|
Glucagon Rescue
Glucagon rescue is the emergency injection of glucagon in case of severe diabetic hypoglycemia. It is needed during seizures and/or unconsciousness by an insulin user who is unable at that point to help themselves. Glucagon will facilitate the release of stored glucose back into the bloodstream, raising the blood glucose level. Rescue has been simplified by the development of the glucagon hypoglycemia rescue kit, consisting of: * biosynthetic human glucagon, in a freeze dried form within a vial, * a sturdy syringe, pre-filled with a sterile diluting solution, and * a conspicuous red or orange colored plastic storage box, which includes instructions. At the first signs of hypoglycemia, an insulin user should treat it immediately by consuming carbohydrate to restore blood glucose to safe levels (thereby preventing progression to severe hypoglycemia). However, not all insulin users can feel and recognize the early signs, particularly when sleeping. This can quickly lead to an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucagon Emergency Rescue Kits Image
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises the concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a medication to treat a number of health conditions. Its effect is opposite to that of insulin, which lowers extracellular glucose. It is produced from proglucagon, encoded by the ''GCG'' gene. The pancreas releases glucagon when the amount of glucose in the bloodstream is too low. Glucagon causes the liver to engage in glycogenolysis: converting stored glycogen into glucose, which is released into the bloodstream. High blood-glucose levels, on the other hand, stimulate the release of insulin. Insulin allows glucose to be taken up and used by insulin-dependent tissues. Thus, glucagon and insulin are part of a feedback system that keeps blood glucose levels stable. Glucagon increases energy expenditure and is elevated under conditions of stress. Glucagon be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetic Hypoglycemia
Diabetic hypoglycemia is a low blood glucose level occurring in a person with diabetes mellitus. It is one of the most common types of hypoglycemia seen in emergency departments and hospitals. According to the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System-All Injury Program (NEISS-AIP), and based on a sample examined between 2004 and 2005, an estimated 55,819 cases (8.0% of total admissions) involved insulin, and severe hypoglycemia is likely the single most common event. In general, hypoglycemia occurs when a treatment to lower the elevated blood glucose of diabetes inaccurately matches the body's physiological need, and therefore causes the glucose to fall to a below-normal level. Signs and symptoms Diabetic hypoglycemia can be mild, recognized easily by the patient, and reversed with a small amount of carbohydrates eaten or drunk, or it may be severe enough to cause unconsciousness requiring intravenous dextrose or an injection of glucagon. Severe hypoglycemic unconsciousne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia (American English), also spelled hypoglycaemia or hypoglycæmia (British English), sometimes called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L), symptoms associated with hypoglycemia, and resolution of symptoms when blood sugar returns to normal. Hypoglycemia may result in headache, tiredness, clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, fast heart rate, sweating, shakiness, nervousness, hunger, loss of consciousness, seizures, or death. Symptoms typically come on quickly. Symptoms can remain even soon after raised blood level. The most common cause of hypoglycemia is diabetes medication, medications used to treat diabetes such as insulin (medication), insulin, sulfonylureas, and biguanides. Risk is greater in diabetics who have eaten less than usual, recently exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
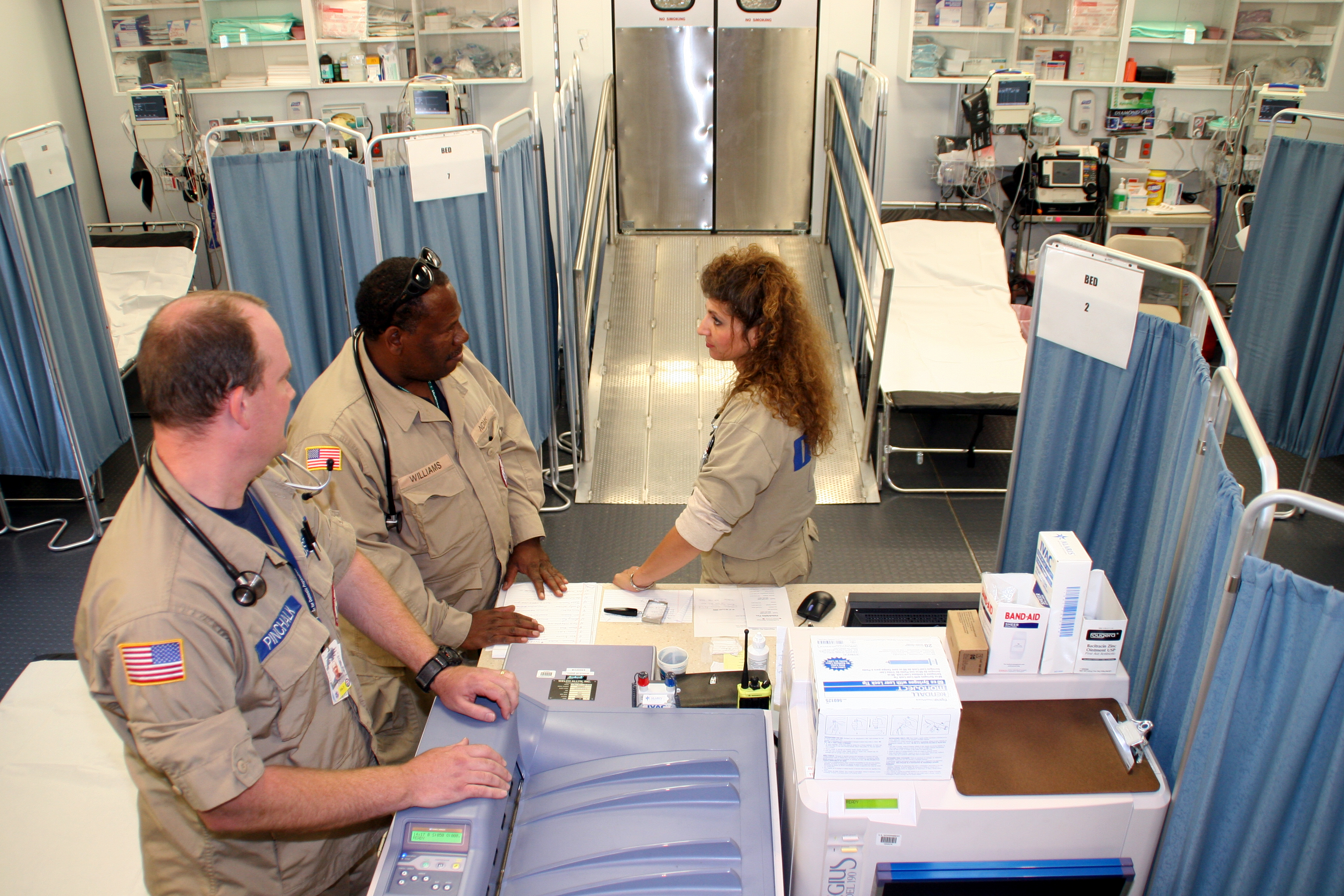
Emergency Department
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the Acute (medicine), acute care of patients who present without prior appointment; either by their own means or by that of an ambulance. The emergency department is usually found in a hospital or other primary care center. Due to the unplanned nature of patient attendance, the department must provide initial treatment for a broad spectrum of illnesses and injuries, some of which may be Medical emergency, life-threatening and require immediate attention. In some countries, emergency departments have become important entry points for those without other means of access to medical care. The emergency departments of most hospitals operate 24 hours a day, although staffing levels may be varied in an attempt to reflect patient volume. History Accident services wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novo Nordisk
Novo Nordisk A/S is a Danish multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Bagsværd, with production facilities in nine countries and affiliates or offices in five. Novo Nordisk is controlled by majority shareholder Novo Holdings A/S (wholly owned by the Novo Nordisk Foundation) which holds approximately 28.1% of its shares and a majority (77.1%) of its voting shares. Novo Nordisk manufactures and markets pharmaceutical products and services, specifically diabetes care medications and devices. Novo Nordisk makes the drug semaglutide, used to treat diabetes under the brand names Ozempic and Rybelsus and obesity under the brand name Wegovy. Novo Nordisk is also involved with hemostasis management, growth hormone therapy, and hormone replacement therapy. The company makes several drugs under various brand names, including Levemir, Tresiba, NovoLog, Novolin R, NovoSeven, NovoEight, and Victoza. Novo Nordisk employs more than 48,000 people globally, and markets it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eli Lilly
Eli Lilly (July 8, 1838 – June 6, 1898) was a Union Army officer, pharmacist, chemist, and businessman who founded Eli Lilly and Company. Lilly enlisted in the Union Army during the American Civil War and recruited a company of men to serve with him in the 18th Independent Battery Indiana Light Artillery. He was later promoted to Major (United States), major and then colonel, and was given command of the 9th Indiana Infantry Regiment. Lilly was captured in September 1864 and held as a prisoner of war until January 1865. After the war, he attempted to run a plantations in the American South, plantation in Mississippi, but it failed and he returned to his pharmacy profession after the death of his first wife. Lilly remarried and worked with business partners in several pharmacies in Indiana and Illinois before opening his own business in 1876 in Indianapolis. Lilly's company manufactured drugs and marketed them on a wholesale basis to pharmacies. Lilly's pharmaceutical f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucagon Instructions Front
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises the concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a medication to treat a number of health conditions. Its effect is opposite to that of insulin, which lowers extracellular glucose. It is produced from proglucagon, encoded by the ''GCG'' gene. The pancreas releases glucagon when the amount of glucose in the bloodstream is too low. Glucagon causes the liver to engage in glycogenolysis: converting stored glycogen into glucose, which is released into the bloodstream. High blood-glucose levels, on the other hand, stimulate the release of insulin. Insulin allows glucose to be taken up and used by insulin-dependent tissues. Thus, glucagon and insulin are part of a feedback system that keeps blood glucose levels stable. Glucagon increases energy expenditure and is elevated under conditions of stress. Glucagon be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-diabetic Drugs
Drugs used in diabetes treat types of diabetes mellitus by decreasing glucose levels in the blood. With the exception of insulin, most GLP-1 receptor agonists ( liraglutide, exenatide, and others), and pramlintide, all diabetes medications are administered orally and are thus called oral hypoglycemic agents or oral antihyperglycemic agents. There are different classes of hypoglycemic drugs, and selection of the appropriate agent depends on the nature of diabetes, age, and situation of the person, as well as other patient factors. Type 1 diabetes or Diabetes mellitus is an endocrine disorder characterized by hyperglycemia due to autoimmune destruction of insulin-secreting pancreatic beta cells or from variable degrees of insulin resistance and deficiency. Chronic hyperglycemia of diabetes can lead to multiorgan damage, resulting in renal, neurologic, cardiovascular, and other serious complications. The treatment for Type 1 diabetes is insulin injection. Type 2 diabetes is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |