|
Gloeophyllum Trabeum
''Gloeophyllum trabeum'' is a species of fungus in the family Gloeophyllaceae The Gloeophyllales are a phylogenetically defined order of wood-decay fungi that is characterized by the ability to produce a brown rot of wood. * * * * It includes a single, identically defined family, the Gloeophyllaceae, in which are inclu .... References Wood-decay fungi Fungal plant pathogens and diseases Fungi described in 1801 Gloeophyllales Taxa named by Christiaan Hendrik Persoon {{Agaricomycetes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pers
Pers may refer to: * Pers, Cantal, France, a commune near Aurillac * Pers, Deux-Sèvres, France, a commune near Poitiers * '' Pers.'', taxonomic author abbreviation for mycologist Christiaan Hendrik Persoon *Persian language PERS may refer to: * Personal Emergency Response System See also * * * Person (other) * Perse (other) Perse may refer to: * Persa (play), a comedy by the Roman playwright Plautus * Perse (mythology) (also Persa or Perseis), an Oceanid and consort of Helios in Greek mythology * The Perse School, an independent co-educational school in Cambridge, ... * Per (other) {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Alphonso Murrill
William Alphonso Murrill (October 13, 1869 – December 25, 1957) was an American mycologist, known for his contributions to the knowledge of the Agaricales and Polyporaceae. In 1904, he became the assistant Curator at the New York Botanical Garden (NYBG). He, along with the NYBG, founded the journal ''Mycologia'' and was its first editor for 16 years. Murrill was known to travel extensively to describe the mycota of Europe and the Americas. He traveled along the East Coast, Pacific Coast, Mexico and the Caribbean. Although Murrill was a very influential person at the NYBG, having worked his way up to become assistant director in 1908, his rather eccentric personality caused problems with his job. He went on annual collecting trips to Mexico, the Caribbean, Europe, and South America, sometimes, without informing any of his colleagues prior. These trips resulted in a cumulative total of 70,000 specimens, 1,400 of which are deposited in the NYBG.William Alphonso Murrill Records ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a Kingdom (biology), kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloeophyllaceae
The Gloeophyllales are a phylogenetically defined order of wood-decay fungi that is characterized by the ability to produce a brown rot of wood. * * * * It includes a single, identically defined family, the Gloeophyllaceae, in which are included the genera ''Gloeophyllum'', ''Neolentinus'', ''Heliocybe'', and ''Veluticeps ''Veluticeps'' is a small genus of wood-rot fungi characterized by the production of resupinate to bracket shaped, perennial, tough, brown fruitbodies, that blacken when KOH solution is applied, and with a smooth to warted or cracked fertile un ...''. References Basidiomycota orders Monotypic fungus taxa {{Agaricomycetes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
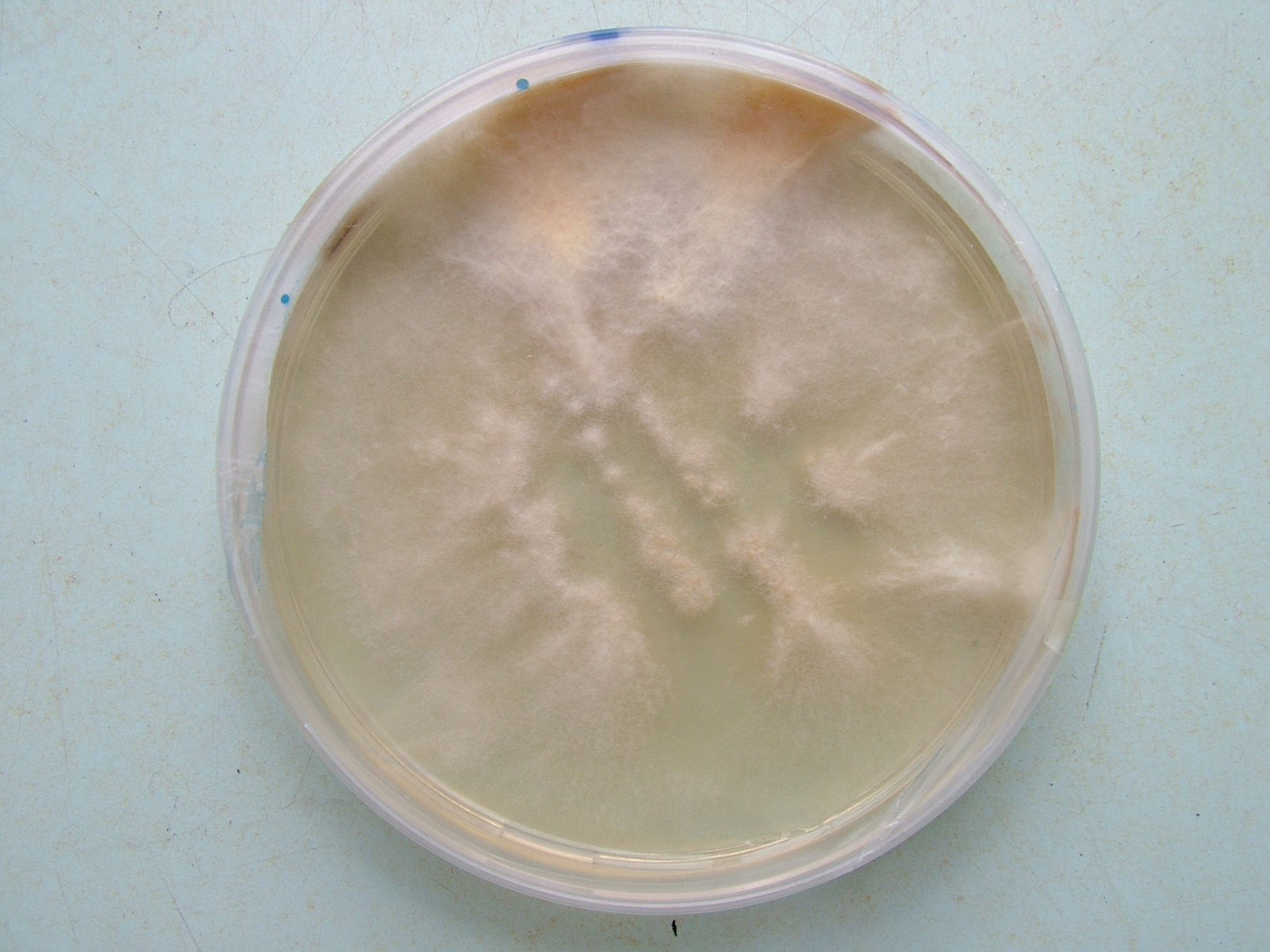
Gloeophyllum Trabeum Culture
The genus ''Gloeophyllum'' is characterized by the production of leathery to corky tough, brown, shaggy-topped, revivable fruitbodies lacking a stipe and with a lamellate to daedaleoid or poroid fertile hymenial surfaces. The hyphal system is dimitic to trimitic. The genus is further characterized by the production of a brown rot of wood. Phylogenetically, it along with several other brown rot Basidiomycota, ''Neolentinus'', ''Heliocybe'', and ''Veluticeps'' form an order called the Gloeophyllales. The most frequently encountered species in the Northern Hemisphere is '' Gloeophyllum sepiarium'', which is commonly found in a dried state on both bark-covered and decorticated conifer stumps and logs, timbers on wharfs, planks on unpainted wooden buildings, wood bridges, and even creosoted railroad ties. Pharmacology An extract An extract is a substance made by extracting a part of a raw material, often by using a solvent such as ethanol, oil or water. Extracts may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
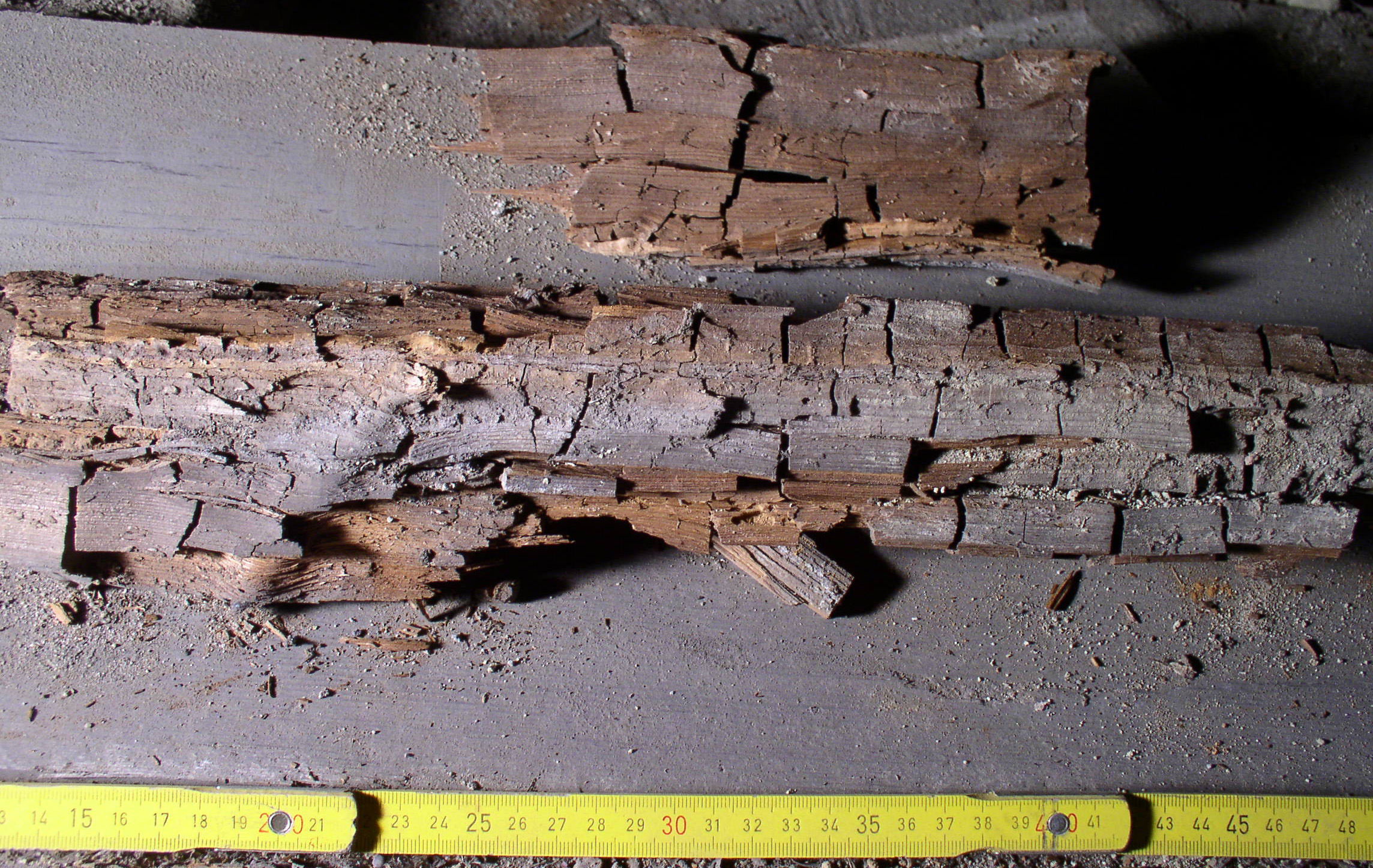
Wood-decay Fungi
A wood-decay or xylophagous fungus is any species of fungus that digests moist wood, causing it to rot. Some species of wood-decay fungi attack dead wood, such as brown rot, and some, such as ''Armillaria'' (honey fungus), are parasitic and colonize living trees. Excessive moisture above the fibre saturation point in wood is required for fungal colonization and proliferation. In nature, this process causes the breakdown of complex molecules and leads to the return of nutrients to the soil. Wood-decay fungi consume wood in various ways; for example, some attack the carbohydrates in wood and some others decay lignin. The rate of decay of wooden materials in various climates can be estimated by empirical models.Viitanen, T. et al. (2010). Towards modelling of decay risk of wooden materials. European Journal of Wood and Wood Products 68:303-313. Wood-decay fungi can be classified according to the type of decay that they cause. The best-known types are brown rot, soft rot, and white ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungal Plant Pathogens And Diseases
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Described In 1801
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloeophyllales
The Gloeophyllales are a phylogenetically defined order of wood-decay fungi that is characterized by the ability to produce a brown rot of wood. * * * * It includes a single, identically defined family, the Gloeophyllaceae, in which are included the genera ''Gloeophyllum'', ''Neolentinus'', ''Heliocybe'', and ''Veluticeps ''Veluticeps'' is a small genus of wood-rot fungi characterized by the production of resupinate to bracket shaped, perennial, tough, brown fruitbodies, that blacken when KOH solution is applied, and with a smooth to warted or cracked fertile un ...''. References Basidiomycota orders Monotypic fungus taxa {{Agaricomycetes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |