|
Giovanni Battista Montano
Giovanni Battista Montano (1534–1621) was an Italian architect, designer and engraver of primary importance as a recorder of Antique Roman architectural remains. Early life Montano was born in Milan and trained primarily as a sculptor and a wood carver. In particular he has done two great carved works in the Basilica of San Giovanni in Laterano and the Church of Santa Maria di Loreto. In the early 1570s, Montano relocated to Rome, where he intensely studied the city’s antique monuments and ruins. Montano was a member of the Accademia di San Luca, and in 1602 he was commissioned by the Carpenters' guild to oversee the completion of the Church of San Giuseppe dei Falegnami, the construction of which had already begun in 1597. Montano designed the façade of the church, but his death in 1621 meant that the work had to be continued by his pupil Giovanni Battista Soria. Numerous wooden furnishings inside the church confirm the craftsmanship of Montano and his workshop. Works Alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Baptista Montano, From The The Lives Of The Artists By Giorgio Vasari
Giovanni may refer to: * Giovanni (name), an Italian male given name and surname * Giovanni (meteorology), a Web interface for users to analyze NASA's gridded data * ''Don Giovanni'', a 1787 opera by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, based on the legend of Don Juan * Giovanni (Pokémon), boss of Team Rocket in the fictional world of Pokémon * Giovanni (World of Darkness), a group of vampires in ''Vampire: The Masquerade/World of Darkness'' roleplay and video game * "Giovanni", a song by Band-Maid from the 2021 album ''Unseen World'' * ''Giovanni's Island'', a 2014 Japanese anime drama film * ''Giovanni's Room'', a 1956 novel by James Baldwin * Via Giovanni, places in Rome See also * * *Geovani *Giovanni Battista *San Giovanni (other) *San Giovanni Battista (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrian's Villa
Hadrian's Villa (; ) is a UNESCO World Heritage Site comprising the ruins and archaeological remains of a large Roman villa, villa complex built around AD 120 by Roman emperor Hadrian near Tivoli, Italy, Tivoli outside Rome. It is the most imposing and complex Roman villa known. The complex contains over 30 monumental and scenic buildings arranged on a series of artificial esplanades at different heights and surrounded by gardens decorated with water basins and nymphaea (fountains). The whole complex covers an area of at least a square kilometre, an area larger than the city of Pompeii. In addition to the villa's impressive layout, many of the buildings are considered masterpieces of Roman architecture, making use of striking curved shapes enabled by extensive use of concrete. They were ingenious for the complex symmetry of their ground plans and are considered unrivalled until the arrival of Baroque architecture in the 17th century, initiated by Borromini, who used Hadrian's Vill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th-century Italian Architects
The 16th century began with the Julian calendar, Julian year 1501 (represented by the Roman numerals MDI) and ended with either the Julian or the Gregorian calendar, Gregorian year 1600 (MDC), depending on the reckoning used (the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The Renaissance in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the Copernican heliocentrism, heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through observational measurement of the SN 1572, 1572 appearance of a Milky Way supernova. These events directly challenged the long-held notion of an immutable universe supported by Ptolemy and Aristotle, and led to major revolutions in astronomy and science. Galileo Galilei became a champion of the new sciences, invented the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1621 Deaths
Events January–March * January 12 – Şehzade Mehmed (son of Ahmed I), Şehzade Mehmed, the 15-year old half-brother of Ottoman Sultan Osman II, is put to death by hanging on Osman's orders. Before dying, Mehmed prays aloud that Osman's reign as Sultan be ruined. * January 18 – The Dutch East India Company formally names its fortress at Jayakarta in Indonesia, calling it Jakarta, Batavia. Upon the independence of the Dutch East Indies as Indonesia in 1945, Batavia will be renamed Jakarta. * January 22 – The Tianqi (era), Tianqi era begins in Ming Dynasty China, six months after Zhu Changluo becomes the Taichang Emperor. * January 24 – Twelve days after the murder of Prince Mehmed on orders of Sultan Osman II, Constantinople is hit by bitter winter weather, leading to rioting by persons who believe that the punishment of Osman is the will of Allah. * January 28 – Pope Paul V (Camillo Borghese) dies at the age of 70 after 15 years as Pont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1534 Births
Year 1534 ( MDXXXIV) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. Events January–March * January 15 – The Parliament of England passes the '' Act Respecting the Oath to the Succession'', recognising the marriage of Henry VIII and Anne Boleyn, and their children as the legitimate heirs to the throne. * February 23 – A group of Anabaptists, led by Jan Matthys, seize Münster, Westphalia and declare it ''The New Jerusalem'', begin to exile dissenters, and forcibly baptize all others. *March 10 – The Portuguese crown divides Colonial Brazil into fifteen donatory captaincies, hereditary titles similar to duchies. * March 30 – The Submission of the Clergy Act 1533 becomes law in England, requiring submission of the clergy, that is, churchmen are to submit to the king and the publication of ecclesiastical laws without royal permission is forbidden. April–June * April 5 (Easter Sunday) – Anabaptist Jan Matthys is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Blunt
Anthony Frederick Blunt (26 September 1907 – 26 March 1983), (formerly styled Sir Anthony Blunt from 1956 until November 1979), was a leading British art historian and a Soviet spy. Blunt was a professor of art history at the University of London, the director of the Courtauld Institute of Art and Surveyor of the Queen's Pictures. His 1967 monograph on the French Baroque painter Nicolas Poussin is still widely regarded as a watershed book in art history.Shone, Richard and Stonard, John-Paul, eds. ''The Books that Shaped Art History'', Introduction. London: Thames & Hudson, 2013. His teaching text and reference work ''Art and Architecture in France 1500–1700'', first published in 1953, reached its fifth edition (in a version slightly revised by Richard Beresford) in 1999, at which time it was still considered the best account of the subject. He was the "fourth man" of the Cambridge Five, a group of Cambridge-educated spies who worked for the Soviets between the 1930s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sant'Ivo Alla Sapienza
Sant'Ivo alla Sapienza (''lit.'' 'Saint Ivo at the Sapienza (University of Rome)') is a Catholic church in Rome. Built in 1642–1660 by the architect Francesco Borromini, the church is widely regarded a masterpiece of Roman Baroque architecture. The church is at the rear of a courtyard at 40, Corso del Rinascimento; the complex is now used by the State Archives of Rome. History In the 14th century, there was a chapel here for the palace of the University of Rome. The University is called ''La Sapienza'', and the church was dedicated to Saint Ivo (or Yves, patron saint of jurists). When a design was commissioned from Borromini in the 17th century, he adapted to the already existing palazzo. He chose a plan resembling a star of David – which would have been recognized at the time as a Star of Solomon, symbolizing wisdom – and merged a curved facade of the church with the courtyard of the palace. The corkscrew lantern of the dome was novel. The complex rhythms of the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassiano Dal Pozzo
Cassiano dal Pozzo (1588 – 22 October 1657) was an Italian scholar and patron of arts. The secretary of Cardinal Francesco Barberini, he was an antiquary in the classicizing circle of Rome, and a long-term friend and patron of Nicolas Poussin, whom he supported from his earliest arrival in Rome: Poussin in a letter declared that he was "a disciple of the house and the museum of cavaliere dal Pozzo." A doctor with interests in the proto-science of alchemy, a correspondent of major figures like Galileo, a collector of books and master drawings, dal Pozzo was a node in the network of European scientific figures. Biography Dal Pozzo was born in Turin, to a noble family originating from Vercelli, the grandson of the first minister of the Grand Duke of Tuscany. He was raised in Florence and educated at the University of Pisa. In 1612 he moved to Rome, where with deft diplomacy he moved among influential and cultivated patrons. After taking up a position as secretary in Cardinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptis Magna
Leptis or Lepcis Magna, also known by #Names, other names in classical antiquity, antiquity, was a prominent city of the Carthaginian Empire and Roman Libya at the mouth of the Wadi Lebda in the Mediterranean. Established as a Punic people, Punic settlement prior to 500 BC, the city experienced significant expansion under Roman Emperor Septimius Severus (), who was born in the city. The Legio III Augusta, 3rd Augustan Legion was stationed here to defend the city against Berbers, Berber incursions. After the legion's dissolution under in 238, the city was increasingly open to raids in the later part of the 3rd century. Diocletian reinstated the city as provincial capital, and it grew again in prosperity until it fell to the Vandals in 439. It was reincorporated into the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Empire in 533 but continued to be plagued by Berber raids and never recovered its former importance. It fell to the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb, Muslim invasion in and was subsequently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
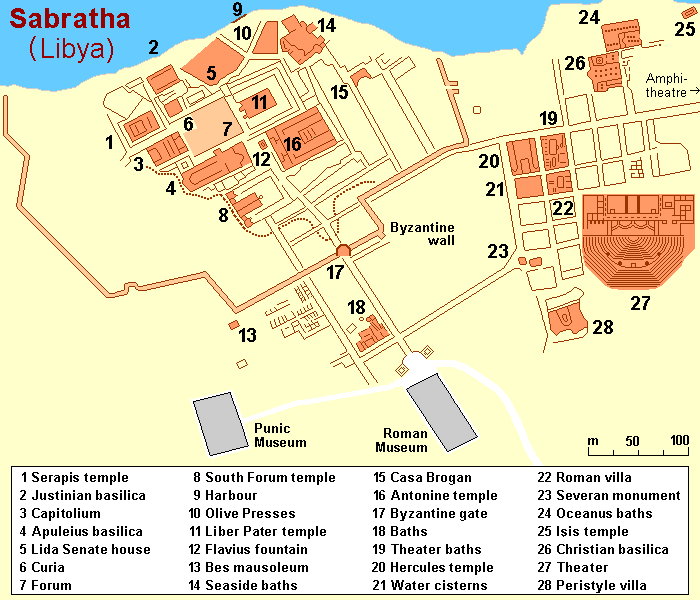
Sabratha
Sabratha (; also ''Sabratah'', ''Siburata''), in the Zawiya District''شعبيات الجماهيرية العظمى''Sha'biyat of Great Jamahiriya accessed 20 July 2009, in Arabic of Libya, was the westernmost of the ancient "three cities" of Roman Tripolis (region of Africa), Tripolis, alongside Oea and Leptis Magna. From 2001 to 2007 it was the capital of the former Sabratha wa Sorman District. It lies on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast about west of modern Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli. The extant archaeological site was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1982. Ancient Sabratha Sabratha's port was established, perhaps about 500BCE, as the Phoenician trading-post of Tsabratan (, , or , ). This seems to have been a Berber language, ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
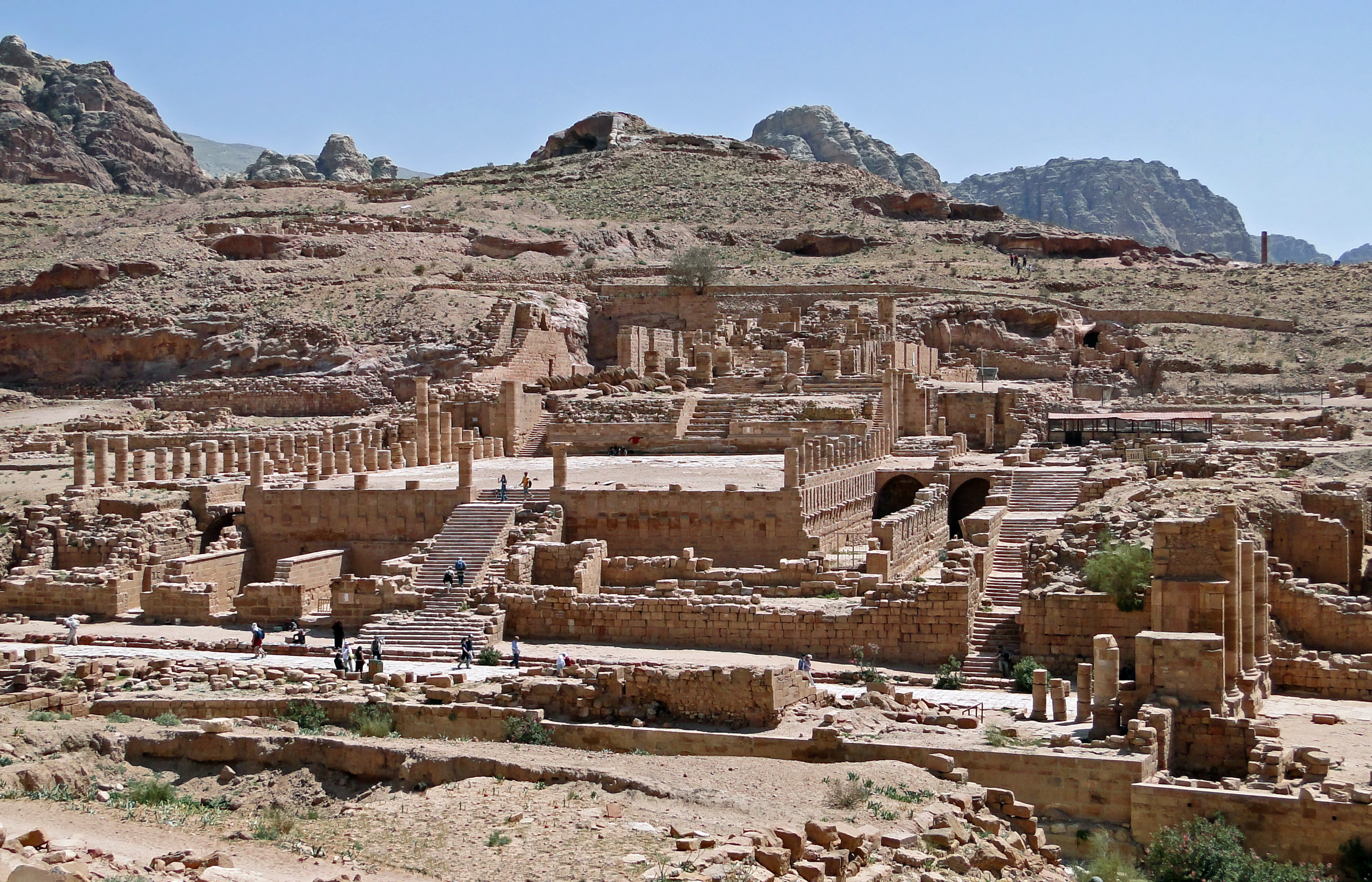
Petra
Petra (; "Rock"), originally known to its inhabitants as Raqmu (Nabataean Aramaic, Nabataean: or , *''Raqēmō''), is an ancient city and archaeological site in southern Jordan. Famous for its rock-cut architecture and water conduit systems, Petra is also called the "Rose City" because of the colour of the sandstone from which it is carved. The city is one of the New 7 Wonders of the World and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The area around Petra has been inhabited from as early as 7000 BC, and was settled by the Nabataeans, a nomadic Arab people, in the 4th century BC. Petra would later become the capital city of the Nabataean Kingdom in the second century BC. The Nabataeans invested in Petra's proximity to the incense trade routes by establishing it as a major regional trading hub, which gained them considerable revenue. Unlike their enemies, the Nabataeans were accustomed to living in the barren deserts and thus were able to defend their kingdom. They were particularly sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |