|
Gharyan Volcanic Field
Gharyan volcanic field is a volcanic field in northwestern Libya, with the towns of Bani Walid, Gharyan, Mizdah and Tarhunah close by. Gharyan is one among several intraplate volcanic fields in Africa, which include Haruj, Hoggar, Jebel Marra and Tibesti. They are linked either with crustal domes or rifts and appear to be the consequence of lithosphere-mantle processes such as mantle plumes. Haruj and Wau en Namus in Libya may be still active. The field has covered an area of about with lava domes, lava flows and volcanic cones such as the shield volcanoes Ras el-Mohor and Ras Tebra. Exposed laccoliths are also common in some parts of the field, such as Kaf El Khalef, Kaf El Tekut, Kaf Mantrus, Kaf el-Tuam and Ras Tuint-Rabib. The location of these vents appears to be controlled by a neighbouring graben and tectonic fractures. The volcanic field developed on a basement formed by Mesozoic limestones. The field has erupted basanite and phonolite with a total volume of about , add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Field
A volcanic field is an area of Earth's crust that is prone to localized volcanic activity. The type and number of volcanoes required to be called a "field" is not well-defined. Volcanic fields usually consist of clusters of up to 100 volcanoes such as cinder cones. Lava flows may also occur. They may occur as a monogenetic volcanic field or a polygenetic volcanic field. Description Alexander von Humboldt observed in 1823 that geologically young volcanoes are not distributed uniformly across the Earth's surface, but tend to be clustered into specific regions. Young volcanoes are rarely found within cratons, but are characteristic of subduction zones, rift zones, or in ocean basins. Intraplate volcanoes are clustered along hotspot traces. Within regions of volcanic activity, volcanic fields are clusters of volcanoes that share a common magma source. Scoria cones are particularly prone to cluster into volcanic fields, which are typically in diameter and consist of several t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lava Dome
In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruptions on Earth are lava dome forming. The geochemistry of lava domes can vary from basalt (e.g. Semeru, 1946) to rhyolite (e.g. Chaiten, 2010) although the majority are of intermediate composition (such as Santiaguito, dacite-andesite, present day) The characteristic dome shape is attributed to high viscosity that prevents the lava from flowing very far. This high viscosity can be obtained in two ways: by high levels of silica in the magma, or by degassing of fluid magma. Since viscous basaltic and andesitic domes weather fast and easily break apart by further input of fluid lava, most of the preserved domes have high silica content and consist of rhyolite or dacite. Existence of lava domes has been suggested for some domed structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tholeiite
The tholeiitic magma series is one of two main magma series in subalkaline igneous rocks, the other being the calc-alkaline series. A magma series is a chemically distinct range of magma compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic magma into a more evolved, silica rich end member. Rock types of the tholeiitic magma series include tholeiitic basalt, ferro-basalt, tholeiitic basaltic andesite, tholeiitic andesite, dacite and rhyolite. The variety of basalt in the series was originally called ''tholeiite'' but the International Union of Geological Sciences recommends that ''tholeiitic basalt'' be used in preference to that term.Le Maitre ''et al.'' 2002 Tholeiitic rock types tend to be more enriched in iron and less enriched in aluminium than calc-alkaline rock types. They are thought to form in a less oxidized environment than calc-alkaline rocks. Tholeiitic basalt is formed at mid-ocean ridges and makes up much of the oceanic crust. Almost all the basalt found on the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkali Basalt
Alkali basalt or alkali olivine basalt is a dark-colored, porphyritic volcanic rock usually found in oceanic and continental areas associated with volcanic activity, such as oceanic islands, continental rifts and volcanic fields. Alkali basalt is characterized by relatively high alkali (Na2O and K2O) content relative to other basalts and by the presence of olivine and titanium-rich augite in its groundmass and phenocrysts, and nepheline in its CIPW norm. Geochemical characterization Alkali basalt is chemically classified as a rock in region B (basalt) of the total alkali versus silica (TAS) diagram that contains nepheline in its CIPW norm. Basalts that do not contain normative nepheline are characterized as sub-alkali basalts, which include tholeiitic basalts and calc-alkaline basalts. Petrography The groundmass of alkali basalt is mainly composed of olivine, titanium-rich augite and plagioclase feldspar and may have alkali feldspar or feldspathoid interstitially, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tephrite
Tephrite is an igneous, volcanic ( extrusive) rock, with aphanitic to porphyritic texture. Mineral content is usually abundant feldspathoids (leucite or nepheline), plagioclase, and lesser alkali feldspar. Pyroxenes (clinopyroxenes) are common accessory minerals. Quartz and olivine are absent. Occurrences include leucite nepheline tephrite from Hamberg bei Neckarelz near Heidelberg, Germany,Frenzel, Gerhard (1953) ''Die Erzparagenese des Katzenbuckels im Odenwald'', Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, Volume 3, Number 6, pages 409-444, DOI: 10.1007/BF01129196 . Retrieved 2012-04-11. phonolite-tephrite at Monte Vulture, Basilicata, Italy and basanite–tephrite intrusions in Namibia Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and e .... References Volcanic rocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaiite
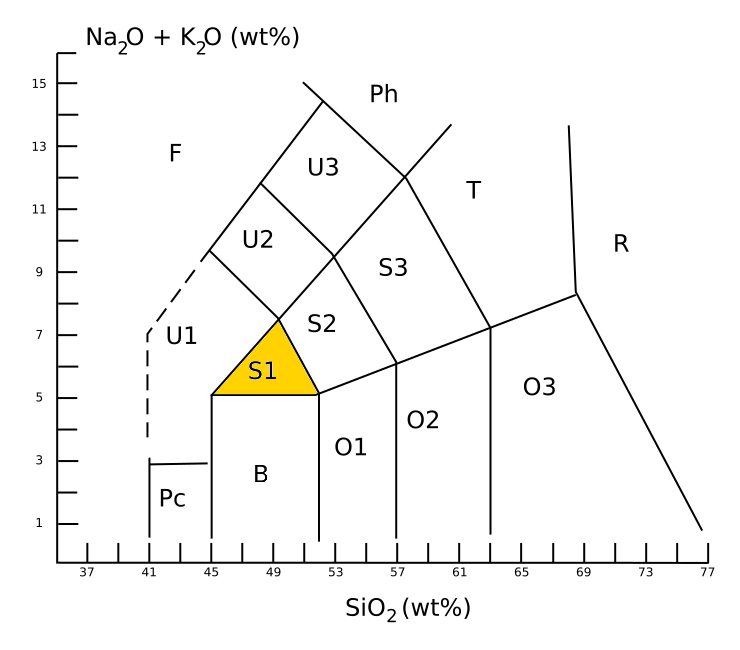
Hawaiite is an olivine basalt with a composition between alkali basalt and mugearite. It was first used as a name for some lavas found on the island of Hawaii. It occurs during the later stages of volcanic activity on oceanic islands such as Hawaii, which happens to be when the alkaline metals are most present. In gemology, hawaiite is a colloquial term for Hawaii-originated peridot, which is a gem-quality form of the mineral olivine. Description Hawaiite is an aphanitic (fine-grained) volcanic rock produced by rapid cooling of lava moderately poor in silica and enriched in alkali metal oxides (potassium oxide plus sodium oxide). It is often impractical to determine the mineral composition of such a fine-grained rock, and so hawaiite is defined chemically. Under the TAS classification, hawaiite is sodic trachybasalt, with a silica content close to 49 wt%, a total alkali metal oxide content close to 6%, and wt% > wt% + 2. This places hawaiite in the S1 field of the TAS dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basaltic Andesite
Basaltic andesite is a volcanic rock that is intermediate in composition between basalt and andesite. It is composed predominantly of augite and plagioclase. Basaltic andesite can be found in volcanoes around the world, including in Central America and the Andes of South America. Description Basaltic andesite is a fine-grained ( aphanitic) igneous rock that is moderately low in silica and low in alkali metal oxides. It is not separately defined in the QAPF classification, which is based on the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, plagioclase feldspar, and feldspathoids, but would fall in the basalt-andesite field. This corresponds to rock in which feldspathoid makes up less than 10% and quartz less than 20% of the total QAPF fraction, and in which at least 65% of the feldspar is plagioclase. Basaltic andesite would be further distinguished from basalt and andesite by a silica content between 52% and 57%. Although classification by mineral content is preferred by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonolite
Phonolite is an uncommon extrusive rock, of intermediate chemical composition between felsic and mafic, with texture ranging from aphanitic (fine-grained) to porphyritic (mixed fine- and coarse-grained). Phonolite is a variation of the igneous rock trachyte that contains nepheline or leucite rather than quartz. Its intrusive equivalent is nepheline syenite. Phonolite is typically fine grained and compact. The name ''phonolite'' comes from the Ancient Greek meaning "sounding stone" due to the metallic sound it produces if an unfractured plate is hit; hence, the English name ''clinkstone'' is given as a synonym. Formation Unusually, phonolite forms from magma with a relatively low silica content, generated by low degrees of partial melting (less than 10%) of highly aluminous rocks of the lower crust such as tonalite, monzonite and metamorphic rocks. Melting of such rocks to a very low degree promotes the liberation of aluminium, potassium, sodium and calcium by meltin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basanite
Basanite () is an igneous, volcanic ( extrusive) rock with aphanitic to porphyritic texture. It is composed mostly of feldspathoids, pyroxenes, olivine, and plagioclase and forms from magma low in silica and enriched in alkali metal oxides that solidifies rapidly close to the Earth's surface. Description Basanite is an aphanitic (fine-grained) igneous rock that is low in silica and enriched in alkali metals. Of its total content of quartz, feldspar, and feldspathoid ( QAPF), between 10% and 60% by volume is feldspathoid and over 90% of the feldspar is plagioclase. Quartz is never present. This places basanite in the basanite/ tephrite field of the QAPF diagram. Basanite is further distinguished from tephrite by having a normative olivine content greater than 10%. While the IUGS recommends classification by mineral content whenever possible, volcanic rock can be glassy or so fine-grained that this is impractical, and then the rock is classified chemically using the TAS class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for lime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles, like the dinosaurs; an abundance of conifers and ferns; a hot greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since Cambrian explosion, complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic. The era began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the largest well-documented mass extinction in Earth's history, and ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, another mass extinction whose victims included the non-avian dinosaurs, Pterosaur, pterosaurs, Mosasaur, mosasaurs, and Plesiosaur, plesiosaurs. The Mesozoic was a time of significant tectonic, climatic, and evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults. Etymology ''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic context by Eduard Suess in 1883. The plural form is either ''graben'' or ''grabens''. Formation A graben is a valley with a distinct escarpment on each side caused by the displacement of a block of land downward. Graben often occur side by side with horsts. Horst and graben structures indicate tensional forces and crustal stretching. Graben are produced from parallel normal faults, where the displacement of the hanging wall is downward, while that of the footwall is upward. The faults typically dip toward the center of the graben from both sides. Horsts are parallel blocks that remain between graben; the bounding faults of a horst typically dip away from the center line of the horst. Single or multiple graben can produce a rift valley. Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |