable to that of the word '' lactose'' in that both contain roots meaning "milk sugar". Lactose is a disaccharide of galactose plus glucose. Structure and isomerism Galactose exists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |