|
Gestrinone
Gestrinone, sold under the brand names Dimetrose and Nemestran among others, is a medication which is used in the treatment of endometriosis. It has also been used to treat other conditions such as uterine fibroids and heavy menstrual bleeding and has been investigated as a method of birth control. Gestrinone is used alone and is not formulated in combination with other medications. It is taken by mouth or in through the vagina. Side effects of gestrinone include menstrual abnormalities, estrogen deficiency, and symptoms of masculinization like acne, seborrhea, breast shrinkage, increased hair growth, and scalp hair loss, among others. Gestrinone has a complex mechanism of action, and is characterized as a mixed progestogen and antiprogestogen, a weak androgen and anabolic steroid, a weak antigonadotropin, a weak steroidogenesis inhibitor, and a functional antiestrogen. Gestrinone was introduced for medical use in 1986. It has been used extensively in Europe but appea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroidogenesis Inhibitor
A steroidogenesis inhibitor, also known as a steroid biosynthesis inhibitor, is a type of drug which inhibits one or more of the enzymes that are involved in the process of steroidogenesis, the biosynthesis of endogenous steroids and steroid hormones. They may inhibit the production of cholesterol and other sterols, sex steroids such as androgens, estrogens, and progestogens, corticosteroids such as glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, and neurosteroids. They are used in the treatment of a variety of medical conditions that depend on endogenous steroids. Steroidogenesis inhibitors are analogous in effect and use to antigonadotropins (which specifically inhibit gonadal sex steroid production), but work via a different mechanism of action; whereas antigonadotropins suppress gonadal production of sex steroids by effecting negative feedback on and thereby suppressing the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis, steroidogenesis inhibitors directly inhibit the enzymatic biosynthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progestogen (medication)
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic'' progestogen. Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy. They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications. Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogens. They are available in a wide variety of formulations and for use by many different routes of administration. Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone. Side effects of progestogens include menstrual irregularities, headaches, nausea, breast tenderness, mood changes, acne, increased hair growth, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progestin
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a '' synthetic'' progestogen. Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy. They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications. Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogens. They are available in a wide variety of formulations and for use by many different routes of administration. Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone. Side effects of progestogens include menstrual irregularities, headaches, nausea, breast tenderness, mood changes, acne, increased hair growth, and change ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progestogen (medication)
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic'' progestogen. Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy. They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications. Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogens. They are available in a wide variety of formulations and for use by many different routes of administration. Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone. Side effects of progestogens include menstrual irregularities, headaches, nausea, breast tenderness, mood changes, acne, increased hair growth, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
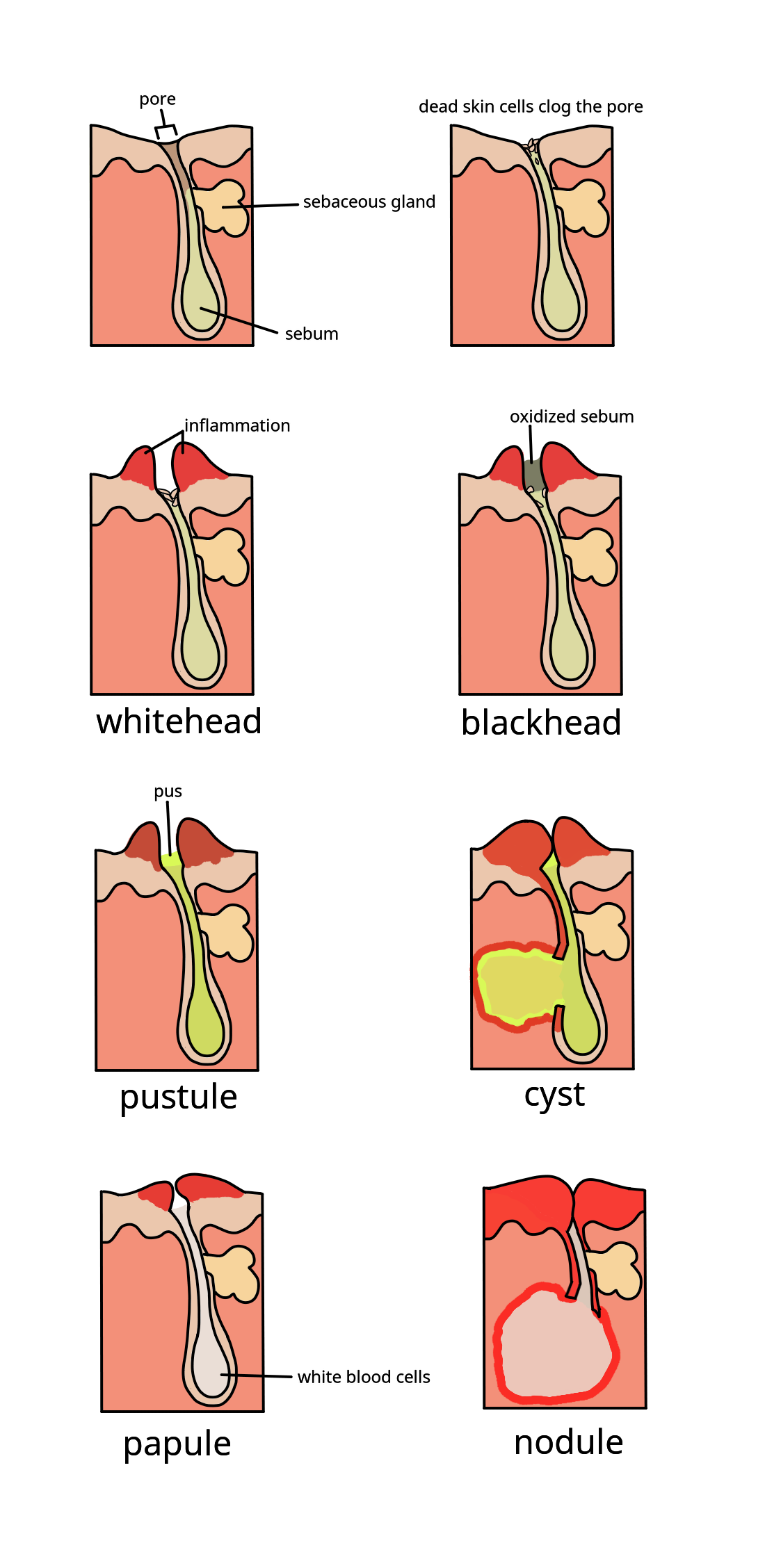
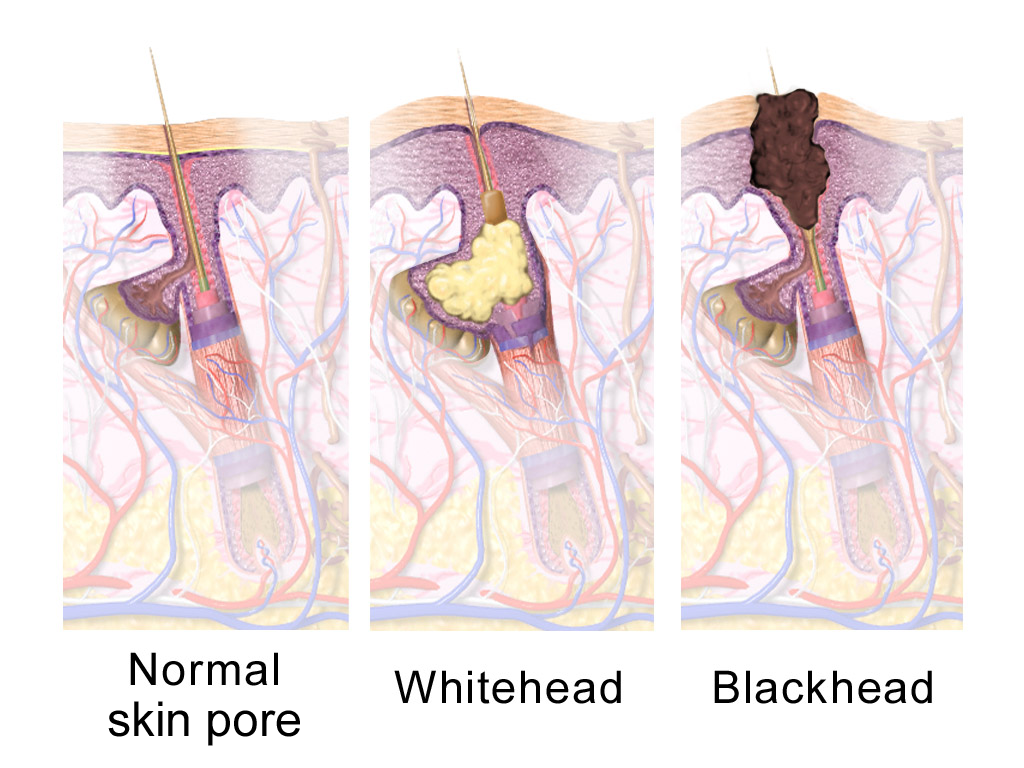
Acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, depression or thoughts of suicide. Susceptibility to acne is primarily genetic in 80% of cases. The roles of diet and cigarette smoking in the condition are unclear, and neither cleanliness nor exposure to sunlight appear to play a part. In both sexes, hormones called androgens appear to be part of the underlying mechanism, by causing increased production of sebum. Another common factor is the excessive growth of the bacterium '' Cutibacterium acnes'', which is present on the skin. Treatments for ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menstrual Abnormalities
A menstrual disorder is characterized as any abnormal condition with regards to a person's menstrual cycle. There are many different types of menstrual disorders that vary with signs and symptoms, including pain during menstruation, heavy bleeding, or absence of menstruation. Normal variations can occur in menstrual patterns but generally menstrual disorders can also include periods that come sooner than 21 days apart, more than 3 months apart, or last more than 10 days in duration. Variations of the menstrual cycle are mainly caused by the immaturity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis, and early detection and management is required in order to minimize the possibility of complications regarding future reproductive ability. Though menstrual disorders were once considered more of a nuisance problem, they are now widely recognized as having a serious impact on society in the form of days lost from work brought about by the pain and suffering experienced by women. These d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrogen Deficiency
Hypoestrogenism, or estrogen deficiency, refers to a lower than normal level of estrogen. It is an umbrella term used to describe estrogen deficiency in various conditions. Estrogen deficiency is also associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, and has been linked to diseases like urinary tract infections and osteoporosis. In women, low levels of estrogen may cause symptoms such as hot flashes, sleeping disturbances, decreased bone health, and changes in the genitourinary system. Hypoestrogenism is most commonly found in women who are postmenopausal, have primary ovarian insufficiency (POI), or are presenting with amenorrhea (absence of menstrual periods). Hypoestrogenism includes primarily genitourinary effects, including thinning of the vaginal tissue layers and an increase in vaginal pH. With normal levels of estrogen, the environment of the vagina is protected against inflammation, infections, and sexually transmitted infections. Hypoestrogenism can also oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pain or pains in the body. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or abnormal physiological state that may be detected during a physical examination, examining the patient history, or diagnostic procedure. These signs are visible or otherwise detectable such as a rash or bruise. Medical signs, along with symptoms, assist in formulating diagnostic hypothesis. Examples of signs include elevated blood pressure, nail clubbing of the fingernails or toenails, staggering gait, and arcus senilis and arcus juvenilis of the eyes. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virilization
Virilization or masculinization is the biological development of adult male characteristics in young males or females. Most of the changes of virilization are produced by androgens. Virilization is most commonly used in three medical and biology of sex contexts: prenatal biological sexual differentiation, the postnatal changes of typical chromosomal male (46, XY) puberty, and excessive androgen effects in typical chromosomal females (46, XX). It is also the intended result of androgen replacement therapy in males with delayed puberty and low testosterone. Prenatal virilization In the prenatal period, virilization refers to closure of the perineum, thinning and wrinkling (rugation) of the scrotum, growth of the penis, and closure of the urethral groove to the tip of the penis. In this context, ''masculinization'' is synonymous with ''virilization.'' Prenatal virilization of genetic females and undervirilization of genetic males are common causes of ambiguous genitalia and inters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hirsutism
Hirsutism is excessive body hair on parts of the body where hair is normally absent or minimal. The word is from early 17th century: from Latin ''hirsutus'' meaning "hairy". It usually refers to a "male" pattern of hair growth in a female that may be a sign of a more serious medical condition, especially if it develops well after puberty. Cultural stigma against hirsutism can cause much psychological distress and social difficulty. Discrimination based on facial hirsutism often leads to the avoidance of social situations and to symptoms of anxiety and depression. Hirsutism is usually the result of an underlying endocrine imbalance, which may be adrenal, ovarian, or central. It can be caused by increased levels of androgen hormones. The amount and location of the hair is measured by a Ferriman-Gallwey score. It is different from hypertrichosis, which is excessive hair growth anywhere on the body. Treatments may include certain birth control pills, antiandrogens, or insulin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seborrhea
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipple, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipple. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals. Structure Location Sebaceous glands are found throughout all areas of the skin, except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There are two types of sebaceous glands, those connected to hair follicles and those that exist independently. Sebaceous glands are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |