|
German (mythology)
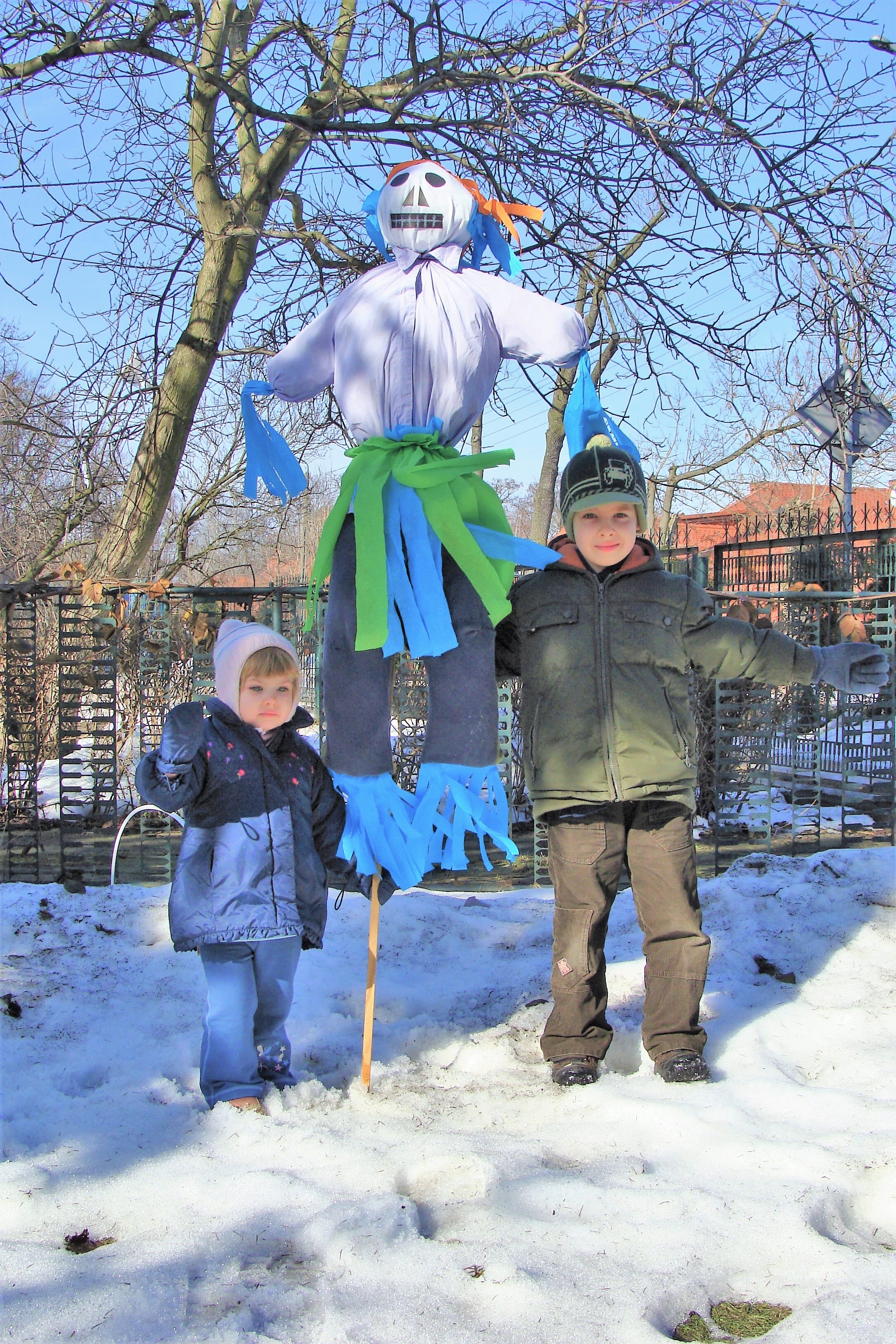
German (''Герман'', GER-man, ) is a South Slavic mythological being, recorded in the folklore of eastern Serbia and northern Bulgaria. He is a male spirit associated with bringing rain and hail. His influence on these precipitations can be positive, resulting in the amount of rain beneficial for agriculture, or negative, with a drought, downpours, or hail. Rituals connected with German included making a doll intended to represent this personage. This effigy of German, made of rags, fired clay, or dried fruits, was rather large, usually with a distinct representation of the male genitals. It was produced and used in rituals exclusively by girls or young women. Janićijević, pages 184-186.Pešikan-Ljuštanović In Eastern Serbia, when a drought developed, girls would make such a doll, and bring it to a river bank. Depending on the regional custom, they would either bury it by the river, or put it in a little coffin and let it float down the river. Two of the girls would then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Slavs
South Slavs are Slavic people who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hungary, Romania, and the Black Sea, the South Slavs today include Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes. In the 20th century, the country of Yugoslavia (from Serbo-Croatian, literally meaning "South Slavia" or "South Slavdom") united a majority of the South Slavic peoples and lands—with the exception of Bulgarians and Bulgaria—into a single state. The Pan-Slavic concept of ''Yugoslavia'' emerged in late 17th-century Croatia, at the time part of the Habsburg monarchy, and gained prominence through the 19th-century Illyrian movement. The Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929, was proclaimed on 1 December 1918, following the unification of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Niš
The University of Niš () is a public university in Serbia. It was founded in 1965. As of the 2018-19 school year, it consists of 13 faculties with 1,492 academic staff and around 20,500 students. It has a university library "Nikola Tesla"; the Faculty of Technology is located in Leskovac, Pedagogy Faculty in Vranje and Agriculture Faculty in Kruševac. History The University of Niš was incorporated as an independent degree-granting institution on 15 June 1965. In 1960 the first undergraduate programs commenced in Niš under the academic patronage of the University of Belgrade. They were institutionalized as the faculties of Law & Economics, Medicine, and Engineering. The university started its independent life with 234 full-time teaching staff and 6,800 students. Timeline *1968: the Department of Electronics grew into the Faculty of Electronic Engineering; *1970: the two departments of the Faculty of Law and Economics became independent faculties; *1971: the Departments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodola And Perperuna
Dodola (also spelled ''Dodole'', ''Dodoli'', ''Dudola'', ''Dudula'' etc.) and Perperuna (also spelled ''Peperuda'', ''Preperuda'', ''Preperuša'', ''Prporuša'', ''Papaluga'' etc.) are rainmaking pagan customs widespread among different peoples in Southeast Europe until the 20th century, found in Albania, Bulgaria, Croatia, Greece, Hungary, Kosovo, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, and Serbia. It is still practiced in remote Albanian ethnographic regions, but only in rare events, when the summer is dry and without atmospheric precipitation. The ceremonial ritual is an analogical-imitative magic rite that consists of singing and dancing done by young girls or boys in processions following a main performer who is dressed with fresh branches, leaves and herbs, with the purpose of invoking rain, usually practiced in times of droughts, especially in the summer season, when drought endangers crops and pastures, even human life itself. According to one interpretation, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caloian
''Caloian'' (also ''Calian(i)'', ''Caloiță'', ''Scaloian'', ''Gherman'', or ''Iene'') was a rainmaking and fertility rite in Romania, similar in some ways to '' Dodola''. Its namesake is a clay effigy, whose sculpting, funeral, exhumation, and eventual destruction are centerpieces of the display. The source of this ritual, as is the case with those of many other local popular beliefs and practices, precedes the introduction of Christianity, although it came in time to be associated with Orthodox Easter or with the Feast of the Ascension. In some variants it was performed on a precisely calculated day two to three weeks after Easter, though local communities could also revive it at other times of the year, specifically during drought. The figurine was generally made from clay and most often by girls, though sometimes also by boys or married women; the ceremony itself would draw in the whole village community as spectators, and, in isolated cases, also had active participation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elijah
Elijah ( ) or Elias was a prophet and miracle worker who lived in the northern kingdom of Israel during the reign of King Ahab (9th century BC), according to the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible. In 1 Kings 18, Elijah defended the worship of the Hebrew deity Yahweh over that of the Canaanite deity Baal. God also performed many miracles through Elijah, including resurrection, bringing fire down from the sky, and ascending to heaven alive. 2 Kings 2:11 He is also portrayed as leading a school of prophets known as "the sons of the prophets." Following Elijah's ascension, his disciple and devoted assistant Elisha took over as leader of this school. The Book of Malachi prophesies Elijah's return "before the coming of the great and terrible day of the ," making him a harbinger of the Messiah and of the eschaton in various faiths that revere the Hebrew Bible. References to Elijah appear in Sirach, the New Testament, the Mishnah and Talmud, the Quran, the Book of Mormon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianized Myths And Imagery
The term Christianized calendar refers to feast days which are Christianized reformulations of feasts from pre-Christian times. Christianization of saints Historian Peter Brown, in his ''The Cult of the Saints: Its Rise and Function in Latin Christianity'', argued that one cannot equate the ancient cults of pagan gods with the later cults of the saints. However, Caesarius of Arles and other churchmen deplored certain customs that from time to time seem to develop around the saints, such as the prolonged drinking of toasts, ostensibly in honor of the saint. The historicity of some Christian saints has been treated skeptically by a number of academics, either because there is a paucity of historical evidence for their origins, or due to resemblances to pre-Christian deities and festivals. Some such local saints, especially those dating to when regions were being Christianized, have been removed from the Calendar of Saints and effectively desanctified by the Catholic Church after i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marzanna
Morana (in Czech, Slovene, Bosnian, Croatian and Montenegrin), Morena (in Slovak and Macedonian), Mora (in Bulgarian), Mara (in Ukrainian), Morė (in Lithuanian), Marena (in Russian), or Marzanna (in Polish) is a pagan Slavic pantheon, Slavic goddess associated with seasonal rites based on the idea of death and rebirth of nature. She is an ancient goddess associated with winter's death, rebirth and dreams. In ancient Slavic rites, the death of the Goddess Morana at the end of winter becomes the wikt:rebirth, rebirth of Spring of the Goddess Kostroma (deity), Kostroma (Russian), Lada or Vesna representing the coming of Spring. Some medieval Christian sources such as the Czech 13th century Mater Verborum compare her to the Greek mythology, Greek goddess Hecate, associating her with sorcery. 15th century Polish chronicler Jan Długosz likened her in his Annales seu cronici incliti regni Poloniae, ''Annales'' to Ceres (Roman mythology), Ceres, the Roman goddess of agriculture (tog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kostroma (tradition)
Kostroma () is an East Slavic fertility goddess. Her name is derived from костёр (kostyor), the Russian word for "bonfire". The rites of Semik were devoted to her. During this festival a disguised girl or a straw figure portrayed Kostroma. First, a scarecrow was honored and revered. Then, participants of the rite mourned the death of Kostroma, and burned or tore the scarecrow. Rituals with Kostroma were aimed at improving soil fertility. The scarecrow of Kostroma is part of East Slavic folklore. Mythology There is a Slavic myth about Kostroma and Kupalo. According to the myth, Kupalo and Kostroma were twins. Their parents were Simargl, the god of fire, and Kupalnitsa, goddess of the night. They were born on the summer solstice. In honor of their birthday, Perun gave Kupalo and Kostroma a Fern flower, but they presented it to people as a sign of the unity of the human world and the world of gods. Once, Kostroma and Kupalo ran into a field (or to the riverbank) to lis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jarilo
Jarylo (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Jarilo, Јарило; ), alternatively Yaryla, Yarilo, Iarilo, Juraj, Jurij, or Gerovit, is an alleged East and South Slavic god of vegetation, fertility and springtime.Leeming, David.''From Olympus to Camelot: The World of European Mythology''. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. 2003. p. 129. Etymology The Proto-Slavic root ''*jarъ'' (''jar'', ''yar''), from Proto-Indo-European ''*yōr-'', ''*yeh₁ro-'', from ''*yeh₁r-'', means "spring" or "summer", "strong", "furious", "imbued with youthful life-force". This youthful life-force was considered sacred in the Slavic pre-Christian religion and the god personifying this sacred force was thus called Jarovit, or hypocoristically Jarilo. Sources The only historic source that mentions this deity is a 12th-century biography of the proselytizing German bishop Otto of Bamberg, who, during his expeditions to convert the pagan tribes of Wendish and Polabian Slavs, encountered festivals in honor of the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrifice
Sacrifice is an act or offering made to a deity. A sacrifice can serve as propitiation, or a sacrifice can be an offering of praise and thanksgiving. Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Greeks, and possibly existed before that. Evidence of ritual human sacrifice can also be found back to at least pre-Columbian civilizations of Mesoamerica as well as in European civilizations. Varieties of ritual non-human sacrifices are practiced by numerous religions today. Terminology The Latin term ''sacrificium'' (a sacrifice) derived from Latin ''sacrificus'' (performing priestly functions or sacrifices), which combined the concepts ''sacra'' (sacred things) and ''facere'' (to make, to do). The Latin word ''sacrificium'' came to apply to the Christian eucharist in particular, sometimes named a "bloodless sacrifice" to distinguish it from blood sacrifices. In individual non-Christian ethnic religions, terms translated as "sacrifice" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
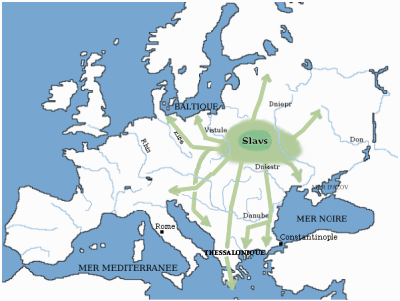
Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and Northern Asia, though there is a large Slavic minority scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, and a substantial Slavic diaspora in the Americas, Western Europe, and Northern Europe. Early Slavs lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately from the 5th to the 10th century AD), and came to control large parts of Central, Eastern, and Southeast Europe between the sixth and seventh centuries. Beginning in the 7th century, they were gradually Christianized. By the 12th century, they formed the core population of a number of medieval Christian states: East Slavs in the Kievan Rus', South Slavs in the Bulgarian Empire, the Principality of Serbia, the Duchy of Croatia and the Banate of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
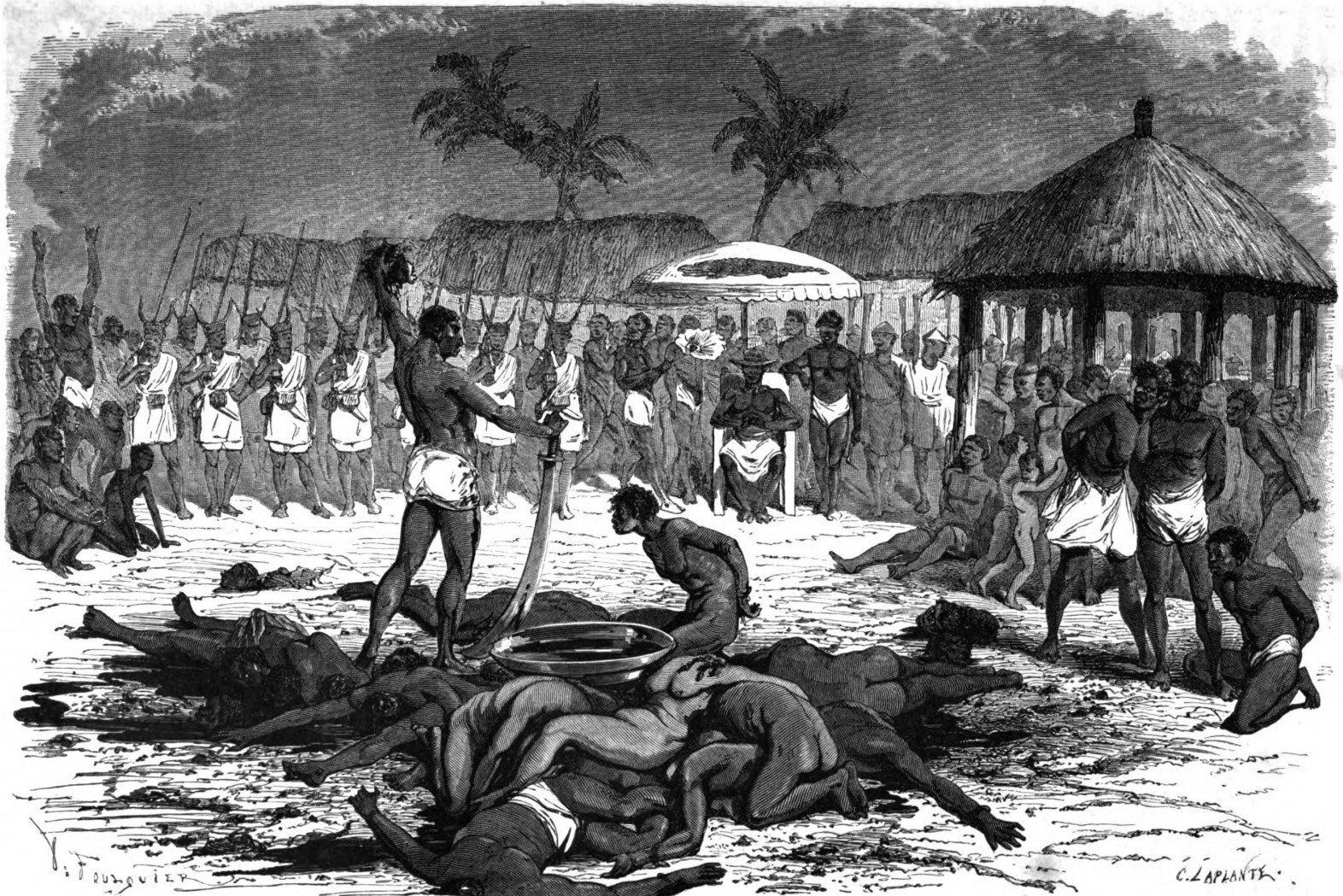
Human Sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease deity, gods, a human ruler, public or jurisdictional demands for justice by capital punishment, an authoritative/priestly figure, spirits of veneration of the dead, dead ancestors or as a retainer sacrifice, wherein a monarch's servants are killed in order for them to continue to serve their master in the next life. Closely related practices found in some tribe, tribal societies are human cannibalism, cannibalism and headhunting. Human sacrifice is also known as ritual murder. Human sacrifice was practiced in many human societies beginning in prehistoric times. By the Iron Age with the associated developments in religion (the Axial Age), human sacrifice was becoming less common throughout Africa, Europe, and Asia, and came to be looked down upon as barbarian, barbaric during classical antiquity. In the New World, Americas, however, human sacrifice cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |