|
Ghaznayn
Ghazni (, ), historically known as Ghaznayn () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana (), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan with a population of around 190,000 people. The city is strategically located along Highway 1, which follows the path that has served as the main road between Kabul and Kandahar for thousands of years. Situated on a plateau at 2,219 metres (7,280 ft) above sea level, the city is south of Kabul and is the capital of Ghazni Province. The name Ghazni derives from the Persian word ''ganj'', meaning "treasure." Ghazni Citadel, the Minarets of Ghazni, the Palace of Sultan Mas'ud III, and several other cultural heritage sites have brought travelers and archeologists to the city for centuries. During the pre-Islamic period, the area was inhabited by various tribes who practiced different religions including Zoroastrianism, Buddhism and Hinduism. Arab Muslims introduced Islam to Ghazni in the 7th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cities Of Afghanistan
The only city in Afghanistan with over 1 million people is its capital, Kabul. The rest are smaller cities and towns. Demographics of Afghanistan, Afghanistan's population is estimated to be between 36–50 million. Of this, 26% were reported to be living in urban areas and the rest in rural areas or the countryside. List The chart below shows 18 cities of Afghanistan with a population over 70,000, by order of population. Population estimates are from 2015. Ancient names Ancient names of places or cities in Afghanistan: Gallery File:Kabul, Afghanistan view.jpg , Kabul is the only city in Afghanistan with over a million residents File:Aerial view of a section of Kandahar in 2013.jpg , Kandahar is the second largest city and the former capital of Afghanistan. The city is located in southern Afghanistan. File: View of Herat in 2009.jpg , Herat is the third largest city and is located in western Afghanistan File: Mi-17 helicopter flies over the northern Afghan city-101113-N- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century Before the Common Era, BCE. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to Western world, the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of bhavana, development which leads to Enlightenment in Buddhism, awakening and moksha, full liberation from ''Duḥkha, dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presidency Armies
The presidency armies were the armies of the three Presidencies of British India, presidencies of the East India Company's Company rule in India, rule in India, later the forces of the the Crown, British Crown in British Raj, India, composed primarily of Indian sepoys. The presidency armies were named after the presidencies: the Bengal Army, the Madras Army and the Bombay Army. Initially, only Europeans served as commissioned or non-commissioned officers. In time, Indian Army units were garrisoned from Peshawar in the north, to Sind in the west, and to Rangoon in the east. The army was engaged in the wars to extend British control in India (the Anglo-Mysore Wars, Mysore, Anglo-Maratha Wars (other), Maratha and Second Anglo-Sikh War, Sikh wars) and beyond (the Anglo-Burmese wars, Burma, Anglo-Afghan War, Afghan, First Opium War, First and Second Opium Wars, and the Expedition to Abyssinia). The presidency armies, like the presidencies themselves, belonged to the Company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Anglo-Afghan War
The First Anglo-Afghan War () was fought between the British Empire and the Emirate of Kabul from 1838 to 1842. The British initially successfully invaded the country taking sides in a succession dispute between emir Dost Mohammad Khan ( Barakzai) and former King Shah Shujah (Durrani), whom they reinstalled upon occupying Kabul in August 1839. The main British Indian force occupied Kabul and endured harsh winters. The force and its camp followers were almost completely massacred during the 1842 retreat from Kabul. The British then sent what was widely termed an " Army of Retribution" to Kabul to avenge the destruction of the previous forces. After recovering prisoners, they left Afghanistan by the end of the year. Dost Mohammed returned from exile in India to resume his rule. It was one of the first major conflicts during the Great Game, the 19th century competition for power and influence in Central Asia between Britain and Russia. Background Causes The 19th century wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durrani Empire
The Durrani Empire, colloquially known as the Afghan Empire, or the Saddozai Kingdom, was an Afghanistan, Afghan empire founded by the Durrani tribe of Pashtuns under Ahmad Shah Durrani in 1747, which spanned parts of Central Asia, the Iranian plateau, and the Indian subcontinent. At its peak, it ruled over present-day Afghanistan, much of Pakistan, parts of northeastern and southeastern Iran, eastern Turkmenistan, and northwestern India. Next to the Ottoman Empire, the Durrani Empire is considered to be among the most significant List of Muslim states and dynasties, Islamic empires of the second half of the 18th century. Ahmad was the son of Muhammad Zaman Khan (an Afghan (ethnonym), Afghan chieftain of the Durrani, Abdali tribe) and the commander of Nader Shah, Nader Shah Afshar. Following Afshar's death in June 1747, Ahmad secured Afghanistan by taking Kandahar, Ghazni, Kabul, and Peshawar. After his accession as the nation's king, he changed his tribal name from ''Abdali'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotaki Dynasty
The Hotak dynasty ( ) was an Afghan monarchy founded by Ghilji Pashtuns that briefly ruled portions of Iran and Afghanistan during the 1720s. It was established in April 1709 by Mirwais Hotak, who led a successful rebellion against the declining Persian Safavid empire in the region of Loy Kandahar ("Greater Kandahar") in what is now southern Afghanistan. In 1715, Mirwais died of natural causes and his brother Abdul Aziz succeeded him. He did not reign long as he was killed by his nephew Mahmud, who deposed the Safavid Shah and proclaimed his own rule over Iran. Mahmud in turn was succeeded by his cousin Ashraf following a palace coup in 1725. Ashraf also did not retain his throne for long, as the Iranian conqueror Nader-Qoli Beg (later Shah), leading the resurgent Safavid banner, defeated him at the Battle of Damghan of 1729. Ashraf Hotak was banished to what is now southern Afghanistan, confining Hotak rule to a small corner of their former empire. In 1738, Hotak rule e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
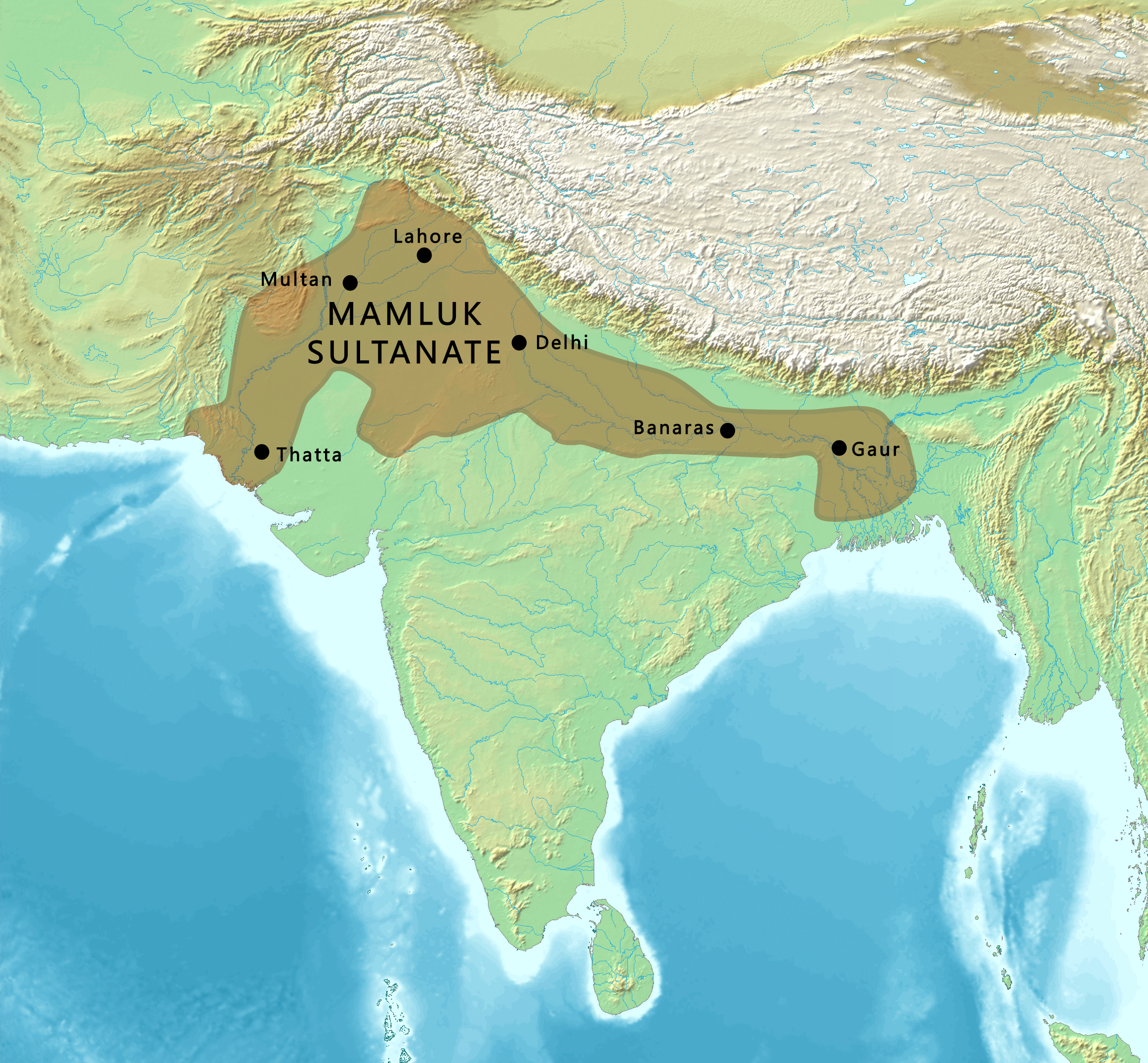
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries.Delhi Sultanate Encyclopædia Britannica The sultanate was established around in the former Ghurid Empire, Ghurid territories in India. The sultanate's history is generally divided into five periods: Mamluk dynasty (Delhi), Mamluk (1206–1290), Khalji dynasty, Khalji (1290–1320), Tughlaq dynasty, Tughlaq (1320–1414), Sayyid dynasty, Sayyid (1414–1451), and Lodi dynasty, Lodi (1451–1526). It covered large swaths of territory in modern-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, as well as some parts of southern Nepal. The foundation of the Sultanate was established by the Ghurid conqueror Muhammad of Ghor, Muhammad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timurids
The Timurid Empire was a late medieval, culturally Persianate, Turco-Mongol empire that dominated Greater Iran in the early 15th century, comprising modern-day Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan, much of Central Asia, the South Caucasus, and parts of contemporary Pakistan, North India, and Turkey. The empire was culturally hybrid, combining Turkic, Mongolic, and Persian influences, with the last members of the dynasty being regarded as "ideal Perso-Islamic rulers". The empire was founded by Timur (also known as Tamerlane), a warlord of Turco-Mongol lineage, who established the empire between 1370 and his death in 1405. He envisioned himself as the great restorer of the Mongol Empire of Genghis Khan, regarded himself as Genghis's heir, and associated closely with the Borjigin. Timur continued vigorous trade relations with Ming China and the Golden Horde, with Chinese diplomats like Ma Huan and Chen Cheng regularly traveling west to Samarkand to buy and sell goods. The empire led to the Tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghurid Dynasty
The Ghurid dynasty (also spelled Ghorids; ; self-designation: , ''Šansabānī'') was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian Tajik origin, which ruled from the 8th-century in the region of Ghor, and became an Empire from 1175 to 1215. The Ghurids were centered in the hills of the Ghor region in the present-day central Afghanistan, where they initially started out as local chiefs. They gradually converted to Sunni Islam after the conquest of Ghor by the Ghaznavid ruler Mahmud of Ghazni in 1011. The Ghurids eventually overran the Ghaznavids when Muhammad of Ghor seized Lahore and expelled the Ghaznavids from their last stronghold. The Ghurids initially ruled as vassals of the Ghaznavids and later of the Seljuks. However, during the early twelfth century the long-standing rivalry between the Seljuks and Ghaznavids created a power vacuum in eastern Afghanistan and Panjab which the Ghurids took advantage of and began their territorial expansion. Ala al-Din Husayn ended the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghaznavids
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a Persianate Muslim dynasty of Turkic peoples, Turkic ''mamluk'' origin. It ruled the Ghaznavid Empire or the Empire of Ghazni from 977 to 1186, which at its greatest extent, extended from the Oxus to the Indus Valley. The dynasty was founded by Sabuktigin upon his succession to the rule of Ghazni Province, Ghazna after the death of his father-in-law, Alp Tigin, who was an ex-general of the Samanid Empire from Balkh. Sabuktigin's son, Mahmud of Ghazni, expanded the Ghaznavid Empire to the Amu Darya, the Indus River and the Indian Ocean in the east and to Rey, Iran, Rey and Hamadan in the west. Under the reign of Mas'ud I of Ghazni, Mas'ud I, the Ghaznavid dynasty began losing control over its western territories to the Seljuk Empire after the Battle of Dandanaqan in 1040, resulting in a restriction of its holdings to modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and Northern India. In 1151, Sultan Bahram Shah lost Ghazni to the Ghurid dynasty, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabuktigin
Abu Mansur Nasir ad-Din wa'd-Dawla Sabuktigin (; 940s – August-September 997) was the founder of the Ghaznavid dynasty, and amir of Ghazna from 977 to 997. Sabuktigin was a Turkic slave who was bought by Alp-Tegin, the commander of the royal guard of the Samanid dynasty. Alp-Tegin established himself as the governor of Ghazna in 962, and died a year later in 963. Afterwards, Sabuktigin built his prestige among other slave soldiers in Ghazna until he was elected by them as their ruler in 977. Sabuktigin expanded his rule down to south of present-day Afghanistan and north of Balochistan. Through conflicts with the Hindu Shahi dynasty of Kabul, he invaded Indian lands, opening the gates of India for the future monarchs of his dynasty. As a vassal of the Samanid Empire, he answered Nuh II's call to help regarding Abu Ali Simjuri's rebellion, defeating the latter in several battles during 994 to 996. Towards the end of his life, Sabuktigin arranged an agreement with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saffarid Dynasty
The Saffarid dynasty () was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian origin that ruled over parts of Persia, Greater Khorasan, and eastern Makran from 861 to 1002. One of the first indigenous Persian dynasties to emerge after the Islamic conquest, the Saffarid dynasty was part of the Iranian Intermezzo. The dynasty's founder was Ya'qub bin Laith as-Saffar, who was born in 840 in a small town called Karnin (Qarnin), which was located east of Zaranj and west of Bost, in what is now Afghanistan. A native of Sistan and a local '' ayyār'', Ya'qub worked as a coppersmith (''ṣaffār'') before becoming a warlord. He seized control of the Sistan region and began conquering most of Iran and Afghanistan, as well as parts of Pakistan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. The Saffarids used their capital Zaranj as a base for an aggressive expansion eastward and westward. They first invaded the areas south of the Hindu Kush, and then overthrew the Tahirid dynasty, annexing Khorasan in 873. By th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |