|
Glasgow Haskell Compiler
The Glasgow Haskell Compiler (GHC) is a native or machine code compiler for the functional programming language Haskell. It provides a cross-platform software environment for writing and testing Haskell code and supports many extensions, libraries, and optimisations that streamline the process of generating and executing code. GHC is the most commonly used Haskell compiler. It is free and open-source software released under a BSD license. History GHC originally begun in 1989 as a prototype, written in Lazy ML (LML) by Kevin Hammond at the University of Glasgow. Later that year, the prototype was completely rewritten in Haskell, except for its parser, by Cordelia Hall, Will Partain, and Simon Peyton Jones. Its first beta release was on 1 April 1991. Later releases added a strictness analyzer and language extensions such as monadic I/O, mutable arrays, unboxed data types, concurrent and parallel programming models (such as software transactional memory and data parallelism) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Marlow
Simon Marlow is a British computer scientist, programmer, author, and co-developer of the Glasgow Haskell Compiler (GHC) for the programming language Haskell. He and Simon Peyton Jones won the SIGPLAN Programming Languages Software Award in 2011 for their work on GHC. Marlow's book ''Parallel and Concurrent Programming in Haskell'' was published in July 2013. Formerly of Microsoft Research, Marlow has worked at Facebook since March 2013. The "noted Haskell guru" is part of the team behind Facebook's open source Haxl project, a Haskell library that simplifies access to remote data. Honours and awards In 2011, he and Simon Peyton Jones Simon Peyton Jones (born 18 January 1958) is a British computer scientist who researches the implementation and applications of functional programming languages, particularly lazy functional programming. Education Peyton Jones graduated fro ... were awarded the SIGPLAN Programming Languages Software Award for their work on GHC. In 2019 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library (computing)
In computing, a library is a collection of System resource, resources that can be leveraged during software development to implement a computer program. Commonly, a library consists of executable code such as compiled function (computer science), functions and Class (computer programming), classes, or a library can be a collection of source code. A resource library may contain data such as images and Text string, text. A library can be used by multiple, independent consumers (programs and other libraries). This differs from resources defined in a program which can usually only be used by that program. When a consumer uses a library resource, it gains the value of the library without having to implement it itself. Libraries encourage software reuse in a Modular programming, modular fashion. Libraries can use other libraries resulting in a hierarchy of libraries in a program. When writing code that uses a library, a programmer only needs to know how to use it not its internal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gzip
gzip is a file format and a software application used for file compression and decompression. The program was created by Jean-loup Gailly and Mark Adler as a free software replacement for the compress program used in early Unix systems, and intended for use by GNU (from which the "g" of gzip is derived). Version 0.1 was first publicly released on 31 October 1992, and version 1.0 followed in February 1993. The decompression of the ''gzip'' format can be implemented as a streaming algorithm, an important feature for Web protocols, data interchange and ETL (in standard pipes) applications. File format gzip is based on the DEFLATE algorithm, which is a combination of LZ77 and Huffman coding. DEFLATE was intended as a replacement for LZW and other patent-encumbered data compression algorithms which, at the time, limited the usability of the compress utility and other popular archivers. "gzip" also refers to the gzip file format (described in the table below). In sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tar (computing)
In computing, tar is a shell command for combining multiple computer files into a single archive file. It was originally developed for magnetic tape storage reading and writing data for a sequential I/O device with no file system, and the name is short for the format description "tape archive". When stored in a file system, a file that tar reads and writes is often called a ''tarball''. A tarball contains metadata for the contained files including the name, ownership, timestamps, permissions and directory organization. As a file containing other files with associated metadata, a tarball is useful for software distribution and backup. POSIX abandoned ''tar'' in favor of '' pax'', yet ''tar'' continues to have widespread use. History The command was introduced to Unix in January 1979, replacing the tp program (which in turn replaced "tap"). The file structure was standardized in POSIX.1-1988 and later POSIX.1-2001, and became a format supported by most modern file ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of the City of Cambridge was 145,700; the population of the wider built-up area (which extends outside the city council area) was 181,137. (2021 census) There is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age, and Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman Britain, Roman and Viking eras. The first Town charter#Municipal charters, town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is well known as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Research
Microsoft Research (MSR) is the research subsidiary of Microsoft. It was created in 1991 by Richard Rashid, Bill Gates and Nathan Myhrvold with the intent to advance state-of-the-art computing and solve difficult world problems through technological innovation in collaboration with academic, government, and industry researchers. The Microsoft Research team has more than 1,000 computer scientists, physicists, engineers, and mathematicians, including Turing Award winners, Fields Medal winners, MacArthur Fellows, and Dijkstra Prize winners. Between 2010 and 2018, 154,000 AI patents were filed worldwide, with Microsoft having by far the largest percentage of those patents, at 20%.Louis Columbus, January 6, 201Microsoft Leads The AI Patent Race Going Into 2019 ''Forbes'' According to estimates in trade publications, Microsoft spent about $6 billion annually in research initiatives from 2002 to 2010 and has spent from $10–14 billion annually since 2010. Microsoft Research has made si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Profiling (computer Programming)
In software engineering, profiling (program profiling, software profiling) is a form of dynamic program analysis that measures, for example, the space (memory) or time complexity of a program, the usage of particular instructions, or the frequency and duration of function calls. Most commonly, profiling information serves to aid program optimization, and more specifically, performance engineering. Profiling is achieved by instrumenting either the program source code or its binary executable form using a tool called a ''profiler'' (or ''code profiler''). Profilers may use a number of different techniques, such as event-based, statistical, instrumented, and simulation methods. Gathering program events Profilers use a wide variety of techniques to collect data, including hardware interrupts, code instrumentation, instruction set simulation, operating system hooks, and performance counters. Use of profilers The output of a profiler may be: * A statistical ''summary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
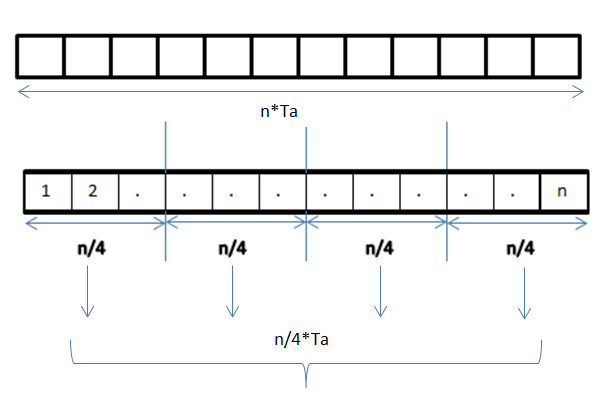
Data Parallelism
Data parallelism is parallelization across multiple processors in parallel computing environments. It focuses on distributing the data across different nodes, which operate on the data in parallel. It can be applied on regular data structures like arrays and matrices by working on each element in parallel. It contrasts to task parallelism as another form of parallelism. A data parallel job on an array of ''n'' elements can be divided equally among all the processors. Let us assume we want to sum all the elements of the given array and the time for a single addition operation is Ta time units. In the case of sequential execution, the time taken by the process will be ''n''×Ta time units as it sums up all the elements of an array. On the other hand, if we execute this job as a data parallel job on 4 processors the time taken would reduce to (''n''/4)×Ta + merging overhead time units. Parallel execution results in a speedup of 4 over sequential execution. The Locality of reference, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Transactional Memory
In computer science, software transactional memory (STM) is a concurrency control mechanism analogous to database transactions for controlling access to shared memory in concurrent computing. It is an alternative to lock-based synchronization. STM is a strategy implemented in software, rather than as a hardware component. A transaction in this context occurs when a piece of code executes a series of reads and writes to shared memory. These reads and writes logically occur at a single instant in time; intermediate states are not visible to other (successful) transactions. The idea of providing hardware support for transactions originated in a 1986 paper by Tom Knight.Tom Knight. An architecture for mostly functional languages.' Proceedings of the 1986 ACM conference on Lisp and functional programming. The idea was popularized by Maurice Herlihy and J. Eliot B. Moss.Maurice Herlihy and J. Eliot B. Moss. ''Transactional memory: architectural support for lock-free data structures.'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monads In Functional Programming
In functional programming, monads are a way to structure computations as a sequence of steps, where each step not only produces a value but also some extra information about the computation, such as a potential failure, non-determinism, or side effect. More formally, a monad is a type constructor M equipped with two operations, which lifts a value into the monadic context, and which chains monadic computations. In simpler terms, monads can be thought of as interfaces implemented on type constructors, that allow for functions to abstract over various type constructor variants that implement monad (e.g. , , etc.). Both the concept of a monad and the term originally come from category theory, where a monad is defined as an endofunctor with additional structure. Research beginning in the late 1980s and early 1990s established that monads could bring seemingly disparate computer-science problems under a unified, functional model. Category theory also provides a few formal requiremen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strictness Analysis
In computer science, strictness analysis refers to any algorithm used to prove that a function in a non-strict functional programming language is strict in one or more of its arguments. This information is useful to compilers because strict functions can be compiled more efficiently. Thus, if a function is proven to be strict (using strictness analysis) at compile time, it can be compiled to use a more efficient calling convention without changing the meaning of the enclosing program. Note that a function f is said to ''diverge'' if it returns \: operationally, that would mean that f either causes abnormal termination of the enclosing program (e.g., failure with an error message) or that it loops infinitely. The notion of "divergence" is significant because a strict function is one that always diverges when given an argument that diverges, whereas a lazy (or non-strict) function is one that may or may not diverge when given such an argument. Strictness analysis attempts to determine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parser
Parsing, syntax analysis, or syntactic analysis is a process of analyzing a string of symbols, either in natural language, computer languages or data structures, conforming to the rules of a formal grammar by breaking it into parts. The term ''parsing'' comes from Latin ''pars'' (''orationis''), meaning part (of speech). The term has slightly different meanings in different branches of linguistics and computer science. Traditional sentence parsing is often performed as a method of understanding the exact meaning of a sentence or word, sometimes with the aid of devices such as sentence diagrams. It usually emphasizes the importance of grammatical divisions such as subject and predicate. Within computational linguistics the term is used to refer to the formal analysis by a computer of a sentence or other string of words into its constituents, resulting in a parse tree showing their syntactic relation to each other, which may also contain semantic information. Some parsing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |