|
Glossematics
In linguistics, glossematics is a structuralist theory proposed by Louis Hjelmslev and Hans Jørgen Uldall. It defines the ''glosseme'' as the most basic unit of language. Hjelmslev and Uldall eventually went separate ways with their respective approaches. Hjelmslev's theory, most notably, is an early mathematical methodology for the analysis of language which was subsequently incorporated into the analytical foundation of current models of functional–structural grammar such as Danish Functional Grammar, Functional Discourse Grammar and Systemic Functional Linguistics. Hjelmslev's theory likewise remains fundamental for modern semiotics. Meaning Glossematics defines the ''glosseme'' as the smallest irreducible unit of both the content and expression planes of language; in the expression plane, the glosseme is nearly identical to the phoneme. In the content plane, it is the smallest unit of meaning which underlies a concept. A ''ewe'', for example, consists of the taxemes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Hjelmslev
Louis Trolle Hjelmslev (; 3 October 189930 May 1965) was a Danish linguist whose ideas formed the basis of the Copenhagen School of linguistics. Born into an academic family (his father was the mathematician Johannes Hjelmslev), Hjelmslev studied comparative linguistics in Copenhagen, Prague and Paris (with Antoine Meillet and Joseph Vendryes, among others). In 1931, he founded the Cercle Linguistique de Copenhague. Together with Hans Jørgen Uldall he developed a structuralist theory of language which he called glossematics, which further developed the semiotic theory of Ferdinand de Saussure. Glossematics as a theory of language is characterized by a high degree of formalism. It is interested in describing the formal and semantic characteristics of language in separation from sociology, psychology or neurobiology, and has a high degree of logical rigour. Hjelmslev regarded linguistics – or glossematics – as a formal science. He was the inventor of formal linguistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Structuralism
Distributionalism was a general theory of language and a discovery procedure for establishing elements and structures of language based on observed usage. The purpose of distributionalism was to provide a scientific basis for syntax as independent of meaning. Zellig Harris defined 'distribution' as follows.“The DISTRIBUTION of an element is the total of all environments in which it occurs, i.e. the sum of all the (different) positions (or occurrences) of an element relative to the occurrence of other elements ��Based on this idea, an analysis of immediate constituents could be based on observing the environments in which an element, such as a word, appears in corpora. Critics of distributionalism, such as Louis Hjelmslev, pointed out that the analysis of occurrence adds nothing to traditional structure analysis, which is based on the hierarchical, step-by-step categorization of elements. Hjelmslev proposed glossematics, which combines the analysis of meaning and form. However, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Grammar
Generative grammar is a research tradition in linguistics that aims to explain the cognitive basis of language by formulating and testing explicit models of humans' subconscious grammatical knowledge. Generative linguists, or generativists (), tend to share certain working assumptions such as the competence–performance distinction and the notion that some domain-specific aspects of grammar are partly innate in humans. These assumptions are rejected in non-generative approaches such as usage-based models of language. Generative linguistics includes work in core areas such as syntax, semantics, phonology, psycholinguistics, and language acquisition, with additional extensions to topics including biolinguistics and music cognition. Generative grammar began in the late 1950s with the work of Noam Chomsky, having roots in earlier approaches such as structural linguistics. The earliest version of Chomsky's model was called Transformational grammar, with subsequent itera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiotics
Semiotics ( ) is the systematic study of sign processes and the communication of meaning. In semiotics, a sign is defined as anything that communicates intentional and unintentional meaning or feelings to the sign's interpreter. Semiosis is any activity, conduct, or process that involves signs. Signs often are communicated by verbal language, but also by gestures, or by other forms of language, e.g. artistic ones (music, painting, sculpture, etc.). Contemporary semiotics is a branch of science that generally studies meaning-making (whether communicated or not) and various types of knowledge. Unlike linguistics, semiotics also studies non-linguistic sign systems. Semiotics includes the study of indication, designation, likeness, analogy, allegory, metonymy, metaphor, symbolism, signification, and communication. Semiotics is frequently seen as having important anthropological and sociological dimensions. Some semioticians regard every cultural phenomenon as being able to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Jørgen Uldall
Hans Jørgen Uldall (; 25 May 1907 Silkeborg, Denmark29 October 1957 Ibadan, Nigeria) was a Danish linguist known for developing the linguistic theory of glossematics with Louis Hjelmslev. Early life Having studied English with Danish linguist Otto Jespersen at the University of Copenhagen he went to London to study phonology with Daniel Jones. Career In 1929 he had a lectureship at the University of Cape Town, and then went back to London to teach phonetics in 1930. While in Cape Town, he corresponded with the doyen of American anthropology Franz Boas at Columbia, who secured him a grant of 2000 dollars to undertake field work on the Maidu language under the auspices of the Archaeological and Ethnographic Survey of California, established by A. L. Kroeber in 1901. On his way from Cape Town made a stop in Hamburg to attend the 24th congress of Americanists, before he and his wife continued their journey to California. He spent 193132 in California working closely togeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formal Linguistics
Formal linguistics is a branch of mathematical linguistics which uses formal languages, formal grammars and first-order logical expressions for the analysis of natural languages. Formal linguistics forms much of the basis of computational linguistics. Since the 1980s, the term is often used to refer to Chomskyan linguistics. Approaches Semiotic Methods of formal linguistics were introduced by semiotics, semioticians such as Charles Sanders Peirce and Louis Hjelmslev. Building on the work of David Hilbert and Rudolf Carnap, Hjelmslev proposed the use of formal grammars to analyse, generate and explain language in his 1943 book ''Prolegomena to a Theory of Language''. In this view, language is regarded as arising from a mathematical relationship between meaning and form. The formal description of language was further developed by linguists including J. R. Firth and Simon Dik, giving rise to modern grammatical frameworks such as systemic functional linguistics and functional discourse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formalism (philosophy)
The term ''formalism'' describes an emphasis on form over content or meaning in the arts, literature, or philosophy. A practitioner of formalism is called a ''formalist''. A formalist, with respect to some discipline, holds that there is no transcendent meaning to that discipline other than the literal content created by a practitioner. For example, formalists within mathematics claim that mathematics is no more than the symbols written down by the mathematician, which is based on logic and a few elementary rules alone. This is as opposed to non-formalists, within that field, who hold that there are some things inherently true, and are not, necessarily, dependent on the symbols within mathematics so much as a greater truth. Formalists within a discipline are completely concerned with "the rules of the game," as there is no other external truth that can be achieved beyond those given rules. In this sense, formalism lends itself well to disciplines based upon axiomatic systems. Reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prague Linguistic Circle
The Prague school or Prague linguistic circle is a language and literature society. It started in 1926 as a group of linguists, philologists and literary critics in Prague. Its proponents developed methods of structuralist literary analysis and a theory of the standard language and of language cultivation from 1928 to 1939. The linguistic circle was founded in the Café Derby in Prague, which is also where meetings took place during its first years. The Prague School has had a significant continuing influence on linguistics and semiotics. After the Czechoslovak coup d'état of 1948, the circle was disbanded in 1952, but the Prague School continued as a major force in linguistic functionalism (distinct from the Copenhagen school or English Firthian – later Hallidean – linguistics). The American scholar Dell Hymes cites his 1962 paper "The Ethnography of Speaking" as the formal introduction of Prague functionalism to American linguistic anthropology. The Prague st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
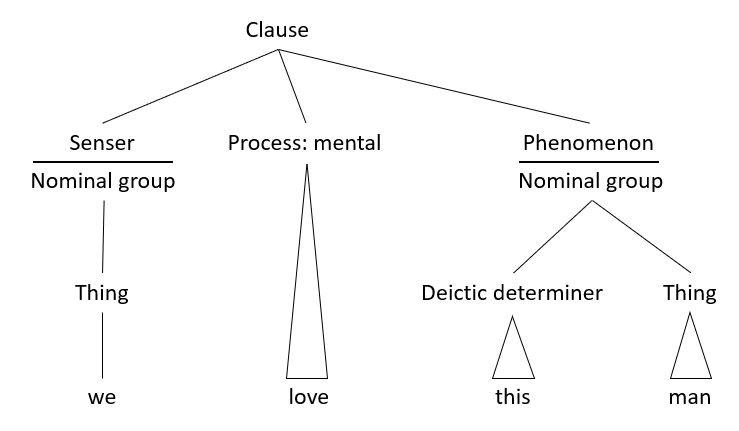
Systemic Functional Linguistics
Systemic functional linguistics (SFL) is an approach to linguistics, among functional linguistics, that considers language as a social semiotic system. It was devised by Michael Halliday, who took the notion of system from J. R. Firth, his teacher (Halliday, 1961). Firth proposed that systems refer to possibilities subordinated to structure; Halliday "liberated" choice from structure and made it the central organising dimension of SFL. In more technical terms, while many approaches to linguistic description place structure and the syntagmatic axis foremost, SFL adopts the paradigmatic axis as its point of departure. ''Systemic'' foregrounds Saussure's "paradigmatic axis" in understanding how language works.Halliday, M.A.K. 2004. Introduction: How Big is a Language? On the Power of Language. In The Language of Science: Volume 5 in the Collected Works of M.A.K. Edited by J.J.Webster. London and New York: Continuum. p. xi. For Halliday, a central theoretical principle is then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Linguistics
Functional linguistics is an approach to the study of language characterized by taking systematically into account the speaker's and the hearer's side, and the communicative needs of the speaker and of the given language community. Linguistic functionalism spawned in the 1920s to 1930s from Ferdinand de Saussure's systematic structuralist approach to language (1916). Functionalism sees functionality of language and its elements to be the key to understanding linguistic processes and structures. Functional theories of language propose that since language is fundamentally a tool, it is reasonable to assume that its structures are best analyzed and understood with reference to the functions they carry out. These include the tasks of conveying meaning and contextual information. Functional theories of grammar belong to structural and, broadly, humanistic linguistics, considering language as being created by the community, and linguistics as relating to systems theory. Function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |