|
Geosaurini
Geosaurinae is a subfamily of metriorhynchid crocodyliforms from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous (Bathonian - Aptian) of Europe, North America and South America. Named by Richard Lydekker, in 1889, it contains the metriorhynchids ''Suchodus'', '' Purranisaurus'', '' Neptunidraco'', '' Tyrannoneustes'', '' Torvoneustes'', '' Dakosaurus'', ''Geosaurus'' and '' Plesiosuchus''. The last four taxa form a tribe within Geosaurinae, the Geosaurini. Geosaurinae is one of two subfamilies of Metriorhynchidae, the other being Metriorhynchinae. These marine reptiles were widespread during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous, their fossilized remains are being frequently found on various places around the world.Daniel Madzia, Sven Sachs, Mark T. Young, Alexander Lukeneder and Petr Skupien (2021)Evidence of two lineages of metriorhynchid crocodylomorphs in the Lower Cretaceous of the Czech Republic ''Acta Palaeontologica Polonica''. doi: https://doi.org/10.4202/app.00801.2020 Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesiosuchus
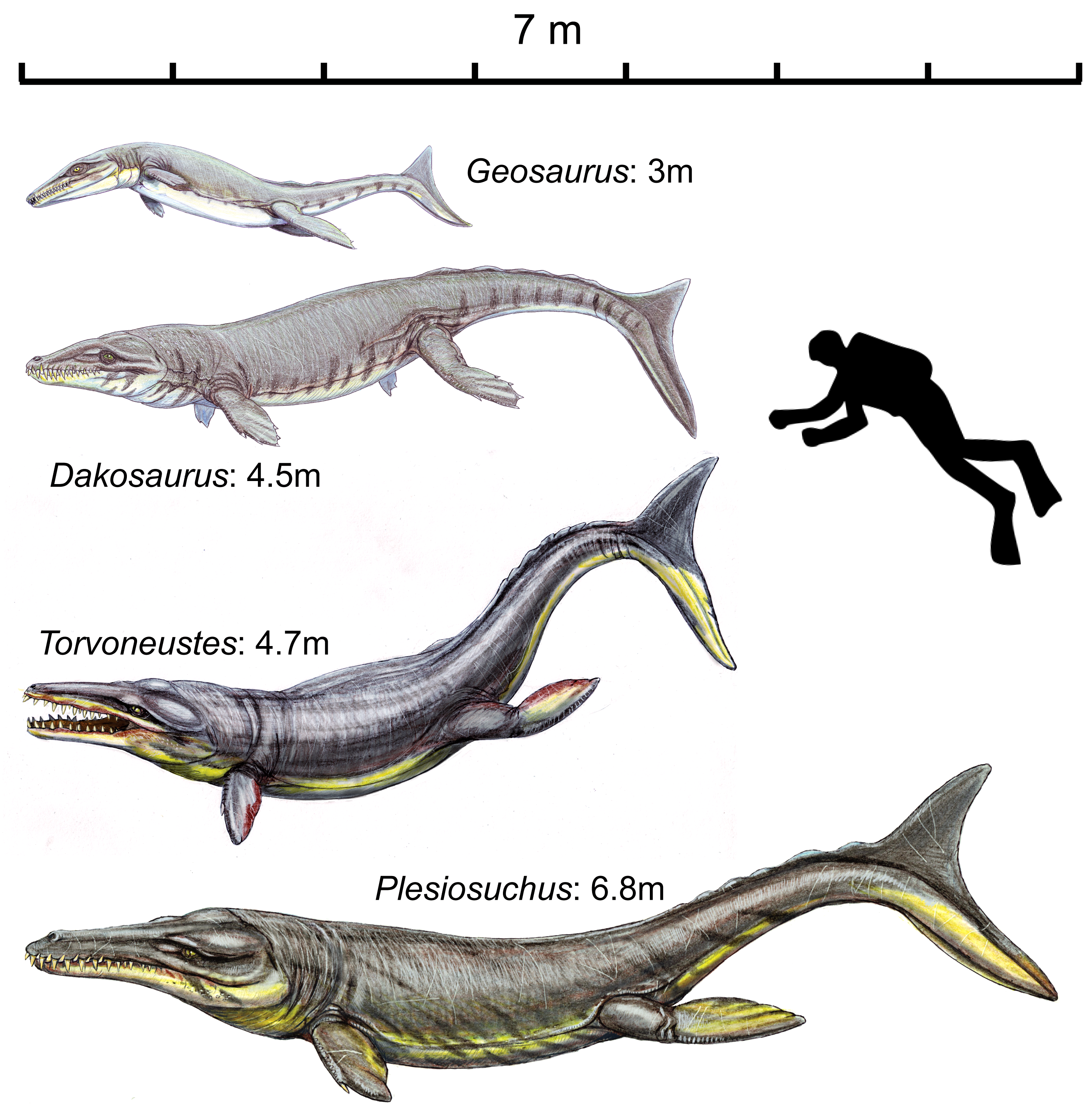
''Plesiosuchus'' is an extinct genus of geosaurine metriorhynchid crocodyliform known from the Late Jurassic (late Kimmeridgian to early Tithonian stage) of Dorset, England and possibly also Spain. It contains a single species, ''Plesiosuchus manselii''. Discovery The type and referred specimens of ''Plesiosuchus'' were discovered by John Clavell Mansel-Pleydell in the 1860s alongside the remains of several other large-bodied marine reptiles along the coast of Dorset. Mansel-Pleydell gave these remains to the British Museum (now in the Natural History Museum) in 1866. Part of the holotype of ''P. manselii'' (NHMUK PV OR40103a) was first described by John Hulke in 1869. He referred it to ''Steneosaurus rostro-minor'' Geoffroy (1825), alongside ''Dakosaurus maximus'' and other specimens. Initially, the skull (NHMUK PV OR40103) was believed to be pliosaurian; it was the preparator Mr Davies that suggested a crocodylian nature for the skull. In 1870, Hulke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torvoneustes Carpenteri
''Torvoneustes'' is an extinct genus of metriorhynchid thalattosuchian. It is known from skull and postcranial remains found in the Kimmeridge Clay Formation of Dorset and Wiltshire, England, and also from Oaxaca, Mexico . The holotype skull of the type species was initially assigned to the species '' Metriorhynchus superciliosus''. Postcranial remains were later discovered from the same quarry as the skull, and then these specimens were recognised as belonging to a new species of '' Dakosaurus'', as ''D. carpenteri''. The species was named to honour Simon Carpenter, an amateur geologist from Frome in Somerset, who discovered the fossils. ''Dakosaurus carpenteri'' was later reassigned to the genus ''Geosaurus'' in 2008. Two years later, it was assigned to its own genus, ''Torvoneustes''. When ''T. carpenteri'' was considered a species of ''Dakosaurus'', its relatively long snout and smaller, more numerous teeth were thought to be features retained from more basal metriorhynch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metriorhynchid
Metriorhynchidae is an extinct family of specialized, aquatic metriorhynchoid crocodyliforms from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous period (Bajocian to early Aptian) of Europe, North America and South America. The name Metriorhynchidae was coined by the Austrian zoologist Leopold Fitzinger in 1843.Fitzinger LJFJ. 1843. ''Systema Reptilium''. Wien: Braumüller et Seidel, 106 pp. The group contains two subfamilies, the Metriorhynchinae and the Geosaurinae. They represent the most marine adapted of all archosaurs. Description Metriorhynchids are fully aquatic crocodyliforms. Their forelimbs were small and paddle-like, and unlike living crocodylians, they lost their osteoderms ("armour scutes"). Their body shape maximised hydrodynamy (swimming efficiency), as they did have a shark-like tail fluke. Like ichthyosaurs and plesiosaurs, metriorhynchids developed smooth, scaleless skin. Metriorhynchids were the only group of archosaurs to become fully adapted to the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggiosaurus
''Aggiosaurus'' is an extinct genus of geosaurine metriorhynchid crocodyliform known from the Late Jurassic (late Oxfordian stage) of Nice, southeastern France. It contains a single species, ''Aggiosaurus nicaeensis'', which was named by H. Ambayrac in 1913.H. Ambayrac. (1913). Découverte d'une mâchoire de reptile jurassique iscovery of a jaw from a Jurassic reptile ''Bulletin Mensuel des Naturalistes des Alpes-Maritimes'' 15:65-68 History of discovery ''Aggiosaurus'' is known only from its holotype, an unnumbered, poorly preserved upper jaw collected by H. Ambayrac in 1912, Maury, E. (1915). New observations on the Jurassic reptile localities on the road from Cap d'Ail to La Turbie. ''Riviera Scientifique. Bulletin de l'Association des Naturalistes de Nice et des Alpes-Maritimes'' 2(1):4-6 preserved in limestone which is now housed in the Muséum d'histoire naturelle de Nice. It was collected from the late Oxfordian-aged locality of Cap d’Aggio-La Turbie, in Nice, France. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ieldraan
''Ieldraan'' is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliform in the family Metriorhynchidae Metriorhynchidae is an extinct family of specialized, aquatic metriorhynchoid crocodyliforms from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous period (Bajocian to early Aptian) of Europe, North America and South America. The name Metriorhync ... from the Jurassic ( Callovian) period of England. The sole species in the genus is ''Ieldraan melkshanensis''. Researchers have derived a body length estimate of based on a long basicranium. References Late Jurassic crocodylomorphs of Europe Middle Jurassic crocodylomorphs Fossil taxa described in 2017 Prehistoric pseudosuchian genera Prehistoric marine crocodylomorphs Middle Jurassic genus first appearances Thalattosuchians Oxford Clay {{jurassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakosaurus Maximus
''Dakosaurus'' is an extinct genus of crocodylomorph within the family Metriorhynchidae that lived during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. It was large, with teeth that were serrated and compressed lateromedially (flattened from side to side). The genus was established by Friedrich August von Quenstedt in 1856 for an isolated tooth named ''Geosaurus maximus'' by Theodor Plieninger in 1846. ''Dakosaurus'' was a carnivore that spent much, if not all, its life out at sea. The extent of its adaptation to a marine lifestyle means that it is most likely that it mated at sea, but since no eggs or nests have been discovered that have been referred to ''Dakosaurus'', whether it gave birth to live young at sea like dolphins and ichthyosaurs or came ashore like turtles is not known. The name ''Dakosaurus'' means "biter lizard", and is derived from the Greek ' ("biter") and -' ("lizard"). Discovery and species The type species ''Dakosaurus maximus'', meaning "greatest biter li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Because it is on the North American Plate, North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland is included as a part of North America geographically. North America covers an area of about , about 16.5% of Earth's land area and about 4.8% of its total surface. North America is the third-largest continent by area, following Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. In 2013, its population was estimated at nearly 579 million people in List of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In Americas (terminology)#Human ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion of a single continent called Americas, America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territory, dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one administrative division, internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands (Leeward Antilles), ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Asce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metriorhynchinae
Metriorhynchinae is a subfamily of metriorhynchid crocodyliforms from the late Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous (Callovian - Valanginian) of Europe, North America and South America. Named by Fitzinger, in 1843, it contains the metriorhynchids ''Maledictosuchus'', '' Gracilineustes'', ''Metriorhynchus'', ''Cricosaurus'' and '' Rhacheosaurus''. The last three taxa form a tribe within Metriorhynchinae, the Rhacheosaurini. Metriorhynchinae is one of two subfamilies of Metriorhynchidae, the other being Geosaurinae. Phylogeny Metriorhynchinae is a stem-based taxon defined in 2009 as the most inclusive clade consisting of '' Metriorhynchus geoffroyii'', but not ''Geosaurus giganteus''. Rhacheosaurini is a stem-based taxon and it was named and defined by Mark T. Young, Mark A. Bell and Stephen L. Brusatte in 2011 as the most inclusive clade including ''Rhacheosaurus gracilis'', but not ''Metriorhynchus geoffroyii'' and ''Gracilineustes leedsi''. The cladogram A cladogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem-based Taxon
Phylogenetic nomenclature is a method of nomenclature for taxa in biology that uses phylogenetic definitions for taxon names as explained below. This contrasts with the traditional approach, in which taxon names are defined by a ''type'', which can be a specimen or a taxon of lower rank, and a description in words. Phylogenetic nomenclature is currently regulated by the ''International Code of Phylogenetic Nomenclature'' (''PhyloCode''). Definitions Phylogenetic nomenclature ties names to clades, groups consisting of an ancestor and all its descendants. These groups can equivalently be called monophyletic. There are slightly different ways of specifying the ancestor, which are discussed below. Once the ancestor is specified, the meaning of the name is fixed: the ancestor and all organisms which are its descendants are included in the named taxon. Listing all these organisms (i.e. providing a full circumscription) requires the full phylogenetic tree to be known. In practice, there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
