|
Gershon Eidelstein
Yerachmiel Gershon Edelstein (; 18 April 1923 – 30 May 2023) was a Soviet Union, Soviet-born Israeli Haredi Judaism, Haredi rabbi who was rosh yeshiva of the Ponevezh Yeshiva, president of the Vaad HaYeshivos, Vaad Hayeshivos, and the spiritual leader of the Degel HaTorah party in Israel. He was widely considered to be a Gadol hador, Gadol Hador by the Litvish community.Jewish World Mourns: Rabbi Gershon Edelstein passes away at age 100 After the death of Rabbi Aharon Yehuda Leib Shteinman in late 2017, Rabbi Edelstein, together with Rabbi Chaim Kanievsky, led the Degel HaTorah movement, representing most of the Litvak-Haredi Judaism, Haredi community. From March 2022, following the death of Rabbi Kanievsky, Rabbi Edelstein assumed sole leadership of the Litvak public.
|
Rabbi
A rabbi (; ) is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi—known as ''semikha''—following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of the rabbi developed in the Pharisees, Pharisaic (167 BCE–73 CE) and Talmudic (70–640 CE) eras, when learned teachers assembled to codify Judaism's written and oral laws. The title "rabbi" was first used in the first century CE. In more recent centuries, the duties of a rabbi became increasingly influenced by the duties of the Clergy, Protestant Christian minister, hence the title "pulpit rabbis." Further, in 19th-century Germany and the United States, rabbinic activities such as sermons, pastoral counseling, and representing the community to the outside all increased in importance. Within the various Jewish denominations, there are different requirements for rabbinic ordination and differences in opinion regarding who is recognized as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gadol Hador
''Gadol'' or ''godol'' (, plural: ''gedolim'' ) (literally "big" or "great" in Hebrew) is used by religious Jews to refer to the most revered rabbis of the generation. Usage The term ''gadol hador'' refers to the "great/est (one of) the generation" denoting one rabbi who is presumed to be even greater than the others. Other variations of the term are ''Gadol Yisrael'' or a ''Gadol BeYisrael'' (plural: Gedolei Yisrael), meaning "great one of the Jewish people". A similar title is ''Rashkebahag'', which is an acronym for ''"Rabbon shel kol bnei hagolah"'' (The sage and teacher of the entire Jewish diaspora). Another term is ''Manhig Yisroel'' (plural: ''Manhigei Yisroel''), literally "leader of Israel". The title ''gadol hador'' is usually only given to one Jewish Sage at a time, while the title ''"Rashkebahag"'' can be given to a few, and the term ''Gedolei Yisrael'' collectively refers to all leading rabbis in the Haredi community. The term is generally applied to rabbinic leade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aunt
An aunt is a woman who is a sibling of a parent or married to a sibling of a parent. Aunts who are related by birth are second-degree relatives. Alternate terms include auntie or aunty. Aunt, auntie, and aunty also may be titles bestowed by parents and children to close friends of one or both parents who assume a sustained caring or nurturing role for the children. Children in some cultures and families may refer to the cousins of their parents as aunt or uncle due to the age and generation gap. The word comes from via Old French ''ante'' and is a family">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ''ante'' and is a family relationship within an extended or immediate family. The male counterpart of an aunt is an uncle, and the reciprocal relationship is that of a niece and nephew, nephew or niece. The gender-neutral term pibling, a shortened form of ''parent's sibling'', may refer to eit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposure. The diseases are caused by specific types of bacterial infection. Epidemic typhus is caused by '' Rickettsia prowazekii'' spread by body lice, scrub typhus is caused by '' Orientia tsutsugamushi'' spread by chiggers, and murine typhus is caused by '' Rickettsia typhi'' spread by fleas. Vaccines have been developed, but none is commercially available. Prevention is achieved by reducing exposure to the organisms that spread the disease. Treatment is with the antibiotic doxycycline. Epidemic typhus generally occurs in outbreaks when poor sanitary conditions and crowding are present. While once common, it is now rare. Scrub typhus occurs in Southeast Asia, Japan, and northern Australia. Murine typhus occurs in tropical and subtropi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rishonim
''Rishonim'' (; ; sing. , ''Rishon'') were the leading rabbis and ''posek, poskim'' who lived approximately during the 11th to 15th centuries, in the era before the writing of the ''Shulchan Aruch'' (, "Set Table", a common printed code of Jewish law, 1563 CE) and following the ''Geonim'' (589–1038 CE). Rabbinic scholars subsequent to the ''Shulchan Aruch'' are generally known as ''acharonim'' ("the latter ones"). The distinction between the and the is meaningful historically; in ''halakha'' (Jewish law) the distinction is less important. According to a widely held view in Orthodox Judaism, the Acharonim generally cannot dispute the rulings of rabbis of previous eras unless they find support from other rabbis in previous eras. On the other hand, this view is not formally a part of ''halakha'' itself, and according to some rabbis is a violation of the halakhic system.See Kesef Mishna (Maamrim 2:2), Kovetz Igros Chazon Ish (2:26) In ''The Principles of Jewish Law'', Orthodox ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemara
The Gemara (also transliterated Gemarah, or in Yiddish Gemore) is an essential component of the Talmud, comprising a collection of rabbinical analyses and commentaries on the Mishnah and presented in 63 books. The term is derived from the Aramaic word and rooted in the Semitic word ג-מ-ר (gamar), which means "to finish" or "complete". Initially, the Gemara was transmitted orally and not permitted to be written down. However, after Judah the Prince compiled the Mishnah around 200 CE, rabbis from Babylonia and the Land of Israel extensively studied the work. Their discussions were eventually documented in a series of books, which would come to be known as the Gemara. The Gemara, when combined with the Mishnah, forms the full Talmud. There are two versions of the Gemara: the Babylonian Talmud (Talmud Bavli) and the Jerusalem Talmud (Talmud Yerushalmi). The Babylonian Talmud, compiled by scholars in Babylonia around 500 CE and primarily from the academies of Sura, Pumbedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chabad
Chabad, also known as Lubavitch, Habad and Chabad-Lubavitch (; ; ), is a dynasty in Hasidic Judaism. Belonging to the Haredi (ultra-Orthodox) branch of Orthodox Judaism, it is one of the world's best-known Hasidic movements, as well as one of the largest Jewish religious organizations. Unlike most Haredi groups, which are self-segregating, Chabad mainly operates in the wider world and caters to nonobservant Jews. Founded in 1775 by Rabbi Shneur Zalman of Liadi (1745–1812) in the city of Liozno in the Russian Empire, the name "Chabad" () is an acronym formed from the three Hebrew words— Chokmah, Binah, Da'at— for the first three sefirot of the kabbalistic Tree of Life after Keter: , "Wisdom, Understanding, and Knowledge"—which represent the intellectual and kabbalistic underpinnings of the movement. The name Lubavitch derives from the town in which the now-dominant line of leaders resided from 1813 to 1915. Other, non-Lubavitch scions of Chabad either disappear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yevsektsiya
A Yevsektsiya ( rus, евсекция, p=jɪfˈsʲektsɨjə; ) was the ethnically Jewish section of the Soviet Communist Party and its main institutions. These sections were established in fall of 1918 with consent of Vladimir Lenin to carry Party ideology and Marxist-Leninist atheism to the Soviet Jewish masses. Pipes, Richard, Russia Under the Bolshevik Regime, New York: Vintage Books, Random House Inc., 1995, , page 363 The Yevsektsiya published a Yiddish periodical, der ''Emes''. According to Walter Kolarz, the Yevsektsiya inside the League of Militant Godless, "had a total of 40,000 Jewish members in 1929, the year when the anti-religious campaign was at its peak. These 'Jewish sections' were much despised by the bulk of Russia's Jewry. Their members were regarded with as much contempt as the Jewish renegades who turned persecutors of the own brethren in the Middle Ages." Mission The Yevsektsiya sought to draw Jewish workers into the revolutionary organisations; chairma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
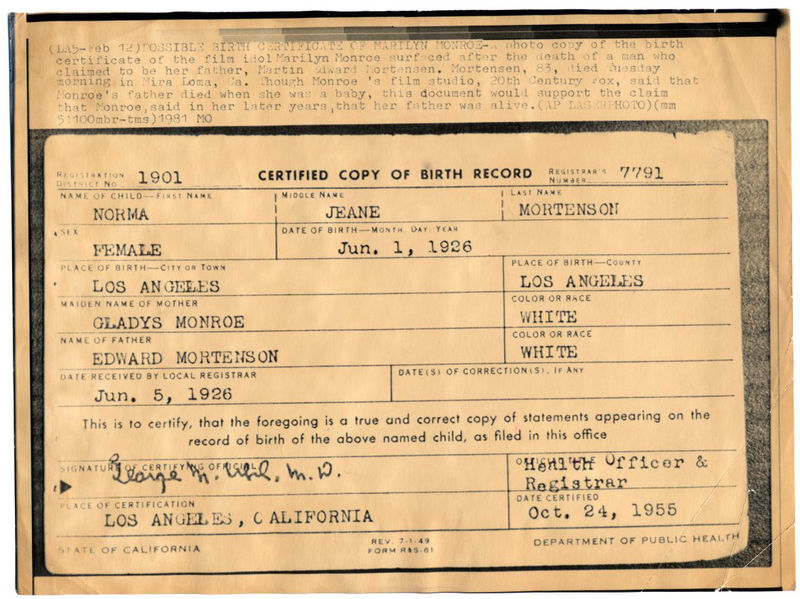
Birth Certificate
A birth certificate is a vital record that documents the Childbirth, birth of a person. The term "birth certificate" can refer to either the original document certifying the circumstances of the birth or to a certified copy of or representation of the ensuing registration of that birth. Depending on the jurisdiction, a record of birth might or might not contain verification of the event by a healthcare professional such as a midwife or doctor. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 17, an integral part of the Sustainable Development Goals, 2030 Agenda, has a target to increase the timely availability of data regarding age, gender, race, ethnicity, and other relevant characteristics which documents like a birth certificate have the capacity to provide. History and contemporary times The documentation of births is a practice widely held throughout human civilization. The original purpose of vital statistics was for tax purposes and for the determination of available mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmud
The Talmud (; ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of Haskalah#Effects, modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish culture, Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The Talmud includes the teachings and opinions of thousands of rabbis on a variety of subjects, including halakha, Jewish ethics, Jewish philosophy, philosophy, Jewish customs, customs, Jewish history, history, and Jewish folklore, folklore, and many other topics. The Talmud is a commentary on the Mishnah. This text is made up of 63 Masekhet, tractates, each covering one subject area. The language of the Talmud is Jewish Babylonian Aramaic. Talmudic tradition emerged and was compiled between the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE and the Arab conquest in the early seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smolensk
Smolensk is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest cities in Russia. It has been a regional capital for most of the past millennium, beginning as the capital of an eponymous principality in the 11th-15th centuries, then the Smolensk Voivodeship of Lithuania and Poland, and Smolensk Governorate and Oblast within Russia. It was the main stronghold of the Smolensk Gate, a geostrategically significant pass between the Daugava and Dnieper rivers, and as such was an important point of contention in the struggle for dominance in Eastern Europe, passing at various times between Lithuania, Poland and Russia. In more recent history, it was captured by Napoleon's Franco–Polish forces and Hitler's Germany during their marches towards Moscow, and was the place of the Smolensk air disaster of 2010. It has a population of Etymology The name of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |