|
Giancarlo Corsetti
Giancarlo Corsetti, (born 1960) is an Italian macroeconomist and Professor of Macroeconomics at the European University Institute in Florence. He is best known in academia for his work on open economy macroeconomics and international economics. In March 2017, the IDEAS/RePEc overall ranking put him as the most influential economist at Cambridge University where he was teaching at the time. Corsetti has previously taught at Cambridge University where he was fellow of Clare College and the director of the Cambridge Institute for New Economic Thinking. Prior to this, he held the Pierre Werner Chair at the European University Institute in Florence , and held positions at the Universities Rome III, Bologna and Yale. He is co-editor of the Journal of International Economics and a research fellow at the Centre for Economic Policy Research, where he served as co-director of the International Macroeconomics Programme between 2004 and 2015. He is a consultant to the European Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York University
New York University (NYU) is a private university, private research university in New York City, New York, United States. Chartered in 1831 by the New York State Legislature, NYU was founded in 1832 by Albert Gallatin as a Nondenominational Christianity, non-denominational all-male institution near New York City Hall, City Hall based on a curriculum focused on a secular education. The university moved in 1833 and has maintained its main campus in Greenwich Village surrounding Washington Square Park. Since then, the university has added an engineering school in Brooklyn's MetroTech Center and graduate schools throughout Manhattan. NYU is one of the largest private universities in the United States by enrollment, with a total of 51,848 enrolled students in 2021. It is one of the most applied-to schools in the country and admissions are considered selective. NYU's main campus in New York City is organized into ten undergraduate schools, including the New York University College ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Monetary Economics
The ''Journal of Monetary Economics'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering research on macroeconomics and monetary economics. It is published by Elsevier and was established in October 1973 by Karl Brunner and Charles I. Plosser. Beginning in 2002, it was merged with the ''Carnegie-Rochester Conference Series on Public Policy''. The latter series was established in 1976 and had been published independently, originally by the North-Holland Publishing Company, now an imprint of Elsevier. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 4.63. Since 2022, its editors are Boragan Aruoba and Yuriy Gorodnichenko. It is widely regarded as one of the most prestigious academic journals in economics and was ranked as top 10 among all economics journals in 2008. See also * List of economics journals The following is a list of scholarly journals in economics containing most of the prominent academic journals in economics. Popular magazine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarterly Journal Of Economics
''The Quarterly Journal of Economics'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal published by the Oxford University Press for the Harvard University Department of Economics. Its current editors-in-chief are Robert J. Barro, Lawrence F. Katz, Nathan Nunn, Andrei Shleifer, and Stefanie Stantcheva. History It is the oldest professional journal of economics in the English language, and second-oldest in any language after the . It covers all aspects of the field—from the journal's traditional emphasis on micro-theory to both empirical and theoretical macroeconomics. Reception According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2015 impact factor of 6.662, ranking it first out of 347 journals in the category "Economics". It is generally regarded as one of the top 5 journals in economics, together with the '' American Economic Review'', ''Econometrica'', the '' Journal of Political Economy'', and '' The Review of Economic Studies''. Notable papers Some of the most inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan And The World Economy
''Japan and the World Economy'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal that was established in 1989 and is edited by Shin-Ichi Fukuda. It contains articles about Japanese economy, including finance, managerial sciences, agriculture Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ..., and economic ties with other countries. External links * Economics journals Quarterly journals English-language journals Elsevier academic journals Academic journals established in 1988 {{econ-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Policy (journal)
''Economic Policy'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal published by Oxford Academic on behalf of the Centre for Economic Policy Research, the Center for Economic Studies (University of Munich), and the Paris School of Economics. The journal was established in 1985 and covers international economic policy topics such as macroeconomics, microeconomics, the labour market, trade, exchange rate, taxation, economic growth, government spending, and migration. The journal had an impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 2.844 in 2016, ranking it 33/347 in the category "Economics". References External links * {{Official website, https://academic.oup.com/economicpolicy Wiley-Blackwell academic journals English-language journals Academic journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nouriel Roubini
Nouriel Roubini (; born March 29, 1958) is a Turkish-born Iranian-American economic consultant, economist, speaker and writer. He is a professor emeritus since 2021 at the Stern School of Business of New York University. Roubini earned a BA in political economics at Bocconi University in Italy and a doctorate in international economics at Harvard University. He was an academic at Yale and a researcher/advisor researching emerging markets. In the 1990s, during the Bill Clinton administration, for one year he was a senior economist in the Council of Economic Advisers. Roubini is a frequent critic of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. Early life Roubini was born in Istanbul, Turkey, to Iranian Orthodox Jewish parents.Loch Adamson (October 12, 2011)"How Nouriel Roubini Became a Research Brand" ''Institutional Investor''. His father was a rug dealer. When he was young, Roubini was expected to go into the rug business himself, and follow in his father's footsteps. When he was a yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willem Buiter
Willem Hendrik Buiter CBE (born 26 September 1949) is an American-British economist. He spent most of his career as an academic, teaching at various universities. More recently, he was the Chief Economist at Citigroup. Early life and education Buiter was born in The Hague, Netherlands on 26 September 1949. He is a national of the United States and the United Kingdom. Willem's father, Harm Buiter, was a Dutch economist, international trades union official and politician of the Labour Party (PvdA), who had served as Mayor of Groningen. Buiter went to the European School in Brussels, Belgium from 1962 to 1967, where he obtained his European Baccalaureate. After studying Political and Social Science for one year at the University of Amsterdam from 1967 to 1968, Buiter went to Emmanuel College, Cambridge, to study Economics and received his B.A. with First-Class Honours in 1971. He was awarded his M.A. in Economics in 1972 and his M.Phil. in Economics in 1973, his fields of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Integration
European integration is the process of political, legal, social, regional and economic integration of states wholly or partially in Europe, or nearby. European integration has primarily but not exclusively come about through the European Union and its policies, and can include cultural assimilation and centralisation. The history of European integration is marked by the Roman Empire's consolidation of European and Mediterranean territories, which set a precedent for the notion of a unified Europe. This idea was echoed through attempts at unity, such as the Holy Roman Empire, the Hanseatic League, and the Napoleonic Empire. The devastation of World War I reignited the concept of a unified Europe, leading to the establishment of international organizations aimed at political coordination across Europe. The interwar period saw politicians such as Richard von Coudenhove-Kalergi and Aristide Briand advocating for European unity, albeit with differing visions. Post-World War II Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasi-experiment
A quasi-experiment is a research design used to estimate the causal impact of an intervention. Quasi-experiments share similarities with experiments and randomized controlled trials, but specifically lack random assignment to treatment or control. Instead, quasi-experimental designs typically allow assignment to treatment condition to proceed how it would in the absence of an experiment. Quasi-experiments are subject to concerns regarding internal validity, because the treatment and control groups may not be comparable at baseline. In other words, it may not be possible to convincingly demonstrate a causal link between the treatment condition and observed outcomes. This is particularly true if there are confounding variables that cannot be controlled or accounted for. With random assignment, study participants have the same chance of being assigned to the intervention group or the comparison group. As a result, differences between groups on both observed and unobserved characteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Contagion
Financial contagion refers to "the spread of market disturbances—mostly on the downside—from one country to the other, a process observed through co-movements in exchange rates, stock prices, sovereign spreads, and capital flows". Financial contagion can be a potential risk for countries who are trying to integrate their financial system with international financial markets and institutions. It helps explain an economic crisis extending across neighboring countries, or even regions. Financial contagion happens at both the international level and the domestic level. At the domestic level, usually the failure of a domestic bank or financial intermediary triggers transmission when it defaults on interbank liabilities and sells assets in a fire sale, thereby undermining confidence in similar banks. An example of this phenomenon is the subsequent turmoil in the United States financial markets. International financial contagion, which happens in both advanced economies and developin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
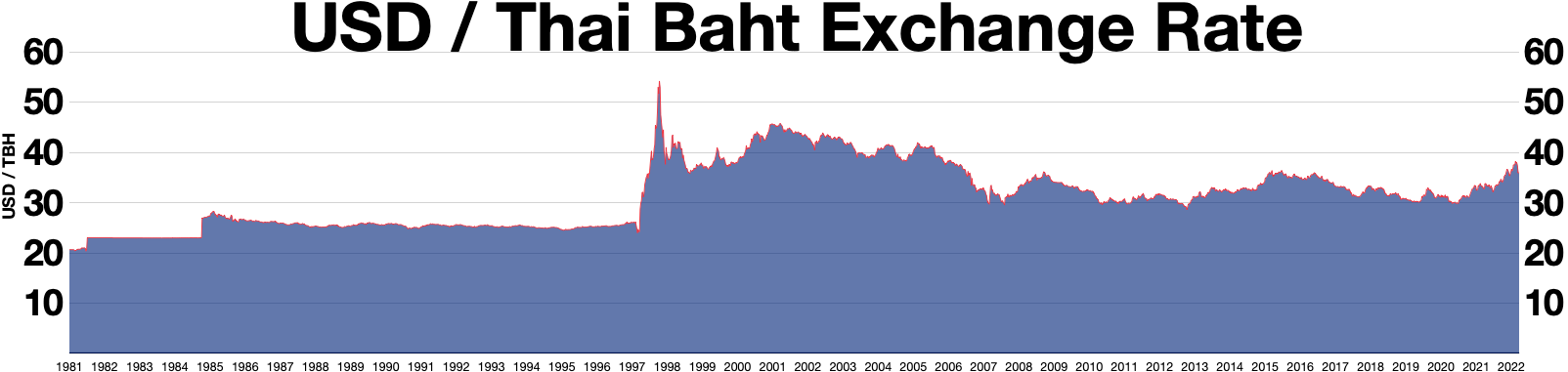
1997 Asian Financial Crisis
The 1997 Asian financial crisis gripped much of East Asia, East and Southeast Asia during the late 1990s. The crisis began in Thailand in July 1997 before spreading to several other countries with a ripple effect, raising fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998–1999 was rapid, and worries of a meltdown quickly subsided. Originating in Thailand, where it was known as the ''Tom yum, Tom Yum Kung crisis'' () on 2 July, it followed the financial collapse of the Thai baht after the Thai government was forced to floating currency, float the baht due to lack of list of circulating currencies, foreign currency to support its currency fixed exchange rate, peg to the U.S. dollar. Capital flight ensued almost immediately, beginning an international chain reaction. At the time, Thailand had acquired a burden of foreign debt. As the crisis spread, other Southeast Asian countries and later Japan and South Korea saw slumping currencies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |