|
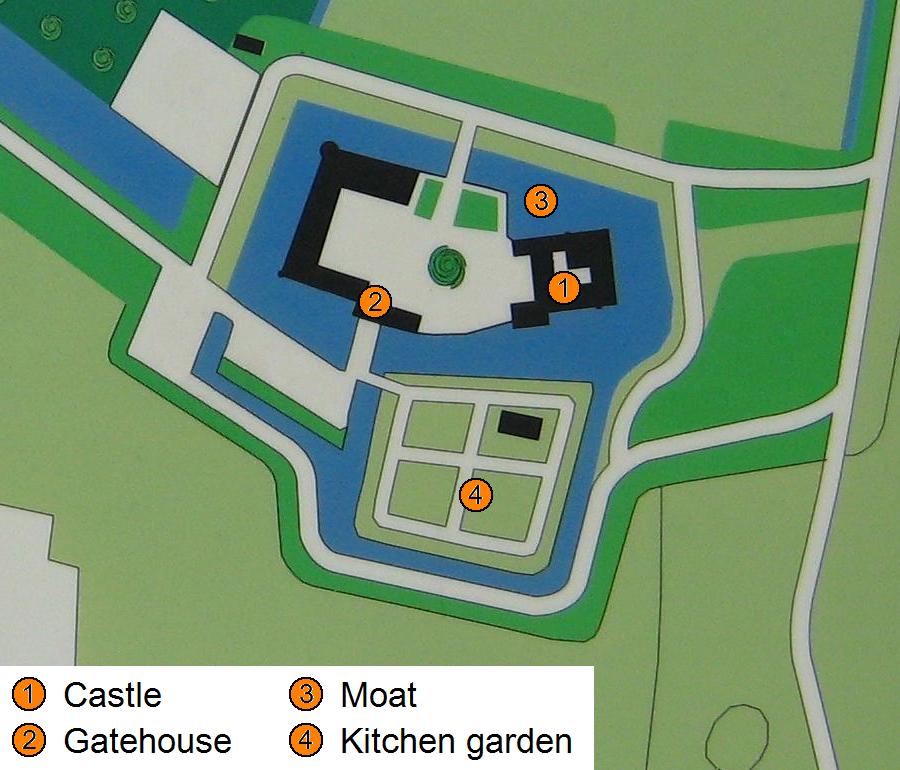
Giessen Castle
Kasteel Giessen was a castle in Giessen, Netherlands. It was rediscovered in 2013, but was not made visible. History Giessen Castle was the first known castle of the Lords of Giessen, who were vassals of the Lords of Altena, seated at nearby Altena Castle in Almkerk. A second, later 'house' of the Lords of Giessen, stood to the north, near the small river Alm, and was mentioned in 1364. A third 'house' stood just west of the first, and was first mentioned in 1328. The exact location of these other houses remains unknown. Giessen Castle was first mentioned in 1296. In that year Arnoud of Giessen was granted his strong house in fief by Willem II of Horne. That is, there is an act dated 5 April 1308. In the act some lords declare that they were present when Arnout of Ghiessen, son of Vastaert of Ghiessen received his from Willem of Horne. It is known that after the death of Vastaert, Jan van Cuijk was arbiter to end the conflict between Vastaert and Willem of Horne. In this capac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giessen, Netherlands
Giessen is a village in the Dutch province of North Brabant. It is located in the municipality of Altena, about 7 km southeast of Gorinchem. History The village was first mentioned in 1178 as Giscen. It is named after a river, however the etymology is unclear. Giessen developed in the Middle Ages along the Afgedamde Maas. The Dutch Reformed church dates was built on a ''terp'' (artificial living hill). It was constructed in the 14th century. In 1755, the tower collapsed due to frequently flooding. The church was enlarged in 1856. Giessen was home to 360 people in 1840. Giessen was a separate municipality until 1973, when it became a part of the former municipality of Woudrichem. Giessen nowadays forms a single urban area with Rijswijk. Sights Giessen is part of the New Dutch Water Line. Fort Giessen has been preserved, and was constructed between 1878 and 1881. In 2013 Giessen Castle was rediscovered in the village. There are no visible traces of this castle, except ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buttress
A buttress is an architectural structure built against or projecting from a wall which serves to support or reinforce the wall. Buttresses are fairly common on more ancient buildings, as a means of providing support to act against the lateral (sideways) forces arising out of inadequately braced roof structures. The term ''counterfort'' can be synonymous with buttress and is often used when referring to dams, retaining walls and other structures holding back earth. Early examples of buttresses are found on the Eanna Temple (ancient Uruk), dating to as early as the 4th millennium BC. Terminology In addition to flying and ordinary buttresses, brick and masonry buttresses that support wall corners can be classified according to their ground plan. A clasping or clamped buttress has an L shaped ground plan surrounding the corner, an angled buttress has two buttresses meeting at the corner, a setback buttress is similar to an angled buttress but the buttresses are set back from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teylingen Castle
Teylingen Castle (Dutch: ''Slot Teylingen'') is a Dutch castle in the municipality of Teylingen, in the town of Voorhout, near the border with Sassenheim. It is presumably the family keep of the noble family , from which the Van Brederode family directly descended. History The castle was originally built to protect the north-south route in Hollandic territory. Later it became a forester's castle for the forestry of the counts of Holland, starting with William IV, count of Holland. One of the best known inhabitants of the castle was Jacoba of Bavaria, who died there. At the time of her death she was married to her fourth husband Frank van Borssele. The drinking cups dug up in the surrounding area are called ''Jacobakanntjes''. The castle was heavily damaged around 1570 during the Eighty Years' War The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Castle
A water castle is a castle whose site is largely defended by water. It can be entirely surrounded by water-filled moats (moated castle) or natural waterbodies such as island castles in a river or offshore. The term comes from European castle studies, mainly German ''Burgenkunde'', but is sometimes used in English-language popular science books and websites, and is mentioned in other more academic works. When stately homes were built in such a location, or a Wasserburg was later rebuilt as a residential manor, the German term becomes Wasserschloss, lit. "water palace/manor". Description Forde-Johnston describes such a site as "a castle in which water plays a prominent part in the defences." Apart from hindering attackers, an abundant supply of water was also an advantage during a siege. Topographically, such structures are a type of low-lying castle. Such a castle usually had only one entrance, which was via a drawbridge and that could be raised for protection in the event of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motte-and-bailey Castle
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy to build with unskilled labour, but still militarily formidable, these castles were built across northern Europe from the 10th century onwards, spreading from Normandy and Anjou in France, into the Holy Roman Empire in the 11th century. The Normans introduced the design into England and Wales. Motte-and-bailey castles were adopted in Scotland, Ireland, the Low Countries and Denmark in the 12th and 13th centuries. Windsor Castle, in England, is an example of a motte-and-bailey castle. By the end of the 13th century, the design was largely superseded by alternative forms of fortification, but the earthworks remain a prominent feature in many countries. Architecture Structures A motte-and-bailey castle was made up of two structures: a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tower House
A tower house is a particular type of stone structure, built for defensive purposes as well as habitation. Tower houses began to appear in the Middle Ages, especially in mountainous or limited access areas, in order to command and defend strategic points with reduced forces. At the same time, they were also used as an aristocrat's residence, around which a castle town was often constructed. Europe After their initial appearance in Ireland, Scotland, the Frisian lands, Basque Country and England during the High Middle Ages, tower houses were also built in other parts of western Europe, especially in parts of France and Italy. In Italian medieval communes, urban ''palazzi'' with a very tall tower were increasingly built by the local highly competitive patrician families as power centres during times of internal strife. Most north Italian cities had a number of these by the end of the Middles Ages, but few now remain, notably two towers in Bologna, twenty towers in Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amsterdam Ordnance Datum
Amsterdam Ordnance Datum or ' (NAP) is a vertical datum in use in large parts of Western Europe. Originally created for use in the Netherlands, its height was used by Prussia in 1879 for defining ', and in 1955 by other European countries. In the 1990s, it was used as the reference level for the United European leveling Network (UELN) which in turn led to the European Vertical Reference System (EVRS). Mayor Johannes Hudde of Amsterdam in a way came up with the idea after he expanded the sea dike after a flood in Amsterdam in 1675. Of course a dike should be storm-resistant to protect a city against flooding, and in this case a margin of "9 feet and 5 inches" (2.67 m - margin is defined in Amsterdam feet) was deemed enough to cope with rising water. So he measured the water level of the adjacent sea arm, ' and compared it with the water level in the canals within the city itself. He found that the water level at an average summer flood in the sea arm (when the water level rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemin De Ronde
A ''chemin de ronde'' (French, "round path"' or "patrol path"; ), also called an allure, alure or, more prosaically, a wall-walk, is a raised protected walkway behind a castle battlement. In early fortifications, high castle walls were difficult to defend from the ground. The ''chemin de ronde'' was devised as a walkway allowing defenders to patrol the tops of ramparts, protected from the outside by the battlements or a parapet A parapet is a barrier that is an extension of the wall at the edge of a roof, terrace, balcony, walkway or other structure. The word comes ultimately from the Italian ''parapetto'' (''parare'' 'to cover/defend' and ''petto'' 'chest/breast'). ..., placing them in an advantageous position for shooting or dropping. References External links * Castle architecture {{castle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altena Castle (Almkerk)
Altena Castle is a former castle in Almkerk. It was home to the lords of Altena, and often of the lords of Horne and Altena. Castle Characteristics All that remains of Altena Castle is its clearly visible motte. Therefore, there can be little doubt that Altena Castle started out as a motte-and-bailey castle. During excavations a large amount of tuff stone was found. This indicates that Altena Castle was built before the procedure to produce brick was reinvented in the Netherlands. This reinvention took place in about 1200. The foundation date is estimated to be around 1150. In time, motte-and-bailey castles were modernized. On 17th century pictures, the remains of the castle are depicted as a polygonal tower on a motte (see Schijnvoet's engraving). This is a somewhat unusual configuration for the Netherlands, where many motte-and-bailey castles were levelled to become circular water castles. Others became shell keeps by building a circular wall on top of the motte e.g. Burcht v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pier (architecture)
A pier, in architecture, is an upright support for a structure or superstructure such as an arch or bridge. Sections of structural walls between openings (bays) can function as piers. External or free-standing walls may have piers at the ends or on corners. Description The simplest cross section of the pier is square, or rectangular, but other shapes are also common. In medieval architecture, massive circular supports called drum piers, cruciform (cross-shaped) piers, and compound piers are common architectural elements. Columns are a similar upright support, but stand on a round base. In buildings with a sequence of bays between piers, each opening (window or door) between two piers is considered a single bay. Bridge piers Single-span bridges have abutments at each end that support the weight of the bridge and serve as retaining walls to resist lateral movement of the earthen fill of the bridge approach. Multi-span bridges require piers to support the ends of sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocarbon Dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon. The method was developed in the late 1940s at the University of Chicago by Willard Libby. It is based on the fact that radiocarbon () is constantly being created in the Earth's atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric nitrogen. The resulting combines with atmospheric oxygen to form radioactive carbon dioxide, which is incorporated into plants by photosynthesis; animals then acquire by eating the plants. When the animal or plant dies, it stops exchanging carbon with its environment, and thereafter the amount of it contains begins to decrease as the undergoes radioactive decay. Measuring the amount of in a sample from a dead plant or animal, such as a piece of wood or a fragment of bone, provides information that can be used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |