|
Georgetown, Prince Edward Island
Georgetown is a community located within the municipality of Three Rivers in Kings County, Prince Edward Island, Canada. It is the Capital of Kings County. Previously incorporated as a town, it was amalgamated with the town of Montague, the rural municipalities of Brudenell, Cardigan, Lorne Valley, Lower Montague, and Valleyfield, and portions of three adjacent unincorporated areas in 2018 to create the town of Three Rivers. History This area of eastern Prince Edward Island traces its history of human settlement to the Mi'kmaq Nation, which long inhabited the area. These people were referred to as ''Epegoitnag'' and for them, the region was an Acadian forest. It had wild game, as well as fruit, berries and wild nuts for gathering, and plentiful marine resources in the nearby rivers and Northumberland Strait. The land in this area was called ''Samkook'', which translates to 'the land of the sandy shore'. Georgetown lies opposite Brudenell Point, which divides the Bru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valleyfield, Prince Edward Island
Valleyfield was a municipality that held community status in Prince Edward Island, Canada. It was incorporated in 1974. On September 28, 2018, it was merged with six other municipalities ( Georgetown, Montague, Brudenell, Cardigan, Lorne Valley, and Lower Montague) and adjacent unincorporated areas to create the town of Three Rivers. See also *List of communities in Prince Edward Island Prince Edward Island is the least populous province in Canada with 154,331 residents as of the 2021 census and is the smallest in land area at . Prince Edward Island's 63 municipalities cover of the province's land mass and were home to of ... References {{PEI Communities in Kings County, Prince Edward Island Former rural municipalities in Prince Edward Island Populated places disestablished in 2018 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George III Of The United Kingdom
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and Ireland from 25 October 1760 until his death in 1820. The Acts of Union 1800 unified Great Britain and Ireland into the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, with George as its king. He was concurrently Duke and Prince-elector of Hanover in the Holy Roman Empire before becoming King of Hanover on 12 October 1814. He was the first monarch of the House of Hanover who was born in Great Britain, spoke English as his first language, and never visited Hanover. George was born during the reign of his paternal grandfather, King George II, as the first son of Frederick, Prince of Wales, and Princess Augusta of Saxe-Gotha. Following his father's death in 1751, Prince George became heir apparent and Prince of Wales. He succeeded to the throne on George II's death in 1760. The following year, he married Princess Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, with whom he had 15 children. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgetown Royalty, Prince Edward Island
Georgetown or George Town may refer to: Places Africa *George, South Africa, formerly known as Georgetown * Janjanbureh, Gambia, formerly known as Georgetown *Georgetown, Ascension Island, main settlement of the British territory of Ascension Island Asia * Georgetown, Prayagraj, India *George Town, Chennai, India *George Town, Penang, capital city of the Malaysian state of Penang Europe * Georgetown, Blaenau Gwent, now part of the town of Tredegar in Wales * Georgetown, Dumfries and Galloway, a location in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland *Es Castell in Minorca, Spain, originally called Georgetown North and Central America Canada *Georgetown, Alberta *Georgetown, Newfoundland and Labrador *Georgetown, Ontario *Georgetown, Prince Edward Island Caribbean *George Town, Bahamas, a village in Exuma District, Bahamas * George Town, Belize, a village in Stann Creek District, Belize *George Town, Cayman Islands, the capital city on Grand Cayman * Georgetown, Saint Vincent and the Grena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Holland (surveyor)
Samuel Johannes Holland (1728 – 28 December 1801) was a Dutch-born Royal Engineer and first Surveyor General of British North America. Life in the Netherlands Holland was born in 1728 in Deventer, the Netherlands. He was baptised on 22 September 1729 in the small Lutheran Church in the Dutch town of Deventer, in the Province of Overijssel. In 1745, he entered the Dutch, or Staatse Leger artillery, and served during the War of the Austrian Succession. He was promoted to lieutenant in 1747. In 1749, Holland married Gertrude Hasse. They had one daughter, who is thought to have died in infancy. In 1754, having possibly made contact with the Duke of Richmond and leaving his wife behind in the Netherlands, Holland emigrated to England to seek advancement under the British flag. Early years in British North America In 1756, Holland, probably with Richmond's aid, became a lieutenant in the Royal Americans, coming to British North America where he would spend the rest of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia versus Kingdom of France, France and Habsburg monarchy, Austria, the respective coalitions receiving by countries including Portuguese Empire, Portugal, Spanish Empire, Spain, Electorate of Saxony, Saxony, Age of Liberty, Sweden, and Russian Empire, Russia. Related conflicts include the Third Silesian War, French and Indian War, Carnatic wars, Third Carnatic War, Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763), Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763), and Spanish–Portuguese War (1762–1763), Spanish–Portuguese War. Although the War of the Austrian Succession ended with the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1748), none of the signatories were happy with the terms, and it was generally viewed as a temporary armistice. It led to a strategic realignment kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Great Britain
Great Britain, also known as the Kingdom of Great Britain, was a sovereign state in Western Europe from 1707 to the end of 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the Kingdom of England (including Wales) and the Kingdom of Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. The unitary state was governed by a single Parliament of Great Britain, parliament at the Palace of Westminster, but distinct legal systems—English law and Scots law—remained in use, as did distinct educational systems and religious institutions, namely the Church of England and the Church of Scotland remaining as the national churches of England and Scotland respectively. The formerly separate kingdoms had been in personal union since the Union of the Crowns in 1603 when James VI of Scotland became King of England an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (, formerly '; or '; ) is a rugged and irregularly shaped island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada. The island accounts for 18.7% of Nova Scotia's total area. Although the island is physically separated from the Nova Scotia peninsula by the Strait of Canso, the long Canso Causeway connects it to mainland Nova Scotia. The island is east-northeast of the mainland with its northern and western coasts fronting on the Gulf of Saint Lawrence with its western coast forming the eastern limits of the Northumberland Strait. The eastern and southern coasts front the Atlantic Ocean with its eastern coast also forming the western limits of the Cabot Strait. Its landmass slopes upward from south to north, culminating in the Cape Breton Highlands, highlands of its northern cape. A large body of saltwater, the ("Golden Arm" in French), dominates the island's centre. The total population at the 2016 Canadian Census, 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
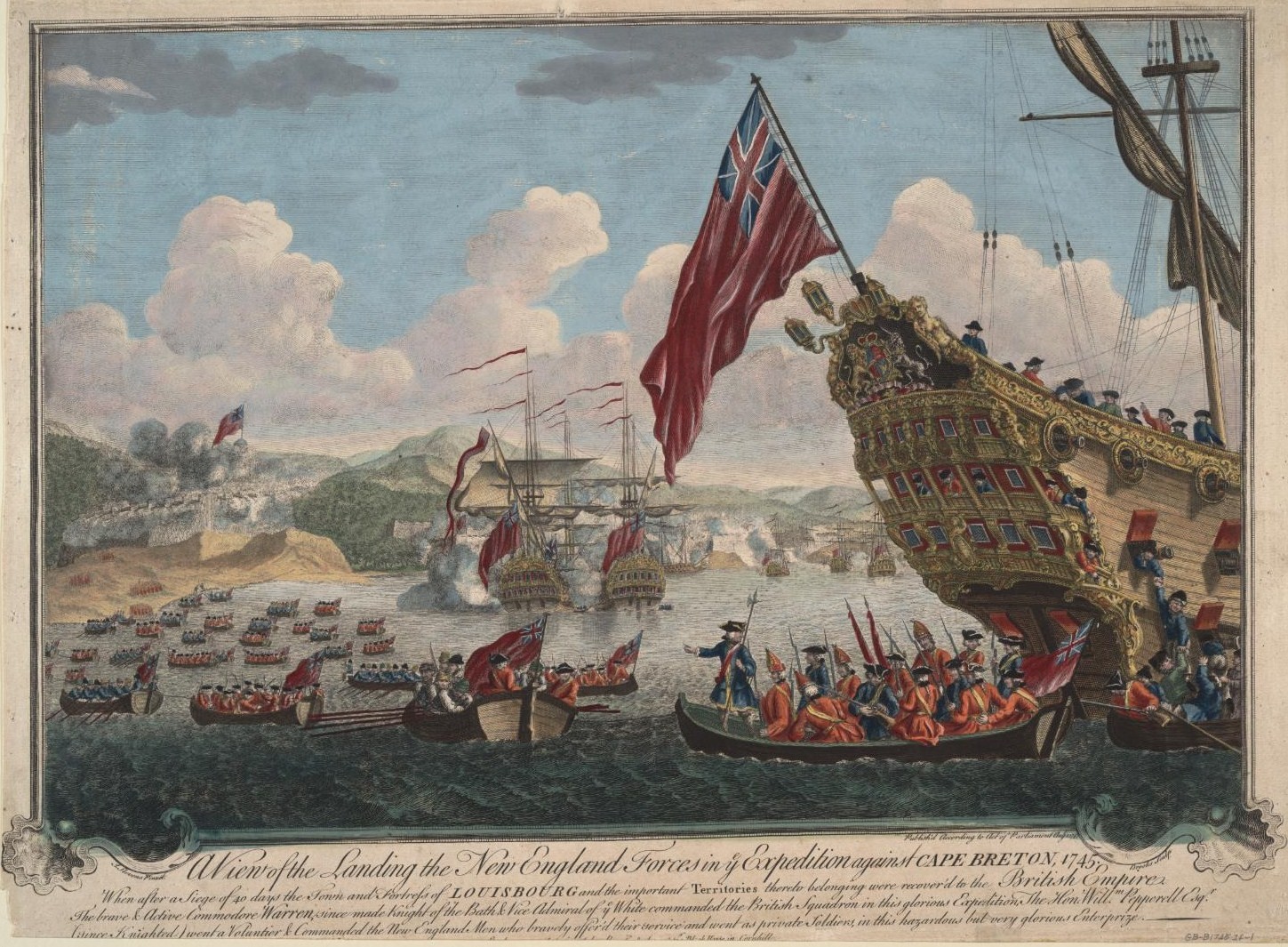
Fortress Of Louisbourg
The Fortress of Louisbourg () is a tourist attraction as a National Historic Sites of Canada, National Historic Site and the location of a one-quarter partial reconstruction of an 18th-century Kingdom of France, French fortress at Louisbourg, Nova Scotia, Louisbourg on Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia. Its two sieges, especially that of 1758, were turning points in the Anglo-French struggle for what today is Canada. The original settlement was founded in 1713 by settlers from Terre-Neuve (New France), Terre-Neuve, and initially called Havre à l'Anglois. Subsequently, the fishing port grew to become a major commercial port and a strongly defended fortress. The fortifications eventually surrounded the town. The walls were constructed mainly between 1720 and 1740. By the mid-1740s Louisbourg, named for Louis XIV of France, was one of the most extensive (and expensive) European fortifications constructed in North America. The site was supported by two smaller garrisons on Île Royale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
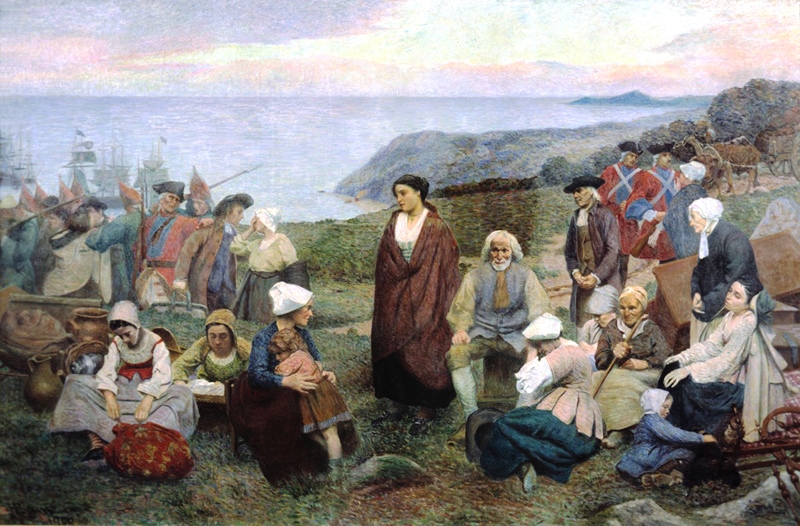
Acadian
The Acadians (; , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, most descendants of Acadians live in either the Northern American region of Acadia, where descendants of Acadians who escaped the Expulsion of the Acadians (a.k.a. The Great Upheaval / ''Le Grand Dérangement'') re-settled, or in Louisiana, where thousands of Acadians moved in the late 1700s. Descendants of the Louisiana Acadians are most commonly known as Cajuns, the anglicized term of "Acadian". Acadia was one of the five regions of New France, located in what is now Eastern Canada's Maritime provinces, as well as parts of Quebec and present-day Maine to the Kennebec River. It was ethnically, geographically and administratively different from the other French colonies such as the French colony of Canada. As a result, the Acadians developed a distinct history and culture. The settlers whose descendants became Acad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
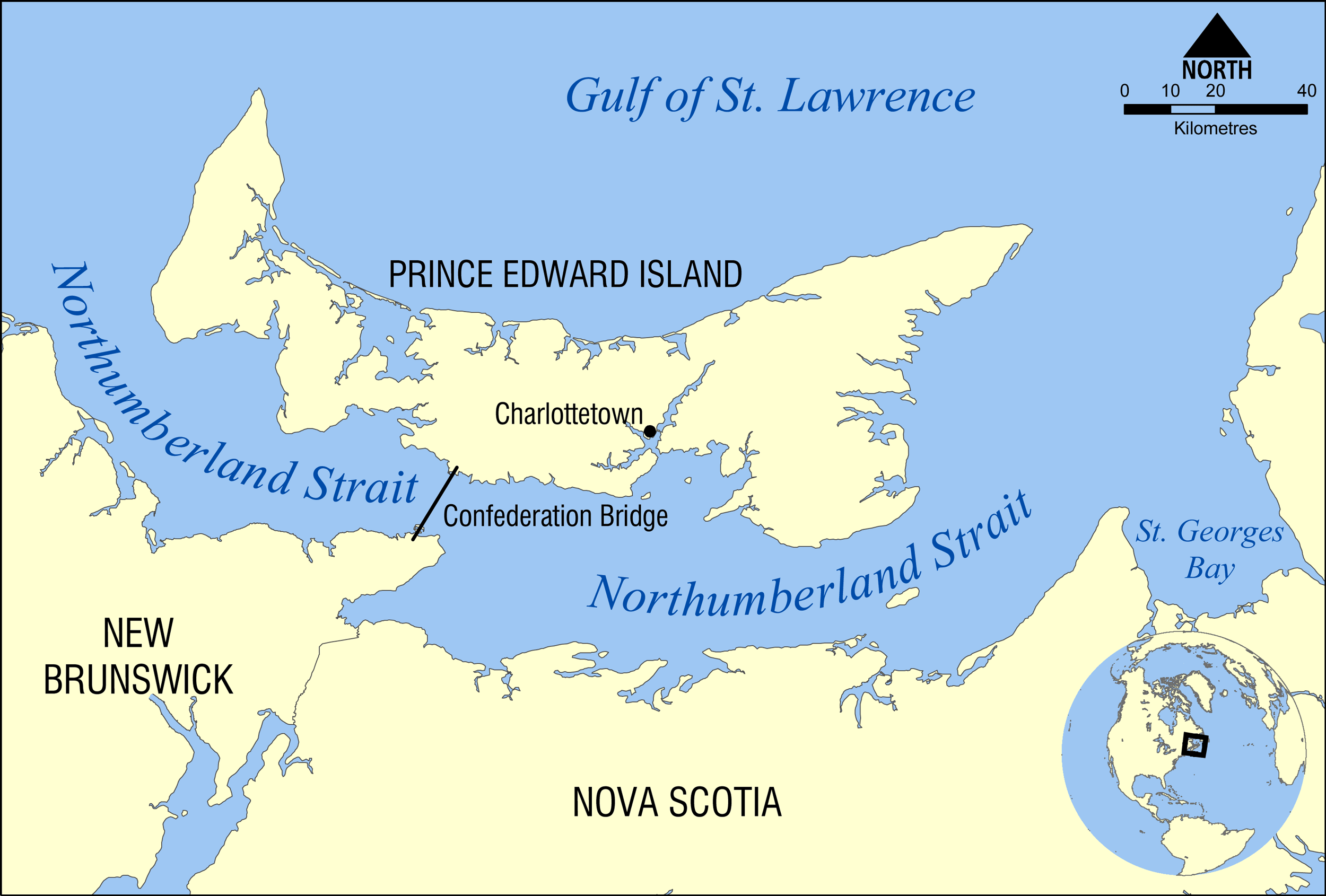
Northumberland Strait
The Northumberland Strait (French: ''détroit de Northumberland'') is a strait in the southern part of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence in eastern Canada. The strait is formed by Prince Edward Island and the gulf's eastern, southern, and western shores. Boundaries The western boundary of the strait is delineated by a line running between North Cape, Prince Edward Island and Point Escuminac, New Brunswick while the eastern boundary is delineated by a line running between East Point, Prince Edward Island and Inverness, Nova Scotia. Hydrography The Northumberland Strait varies in depth between 17 and 65 metres, with the deepest waters at either end. The tidal patterns are complex; the eastern end has the usual two tides per day, with a tidal range of 1.2 to 1.8 metres, while the western end effectively has only one tide per day. The strait's shallow depths lend to warm water temperatures in summer months, with some areas reaching 25° C, or 77° F. Consequently, the strait is re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |