|
Gibberellic Acid
Gibberellic acid (also called gibberellin A3 or GA3) is a hormone found in plants and fungi. Its chemical formula is C19H22O6. When purified, it is a white to pale-yellow solid. Plants in their normal state produce large amounts of GA3. It is possible to produce the hormone industrially using microorganisms.Camara, M. C. et al (2015) General Aspects and Applications of Gibberelins and Gibberellic Acid in Plants. In: Hardy, J.. (Org.). Gibberellins and Gibberellic Acid: Biosynthesis, Regulation and Physiological Effects. 1ed.Hauppauge: Nova Science Publishers, 2015, v., p. 1-21. Gibberellic acid is a simple gibberellin, a pentacyclic diterpene acid promoting growth and elongation of cells. It affects decomposition of plants and helps plants grow if used in small amounts, but eventually plants develop tolerance to it. GA stimulates the cells of germinating seeds to produce mRNA molecules that code for hydrolytic enzymes. Gibberellic acid is a very potent hormone whose natural occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Hormone
Plant hormones (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, including embryogenesis, the regulation of Organ (anatomy), organ size, pathogen defense, Stress (biology), stress tolerance and Reproduction, reproductive development. Unlike in animals (in which hormone production is restricted to specialized glands) each plant cell is capable of producing hormones. Frits Warmolt Went, Went and Thimann coined the term "phytohormone" and used it in the title of their 1937 book. Phytohormones occur across the plant kingdom, and even in algae, where they have similar functions to those seen in vascular plant, vascular plants ("higher plants"). Some phytohormones also occur in microorganisms, such as unicellular fungus, fungi and bacteria, however in these cases they do not play a hormonal role and can better be regarded as secondary metabolites. Characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactones
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters. They are derived from the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids by esterification. They can be saturated or unsaturated. Lactones are formed by lactonization, the intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids. Nomenclature Greek prefixes in alphabetical order indicate ring size. Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH and the -COOH groups along said backbone. The first carbon atom after the carbon in the -COOH group on the parent compound is labelled α, the second will be labeled β, and so forth. Therefore, the prefixes also indicate the size of the lactone ring: α-lactone = 3-membered ring, β-lactone = 4-membered, γ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of Hydrocarbon, hydrocarbons, conferring Hydrophile, hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur. History The flammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of alcohol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan, J� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Hormones
Plant hormones (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, including embryogenesis, the regulation of Organ (anatomy), organ size, pathogen defense, Stress (biology), stress tolerance and Reproduction, reproductive development. Unlike in animals (in which hormone production is restricted to specialized glands) each plant cell is capable of producing hormones. Frits Warmolt Went, Went and Thimann coined the term "phytohormone" and used it in the title of their 1937 book. Phytohormones occur across the plant kingdom, and even in algae, where they have similar functions to those seen in vascular plant, vascular plants ("higher plants"). Some phytohormones also occur in microorganisms, such as unicellular fungus, fungi and bacteria, however in these cases they do not play a hormonal role and can better be regarded as secondary metabolites. Characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
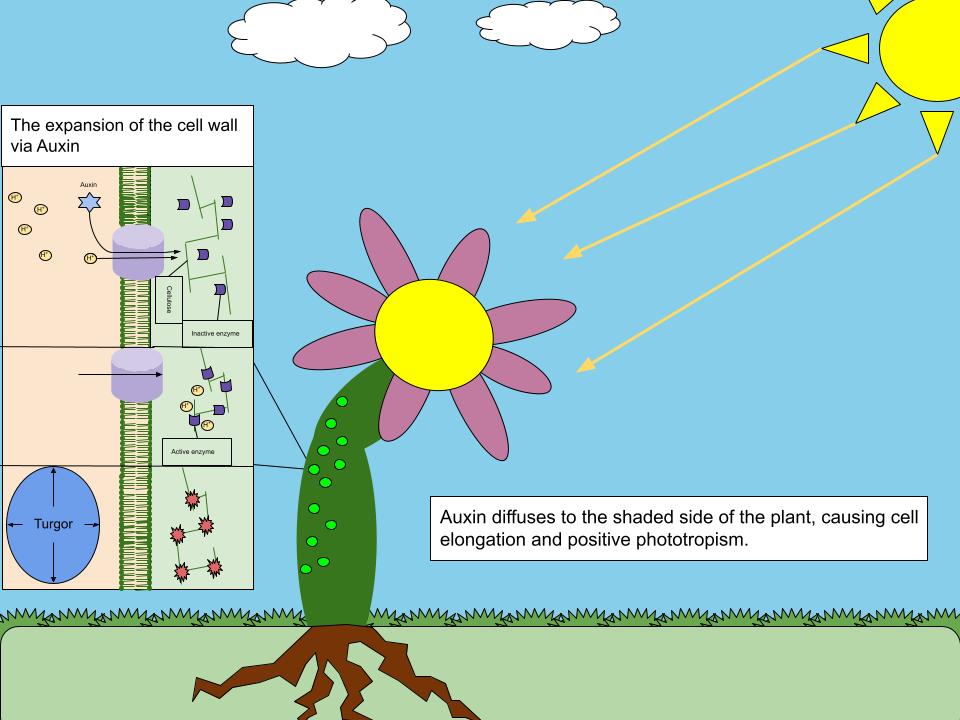
Auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essential for plant body development. The Dutch biologist Frits Warmolt Went first described auxins and their role in plant growth in the 1920s. Kenneth V. Thimann became the first to isolate one of these phytohormones and to determine its chemical structure as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Went and Thimann co-authored a book on plant hormones, ''Phytohormones'', in 1937. Overview Auxins were the first of the major plant hormones to be discovered. They derive their name from the Greek word ( – 'to grow/increase'). Auxin is present in all parts of a plant, although in very different concentrations. The concentration in each position is crucial developmental information, so it is subject to tight regulation through both metabolism and transp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6-Benzylaminopurine
6-Benzylaminopurine, benzyl adenine, BAP or BA is a first-generation synthetic cytokinin that elicits plant growth and development responses, setting blossoms and stimulating fruit richness by stimulating cell division. It is an inhibitor of respiratory kinase in plants, and increases post-harvest life of green vegetables. Influence of cytokinin as 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP) in combination with other methods on postharvest green color retention on broccoli heads and asparagus spears, showed positive results for quality retention. Treatment with 10 and 15 ppm BAP can be used to extend shelf life of fresh-cut broccoli florets and shredded cabbage during storage at 6±1°C at commercial level. It can be used to extend the shelf life of flowers and cut greens in floristry. The shelf life of cut shoots of ''Polygonatum multiflorum'' 'Variegatum' kept in water is about 7 days. To extend their life after cutting, conditioning with gibberellic acid or BA is used. This doubles their possib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibberellin
Gibberellins (GAs) are plant hormones that regulate various Biological process, developmental processes, including Plant stem, stem elongation, germination, dormancy, flowering, flower development, and leaf and fruit senescence. They are one of the longest-known classes of plant hormone. It is thought that the selective breeding (albeit unconscious) of crop strains that were deficient in GA synthesis was one of the key drivers of the "Green Revolution, green revolution" in the 1960s, a revolution that is credited to have saved over a billion lives worldwide. Chemistry All known gibberellins are Diterpene#Diterpenoids, diterpenoid acids synthesized by the terpenoid pathway in plastids and then modified in the endoplasmic reticulum and cytosol until they reach their biologically active form. All are derived via the ''ent''-gibberellane skeleton but are synthesised via ''ent''-kaurene. The gibberellins are named GA1 through GAn in order of discovery. Gibberellic acid, which was the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abscisic Acid
Abscisic acid (ABA or abscisin II) is a plant hormone. ABA functions in many plant developmental processes, including seed and bud dormancy, the control of organ size and stomatal closure. It is especially important for plants in the response to environmental stresses, including drought, soil salinity, cold tolerance, freezing tolerance, heat stress and heavy metal ion tolerance. Discovery In the 1940s, Torsten Hemberg, while working at the University of Stockholm, found evidence that a positive correlation exists between the rest period and the occurrence of an acidic ether soluble growth inhibitor in potato tubers. In 1963, abscisic acid was first identified and characterized as a plant hormone by Frederick T. Addicott and Larry A. Davis. They were studying compounds that cause abscission (shedding) of cotton fruits (bolls). Two compounds were isolated and called abscisin I and abscisin II. Abscisin II is presently called abscisic acid (ABA). In plants Function ABA was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malting
Malting is the process of steeping, germinating, and drying grain to convert it into malt. Germination and sprouting involve a number of enzymes to produce the changes from seed to seedling and the malt producer stops this stage of the process when the required enzymes are optimal. Among other things, the enzymes convert starch to sugars such as maltose, maltotriose and maltodextrines. The malt is mainly used for brewing or whisky making, but can also be used to make malt vinegar or malt extract. Various grains are used for malting, most often barley, sorghum, wheat or rye. Several types of equipment can be used to produce the malt. Traditional floor malting germinates the grains in a thin layer on a solid floor, and the grain is manually raked and turned to keep the grains loose and aerated. In a modern malt house the process is more automated, and the grain is germinated on a floor that is slotted to allow air to be forced through the grain bed. Large mechanical turners, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzyladenine
6-Benzylaminopurine, benzyl adenine, BAP or BA is a first-generation synthetic cytokinin that elicits plant growth and development responses, setting blossoms and stimulating fruit richness by stimulating cell division. It is an inhibitor of respiratory kinase in plants, and increases post-harvest life of green vegetables. Influence of cytokinin as 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP) in combination with other methods on postharvest green color retention on broccoli heads and asparagus spears, showed positive results for quality retention. Treatment with 10 and 15 ppm BAP can be used to extend shelf life of fresh-cut broccoli florets and shredded cabbage during storage at 6±1°C at commercial level. It can be used to extend the shelf life of flowers and cut greens in floristry. The shelf life of cut shoots of ''Polygonatum multiflorum'' 'Variegatum' kept in water is about 7 days. To extend their life after cutting, conditioning with gibberellic acid or BA is used. This doubles their possib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |